![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
BASICS
|
.
|
|
|
Density
|
Density = Mass/Volume --> [kg/m^3]
|
|
|
Density of Water
|
1g/cm^3 = 1000kg/m^3
|
|
|
Charge Density
|
Charge Density = Charge/Volume --> ion
e.g. Which has greater charge density? Li ion --> Li+ Greater charge density Na ion --> Na+ Larger atom |
|
|
Specific Gravity (SG)
|
Specific Gravity = Density (substance)/Density (water)
No units |
|
|
Avagadro's Number (NA)
|
NA = 6.002214...x10^23 mol-1 --> 6 x 10^23 mol-1
NA = # of stuff per mol |
|
|
Diatomics @ STD conditions
|
Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
H2(g) N2(g) F2(g) O2(g) I2(s) Cl2(g) Br(l) |
|
|
Empirical Formula
|
Ratio of atoms
e.g. HO |
|
|
Molecular Formula
|
Multiple of empirical formula
e.g. H2O2 |
|
|
Lewis Dot Structure
|
Shows Valence e-
-Shows chemical reactivity: All atoms in a column have the same valance electrons--> same chemical compounds -Reactivity: < 4 valence e- : lose e-, cation > 4 Valence e- : gain e-, anionic |
|
|
Non-Octet Exceptions
|
Less than octet: H(2), He(2), Li(2), B(6), Be(4)
More than octet: P(10), S(12) Odd-summed: ClO2 --> 7 +6 + 6 = 19 (radical) Paramagetism |
|
|
Paramagetism
|
Paramagnetic - present/absence of radical
- unpaired electrons present - attracted to magnetic field (B) Diamagnetic - no unpaired e- - repelled by B |
|
|
Formal Charge (FC)
|
Charge on atoms within molecules
FC = V (valence) - 1/2 B (bonded) - L (lone pairs) |
|
|
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
|
.
|
|
|
4 Forces of Nature
|
1) strong nuclear force -> binds nucleus
2) electromagnetic force -> attracts/repels based on charge 3) weak nuclear force -> interconverts neurons <-> protons 4) gravity -> accelerations downward |
|
|
Mass-energy
|
E = MC^2
|
|
|
Binding Energy (EB)
|
EB = MC^2
Sum of mass at nucleons in the nucleus is < individual nucleuons =mass defect =amount of energy lost when forming nucleus =Amount of E to break apart nucleus |
|
|
Forming Bonds
|
Exothermic Reaction
|
|
|
Breaking Bonds
|
Endothermic Reaction
|
|
|
Atomic Structure
|
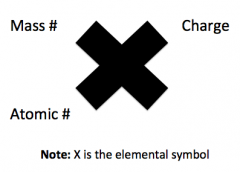
|
|
|
Mass Number
|
Mass # = Protons + Neutrons
Identifies Isotopes Not on periodic table |
|
|
Atomic Number
|
Atomic # = Number of protons
Identifies element |
|
|
Charge
|
Charge = Protons - Electrons
Identifies ions |
|
|
Decay modes/particles
|
1) alpha
2) B- = Beta emission 3) B+ = Positron emission 4) EC = e- capture (rare!) 5) Gamma Rays Note: All decay modes - always exothermic |
|
|
1) a = alpha
|
a = 4/2He2+
Atomic # decreases by 2 Increased molecular weight |
|
|
2) B- = Beta emission
|
Atomic # increases by 1
High n/p+ ratio |
|
|
3) B+ = Positron emission
|
Atomic # decreases by 1
High p+/n ratio |
|
|
4) EC = e- capture (rare!)
|
Atomic # decreases by 1
Combine e- + p+ = n Mass # stays the same |
|
|
5) Gamma Rays
|
Atomic # stays the same
EM (emits) radiation |
|
|
Decay - FInding daughter nuclei
|
D (daughter nuclei) = P (parent) - (Decay)
|
|
|
Half-life (t1/2)
|
Amount of time for 1/2 a sample to decay.
Short t1/2 --> More Dangerous ***USE TABLES TO SOLVE!!!*** |

