![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
232 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1st grade readiness?
|
know address and DoB
ID upper and lower case letters |
|
|
|
Anti smooth muscle Ab
|
Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis
|
|
|
|
Antimitochondrial antibodies
|
primary biliary cirrhosis
|
high alkphos levels
90% female 30-65 yoa |
|
|
Barbituate / sedative overdose
|
coma
bradycardia bradypnea hypotension hypothermia hyporeflexia hypoactive bs decreased mm activity |
|
|
|
Chancroid vs Chancre sore
|
Chancroid: Haemophilus ducreyi
Chancre: syphilis |
Chancroid: soft edged ulcer; painful with inguinal adenopathy
Chancre: painless, hard circumferencial |
|
|
Common causes of meningitis in HIV patients?
|
cryptococcus
CMV Toxoplasmosis JC virus (PML) |
|
|
|
Conditions associated with choanal atresia
|
CHARGE syndrome
Crouzon Pfeiffer Antley bixler |
CHARGE-coloboma, heart, atresia choanae, retarded growth, genital, ear
Crouzon-first branchial arch syndrome-maxilla, mandible-low set ears, cranial synostosis, exophthalmos, hypertelorism,Psittichorhina (beak like nose) Pfeiffer: craniosynostosis Antley bixler: brachycephaly, craniosynostosis of both coronal and lambdoid sutures, facial hypoplasia; bowed ulna and femur, synostosis of the radius, humerus, and trapezoid; camptodactyly (fused interphalangeal joints in the fingers), thin ilial wings, renal malformations. |
|
|
digital clubbing
aka |
hypertrophi pulmonary osteoarthropathy
|
|
|
|
episcleritis / scleritis
|
high association with autoimmune dz
MC unilateral Si/Sx: eye pain, photophobia, erythema, perforation is associated with sclertis Tx: topical steroids, NSAIDS, surgery |
|
|
|
Hepatitis transmission
|
HAV: fecal-oral
HBV: parenteral, sexual HCV: blood, IV drug, sex HDV: requires HBsAg HEV: enterically, water-borne epidemics |
HBV: reverse transcriptase DNA dependant DNA polymerase
|
|
|
Hospital aquired UTI
think? |
E. coli
Proteus Klebsiella Serrtia Pseudomonas |
|
|
|
CSF characteristics:
increased pressure, increased protein Increased glc predominant lymphs, think? |
fungal of TB meningitis
|
|
|
|
If urine is nitrite positive, think
|
gram neg bt
|
|
|
|
inflammation of eyelid margins
|
MCC: staph aureus, staph epidermis, seborrhea
burning, itching, erythema, scaling, ulceration of lid margin Tx: topical antibiotics, daily cleanser |
|
|
|
Kindergarted readiness?
|
separation from parents
10-15 min attention colors count to 10 sit quietly retell a story identify some letters print name |
|
|

What is this
unique finding that disappears in 6 months |
Fetal alcohol syndrome
|
hirsutism that dissipates over 6 months
|
|
|
Si/Sx of acute liver failure
|
def: hepatic decompensation occurring within weeks or a few months after the diagnosis of liver disease. presentation suggests
(encephalopathy, manifested by a disturbed sleep-awake cycle (a characteristic of stage 1 encephalopathy) and drowsiness. deteriorating liver synthetic function (hypoalbuminemia, hypoglycemia, and coagulopathy) |
|
|
|
MC eye finding in Sturge-Weber?
|
glaucoma
|
|
|
|
chalazion
|
a subacute or chronic inflammation of the meibomian glands and is a lipogranulomatous nodule.
usually responds well to warm compresses |
|
|
|
eye stye
|
(external hordeolum) is inflammation, usually representing bacterial infection, of the sebaceous gland (gland of Zeis) or sweat gland (gland of Moll) of the eyelash follicle and occurs at the lid margin.
It is generally self-limited and often resolves spontaneously. |
|
|
|
reduced-to-absent fetal movement, polyhydramnios, and short umbilical cord
Think? |
arthrogryposis
|
|
|
|
Which two drug classes are most likely to cause chronic headaches from overuse for headache pain
|
opiates and barbituates
|
|
|
|
What does the term legally blind mean?
|
Corrected vision of 20/200 in the best eye
|
|
|
|
What is the classic presentation of mumps
|
parotitis (swelling), H/A, malaise, fever
|
|
|
|
What complications should you think of with mumps?
|
orchitis, meningoencephalitis, pancreatitis, myocarditis, and oophoritis
|
|
|
|
What is the role of human milk fortifier in the NICU?
|
provide the additional protein load needed in the preterm infant
|
|
|
|
elevated lactate dehydrogenase concentration, tachypnea, oxygen desaturations, low-grade fever, and diffuse bilateral pulmonary infiltrates. Think?
|
Pneumocystis jiroveci (previously P carinii)
|
|
|
|
This bacterium has been isolated from unfiltered, unpasteurized apple juice.
|
enteropathic ecoli
|
|
|
|
initial fluid resuscitation for VLBW preterm infants
|
D10 (no electrolytes needed within first 24 hours)
|
|
|
|
Sever disease
|
calcaneal apophysitis, an overuse injury.
most specific finding is pain with lateral and medical compression over the heal. treat with heal stretching exercises. |
|
|
|
he most common cause of hypoglycemia in early childhood
|
ketotic hypoglycemia, which seems to result from an imbalance between glucose utilization and production through hepatic, and to a lesser extent, renal glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
|
|
|
|
chronic granulomatous disease-what is it?
what type of organisms are they susceptible to? |
-a defect in the phagocytic NADPH oxidase system that prevents phagocytes from adequately killing catalase-positive organisms.
-Staphylococcus aureus, and a number of enteric gram-negative rods (including Salmonella, Serratia marcescens, Burkholderia cepacia), Aspergillus, Acinetobacter, and Nocardia. oxidative burst test, the ability of the patient's white blood cells (WBCs) to oxidize a rhodamine dye is assessed by flow cytometry |
|
|
|
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP)
|
-a small-vessel vasculitis
-involvement of the joints, skin, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and kidneys. -dermatologic manifestation is a purpuric rash over the extensor surfaces (often the buttocks and lower extremities) |
|
|
|
Treatment and prognosis of HSP?
|
big picture: amount of renal disease predicts severity
-if gross hematuria, or proteinuria-need renal bx and possible immunosuppressive therapy. Microscopic hematuria is not concerning, but monitor often. |
|
|
|
history of recurrent sinusitis, pneumonia, and decreased immunoglobulin concentrations
Think? |
common variable immunodeficiency
|
|
|
|
x-linked agammaglobulinemia vs. common variable immunodeficiency
|
x-linked has low level of B cell concentration; whereas, CVID has normal number of B cell
|
|
|
|
x-linked agammagobulinemia
|
a mutation affecting the Btk tyrosine kinase, halts B cell development at the pro- and pre-B cell in the bone marrow, with very few (usually <1%) B cells moving out of the bone marrow. Patients classically present in early infancy (ie, 4 to 6 months of age), when passive maternal antibody wanes and the B-cell defect prohibits mature B-cell and immunoglobulin production in the infant.
|
|
|
|
Severe combined immunodeficiency
defect? classic presentation? treatment? |
most often is due to a defect in the common gamma chain that is vital for intracellular signaling for interleukin (IL)-2, -4, -7, -9, -15, and -21 receptors. The defect impairs cellular function due to low concentrations of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells.
Patients typically present within the first 6 months after birth with failure to thrive, chronic diarrhea, and an eczematous rash that often is mistaken for atopic dermatitis. Immediate recognition and diagnosis is crucial because bone marrow transplantation prior to age 4 months of age is associated with improved survival. |
|
|
|
Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)
defect? presentation? treatment? |
triad of severe eczema, sinopulmonary infections, and thrombocytopenia, although only 5% to 10% of patients have all three features at presentation. Concentrations of IgM may be low, although IgG, IgA, B-cell, and T-cell concentrations are normal. WAS, an X-linked disease, is due to defects in the WAS protein that is a regulator in actin polymerization and hematopoietic cell development. Treatment includes stem cell transplantation, IVIG, management of bleeding diathesis, and antibiotics.
|
|
|
|
child with intellectual disability and hypercalcemia
Think: |
Williams syndrome
|
|
|
|
WIlliams syndrome-describe the vascular involvement and etiology
|
MC: supravalvular aortic stenosis, but really widespread vascular involvement, including pulmonary artery stenosis, coarctation of the aorta, aortic hypoplasia, and renal artery stenosis.
etiology: a microdeletion chromosome 7 (7q11.23). This microdeletion involves the elastin gene and some 25 to 27 other genes |
|
|
|
Describe the non vascular involvement of Williams syndrome
|
infantile hypercalcemia, which can lead to hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis that usually resolves by 1 to 2 years of age.
Developmental problems-(IQ) scores ranging from 40 to 90. Language is relatively preserved, with fluent speech and better-than-expected vocabulary than predicted by the IQ. Children who have WS struggle with visuospatial relationships and understanding math concepts. Although they function well socially and have friendly demeanors, they do exhibit some phobias and anxiety. The phenotypic physical features of WS include broad forehead, small nose, long philtrum, wide mouth, and full lips. Some of these features soften somewhat into adulthood, but others persist. |
|
|
|
how often should you screen for Chlamydia
|
under age 25, yearly
high risk, under 25, q 6 months |
|
|
|
Malaria prophylaxis
|
Choroquine
Atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, and mefloquine are indicated for the treatment or prevention of malaria in areas where chloroquine-resistant strains have emerged |
|
|
|
common causes of bronchiolitis in infants and children
|
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, parainfluenza viruses, influenza, and human metapneumovirus (hMPV)
|
|
|
|
patchy hair loss with pitting of the nails
|
Alopecia areata
|
|
|
|
Alopecia areata
|
patchy hair loss with pitting edema
etiology unknown, but there is an association with autoimmune disorders |
|
|
|
names for different patterns of hair loss
|
patchy loss is called alopecia areata, complete scalp hair loss is alopecia totalis, and loss of all scalp and body hair is termed alopecia universalis.
|
|
|
|
Nevus sebaceous
|
Nevus sebaceus is present at birth in two thirds of cases and occurs as a single oval-to-linear plaque. During infancy, the lesion is smooth-to-papillated, waxy, and hairless; during puberty, sebaceous glands hypertrophy, producing a more elevated and verrucous appearance.
|
|
|
|
prenatal phenytoin syndrome
|
prenatal phenytoin exposure is associated with a broad, low nasal bridge; epicanthal folds; wide-spaced eyes (hypertelorism); cardiovascular abnormalities; and distal digital hypoplasia (fetal hydantoin syndrome)
|
|
|
|
Infection with Scarlet fever is almost indistinguishable from what other bacterial infection?
What clinical signs distinguish it? |
Arcanobacterium (formerly Corynebacterium) haemolyticum, a gram-positive bacillus that grows slowly as small colonies with narrow bands of hemolysis on blood-enriched agar.
Except for the absence of palatal petechiae and strawberry tongue, the clinical illness caused by A haemolyticum is indistinguishable from that caused by group A Streptococcus and is manifested by fever, pharyngeal exudate, and cervical lymphadenopathy. |
|
|
|
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) is characterized by the triad of:
|
hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute renal failure
|
|
|
|
prognostic factors for predicting HUS
|
1) the use of antimotility agents in the first 3 days of illness
2) vomiting in children younger than 5.5 years of age 3) a white blood cell count greater than 13.0x103/mcL (13.0x109/L) in the first 3 days of illness. The risk of developing HUS was increased sevenfold when the white blood cell count was greater than 13.0x103/mcL (13.0x109/L). |
|
|
|
if not resolved by what age, dacrostenosis should be probed open
|
1 year
|
|
|
|
Dacrostenosis most commonly resolves by what age?
|
8 months
|
|
|
|
what is the classic sign of small vessel disease?
|
palpable purpura
|
|
|
|
what bacteria is seen in acne?
|
Propionibacterium acnes
|
|
|
|
MCC of hair loss
|
tinea capitis
trichotillomania alopecia areata |
|
|
|
compare:
1. neonatal sebaceous hyperplasia 2. neonatal neonatorium |
both result from maternal hormones
1. shiny, yellow papules - resolves in a few weeks 2. peaks at 2 months |
|
|
|
compare neonatal:
1. milia 2. erythema toxicum 3. mongolian spots |
1. extension of dead skin and oily material in hair follicles; resolve within 1st month
2. blotchy red spots with overlying white or yellow papules or pustules. resolves within a few days of life 3. malanocytes arrested in migration from neural crest to epidermis, may resolve within first few years of life. |
|
|
|
chalazion
|
inflammation of meibomian (tarsal) gland leading to formation of the granuloma. nontender firm nodules on eyelids. Tx: warm compresses, excission if necessary, MC will subside spontaneously over months
|
|
|
|
diskitis
|
pyogenic infxn of disk space.
uncommon primary infection of nucleus pulposus with secondary involvement of cartilagenous end plate and vertebral body. MC < 10 yoa. mod/severe pain inc. ESR |
|
|
|
Mt'l encephalopathy
|
mut'n in either nuclear or mt'l DNA.
1. MELAS (mt'l encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke like episode) 2. MERRF (mt'l encephalopathy with ragged red fibers) 3. Reye syndrome |
|
|
|
MELAS
|
mt'l encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke like episode.
-pt mut'n in tRNA in mt'l DNA =leucine -prior to 15 yoa with hemianopia or cortical blindness -typically short stature -die by 20 yoa Dx: mm bx |
|
|
|
MERRF
|
mt'l encephalopathy with ragged red fibers.
tRNA in mt'l DNA mut'n = lysine child or adult looks simalr to Friedreich's ataxia normal, then develop progressive epilepsy, cerebellar ataxia, dysarthria |
|
|
|
Reye's syndrome
|
microvesicular steatosis and aberrant mt'l metabolism.
can ocur with varicella-zoster or influenza b infection with ASA. -recurrent reyes like syndrome is seen in kids with genetic defects of fatty acid oxidation |
|
|
|
PANDAS
|
pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric d/o.
behavioral problems, OCD, tics with an antecedent GABHS infn. ?in dz spectrum of syndenham's chorea. ? autoimmune attack of basal ganglia triggered by GAS infection. |
|
|
|
epiglottitis
|
supraglottic tissue
MCC: h. influenzae type b other causes: S. pyogenes, S. pneumo, S. aureas Age: 2-6 yoa Si/Sx: "hot potato voice" ins. stridor, drooling, toxic tripod position, NO cough. Tx: Refampin PPx, Ceftriaxone, secure airway |
|
|
|
Tetanus tx?
|
rapid human tetanus Ig.
IV PCN or metronidazole surgical excision and debridement of wound, mm relaxent i.e. diazepam to promote relaxation and sz control. dark room, sedation, intubation |
|
|
|
linezolid
|
class: oxazolidinone PO=IV
Tx: Resistant GP superior to vanc for MESA PNA, some atypical mycobt, broad tissue penetration. toxic: diarrhea in 30%, thrombocytopenia - weekly CBC, may prolong neutropenia in CA pt. |
|
|
|
Hypomelanosis of Ito
|
congenital skin disorder
linear or whorled hypopigmentaition. Follows lines of Blaschko = the path of embryonic neural crest cell migration. 25% microcephalic 40% sz 70% dec IQ |
|
|
|
Alopecia Areata
|
total hair loss in localized area.
etiology: immunologic mediated, infiltration of lymphocytes may be relapsing/remitting Tx: high rates of spontaneous resolution/regrowth within 12 months. +/- steroids. minoxidil or other immune modulation |
|
|
|
skin findings in Rubella (german measles)
|
pink macules and papules.
initially on face and spread inferiorly within 24 hrs. |
|
|
|
skin findings in measles
|
erythematous macules and papules initially along hairline, spreading inferiorly within 2-3 days. fade within 4-6 days with subsequent desquamation
|
|
|
|
skin findings in hand, foot, mouth
|
vesicles rapidly upen to painful ulcers.
soft palate is common gray blisters on hands/feet on background erythema |
|
|
|
skin findings in RMSF
|
2-6 mm blanchable macules -wrists, forarms, ankles, palms, soles. spread centrally within 6-18 hr, deep red papules over 1-3 days. within 2-4 days, exanthem is no longer blanchable
|
|
|
|
skin findings in erythema infectiosum
|
"slapped cheeks" +/- palms/soles. mucous membranes may have red spots
|
|
|
|
skin findings in meningococcemia
|
discrete, pink macules, papules, and petechiae over trunk, extremities, and palate
|
|
|
|
skin findings in gonococcemia
|
erythematous macules over arms and legs evolve into hemorrhagic, painful pustules within 2-3 days
|
|
|
|
skin findings in syphilis
|
primary: painless "button-like" chancre with indurated border
secondary: multiple, discrete, firm, "ham colored" papules scattered symmetrically over trunk, palm, soles, and genitals. Condyloma lata: soft, flat topped pink papules in anogenital region. tertiary: some untreated develop brown, firm plaques on body |
|
|
|
skin findings in lyme dz
|
Erythema chronicum migrans - expanding, erythematous annular plaque with central clearing
|
|
|
|
skin findings in Kawasaki dz
|
papules/plaques in stocking/glove pattern 1-3 days s/p onset of fever. the spreads to involve entire body. last an average of 12 days.
|
|
|
|
PPx for recurrent UTIs
|
TMP-SMX
|
|
|
|
PPX for pneumocystis carinni pneumonia
|
TMP-SMX, dapsone, pentamidine
|
|
|
|
PPX for endocarditis with surgical or dental procedures
|
PCN
|
|
|
|
Amphotericin B
|
MoA: binds ergosterol (fungi)
Tx: systemis mycosis - cryptococcus, blastomycosis, coccidoides, aspergillosis, histoplasma, candida, mucor mycosis. does not cross BBB, therefore, introthecal dosing for meningitis toxic: hypotn, nephrotx, arrythmia, anemia, IV phlebitis |
|
|
|
Crigler Najjar II syndrome
|
AD
mut'n in glucuronyl transferase activity infants are Asx kericterus unusual Tx: phenobarbital 7-10 days |
|
|
|
Copper deficiency
|
metaphyseal irregularity
poor feeding, irritable neutropenia Cu is component of cytochrome C and lysyl oxidase (enzyme critical to collagen and bone formation) Nl: vit D values |
|
|
|
Alagille syndrome
|
no or dec number of bile ducts.
progressive destruction of the ducts. si/sx - unusual facies (broad forehead, hypertelorism, underdeveloped mandible), ocular abnormalities, CV abnormalities (PPS), tubulointerstitial nephropathy, vertebral defect. Px: increased choleterol, neurologic complications |
|
|
|
unconjugaed hyperbili
|
if nl retic: infxn, CHF, drugs, gilbert's, crigler najjar type II
if inc retic: autoimmune hem anemia, drug induced hem anemia, PNH, RBC membrane defect, RBC enzyme defect, DIC, trasfusion rxn, HUS, hemoglobinopathy |
|
|
|
define conjugated hyperbili
|
> 20% or total or > 2 mg/dL
|
|
|
|
conjugated hyperbili
|
if increased AST/ALT more than Alk phos: infxn, EBV, hepatitis, wilsons, drugs/toxins, autoimmune hepatitis.
if increased alk phos more than AST/ALT, think obstruction |
|
|
|
autoimmune hepatitis - labs?
|
ANA, ASMA, anti - LKM
|
|
|
|
C.I. to measles vaccines
|
pregnancy, TB, immunocompromised, egg or neomycin allergy
|
|
|
|
when you see (number) in a newborn think:
1. increased Ca 2. polydactyly 3. polysplenia 4. hypogonadism |
1. williams
2. trisomies 3. left - right symmetry 4. CAH, prader - willi, turners |
|
|
|
classic presentation of botulism
Tx? |
acute b/l CN palsies associated with symmetric descending weakness, no fever, no sens deficits.
Tx: equine trivalent antitoxins |
|
|
|
spondoylolysis
|
fxr of pars interarticularis due to repetative stress on the arch.
etiology: new bone formation in areas where the annular ligament is stressed. 1. congenital: cervical 2. acquired: lumbar, MC L5 (85% of cases) -scottie dog sign |
|
|
|
oppositional defiant d/o
|
impairment in social and academic functioning. - refusal to follow rules.
+/- going onto conduct d/o |
|
|
|
conduct d/o
|
violation of basic rights of others.
40% go onto antisocial personality d/o. Tx: antipsychotics, lithium, SSRIs. |
|
|
|
ADHD
|
3 types: inattentive, hyperactive-impulsive, combined
> 6 months, in 2 settings, onset prior to 7 yoa. 20% have sx into adulthood |
|
|
|
2 groups of fluoroquinolones
|
1. primarily gram neg: cipro
2. resp: good gram neg and gram pos, usually aerobic activity: moxi-, levo-, gemi-, loma-, MRSA becomes resistent if only agent used. |
|
|
|
congenital syphilis
|
saber shins, saddle nose, deafness
|
|
|
|
argyll robertson pupils
|
tertiary syphilis
|
|
|
|
syphilis bt
|
treponoma pallidum
|
|
|
|
tabes dorsalis
|
tertiary syphilis - broad based ataxia, + romberg, charcot jts.
|
|
|
|
fetal anticonvulsant syndrome
|
phenytoin, carbamazapine, valproate, phenobarb.
midface hypoplasia, ocular hypertelorism, cleft lip +/- palate. nail hypoplasia, heart defects, dec bili at birth, withdrawal - tremulousness, inc activity |
|
|
|
pupils that constrict with accommodation, but don't react to light, think?
|
syphilis
|
|
|
|
4 p - syndrome
|
wolf hirshhorn sydrome.
prenatal onset growth def., prominent glabella, microcephaly, cleft lip +/- palate, profound MR |
|
|
|
pediculosis
|
lice - permethrin rinse
|
|
|
|
cutaneous larva migrans
|
-eruption caused by several larval nematodes not usually parasitic to humans.
-MC: Ancylostoma braziliena (hookworm to dogs/cars)-eggs in feces then hatch, larvae penetrate human skin and migrate along epidermal-dermal jxn. Si/Sx: raised, erythematous, serpiginous tracks, occasionally forming bullae, single or multiple - usually on extremity or buttocks. Tx: usually self limited, thiabensazole if warrents tx. |
|
|
|
scabies
|
female mite: Sarcoptes scabri huminis
-mite exudes keratolytic substance and burrows into stratum corneum depositing eggs and feces daily, eggs hatch, mature in 2-3 weeks and repeat cycle. Tx: permethin (lindane can be used, but neurotoxic to infants) |
|
|
|
congenital varicella syndrome
|
1st 20 weeks gestation
-limb hypoplasia, scarring, vesicular rash, neurologic deficits |
|
|
|
Pompe's dz
|
AR
def in acid alpha-1,4-glucosidase; therefore, mannose cannot turn into glucose. glycogen in heart and skeletal -macroglossia, hypotonia, hepatomegaly -death by 1-2 yoa -juvenile form is milder with little to no heart involvement, death is secondary to resp. failure. Tx: enzyme replacement-delays progression |
|
|
|
Ectopia lentis
|
subluxation of lens leading to iridodonesis (iris quivering) and myopia.
later complications: astigmatism, optic atrophy, glaucoma, cataracts, retinal detachment. |
|
|
|
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
|
AR
defect in DNA repair mechanisms predisposing to certain skin conditions - basal and squamous skin Ca |
|
|
|
Hurler's dz
|
AR / MPS
-def of alpha-L-idoronidase -severe, progressive, death by 10 yoa -MR, heart dz, corneal clouding, organomegally, coarse facies, dystosis multiplex, obstructive airway dz, enlarged tongue, hearing loss, limited language. Tx: BMT, enzyme replacement |
|
|
|
Fluorquinolones
|
MoA: inhibit DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) - cidal PO=IV
Tx: pseudomonas / GN / PCN resistant strep pneumo toxic: GI, HA, dizzy, photosensitivity, no evidence of cartilage toxicitiy in juvenile animals. reports of achiles tendon rupture esp if on steroids. leg cramps, myalgia. C.I. in pregnancy and kids b/c of cartilage. |
|
|
|
rapid correction of ____ leads to cerebellar pontine myelinosis
|
hyponatremia
|
|
|
|
cardiac silhouette for:
1. ToF 2. transposition 3. TAPVR |
1. boot shaped with dec pulm vasc markings and hypoplastic main pulm artery. 25% have right aortic arch.
2. egg shaped 3. snowman shaped, left vent vein, left innominate vein, dilated SVC. |
|
|
|
rheumatic fever
|
follows pharyngitis by 1-5 weeks.
-Aschcoff bodies in myocardium -Jones criteria + ASO titer Tx: PCN IM x 1, 75% recover in 6 weeks, 5% still with Sx at 6 months 65% recur (10% after 10 years) |
|
|
|
Jones criteria
|
Rheumatic fever: 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor
Major: Joints, cardiac (MR > AR ? TR), nodules, erythema marginatum, syndenham's chorea. Minor: arthralgia, fever, inc ESR/CRP, inc P-R interval |
|
|
|
S.E. of methimazole and propylthiuracid
|
MC: rashes, arthritis, arthralgias
rare: hepatitis (PTU --> hepatic failure), neutropenia, agranulocytosis, systemic vaculitis --> hematura (more common with PTU) |
|
|
|
At what size lesion with GAS or MRSA should one begin Tx?
|
5 cm
|
|
|
|
chronic urticaria
|
recurrent symptoms of urticaria > 6 weeks.
30-50% = autoimmune (circulating autoantibodies against IgE receptor (FceRI) on mast cells and basophiles. |
|
|
|
physiologic anemia of infancy occurs when?
|
6 weeks to 3 months
|
|
|
|
infantile spasms
|
4-8 month
short lived symmetric contractions of neck, trunk, and extremities - up to 100/day. symptomatic type is MC seen with CNS malformations, brain injuries, TS, IEoM --> poorer outcome cryptogentic type: better outcome, uneventful birth hx - reach developmental milestones before onset. |
|
|
|
bt'l cidal Abx
|
PCNs, cephs, vanc, aminoglycosides, fluouroquinolones, metronidazole.
|
|
|
|
chronicially corticosteroid dependant kid with varicella infxn
|
dz could be devastating if give stress dose (3-6 x nl) therefore, may just need to give 2 x nl dose to balance b/t need for stress dose and making immunocompromised
|
|
|
|
latent TB infxn is defined as:
what to do? |
+PPD, neg CXR
INH x 9 months |
|
|
|
prophylaxis of INH resistant TB strain
|
rifampin x 6 months
|
|
|
|
mulberry lesion in retina
think: |
tubero sclerosis
|
|
|
|
spot urine protein to creatinine ratio - what is nl?
|
< 2
|
|
|
|
what type of allergy does eczema go along with
|
food
|
|
|
|
monitor what with amphotericin B therapy
|
hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia b/c of renal effects.
|
|
|
|
juvenile nephronophthises (NPH)
|
AR with Joubert syndrome with aplasia of cerebellar vermis --> ataxia and retinal coloboma/ retinitis pigmentosa, hepatic fibrosis and skeletal deformities.
can be seen in Senior-Loken syndrome which involves the eye with tapetoretinal degeneration, retinitis pigmentation --> blindness. nystagmis, coloboma, cataracts. -polyuria, polydypsia, short stature, azotemia, anemia, proteinuria, chronic tubulointerstial dz --> ESRD. median age of onset: 13 yoa. renal bx: tubular damage, interstitial fibrosis, nl glomeruli, cysts in advanced dz. |
|
|
|
Alports syndrome
|
X linked
alpha 5 chain of type IV collagen hematuria, high freq sensorineural hearing loss, anterior lenticonis (and occasionally cataracts.) |
|
|
|
Lowe syndrome
|
x-linked d/o
fanconi syndrome MR cong cataracts |
|
|
|
nephropathic cystinosis
|
AR
a LSD fanconi, FTT, cystine crystal deposition within the cornea, severe photophobia |
|
|
|
duodenal atresia
|
failure to recanalize lumen after solid phase of intestinal development. 20-30% --> down's syndrome.
"double-bubble" look for malrotation, esophageal atresia, and cong heart dz. |
|
|
|
volvulus
|
severe epigastric pain
intractable retching with emesis "bird beak" |
|
|
|
MCC of bowel obstruction in 2 mon to 5 yoa
|
intussusception
a: viral - enterovirus in summer, rota in winter b: a "lead pt" - Meckels, polyp, lymphoma, HSP, CF classic triad: colicky abd'l pain, bilious vomiting, current jelly stools, RUQ mass |
|
|
|
Dance's sign
|
absence of bowel in RLQ
think: intussusseption |
|
|
|
pseudokidney sign
|
superimposed hypoechoic (edematous walls of bowel) and hperechoic (areas of compressed mucosal layers)
think: intussusseption |
|
|
|
which food allergies may be outgrown?
|
3-5 yoa:
milk, egg, soy, wheat |
|
|
|
when should you give a febrile child with stridor corticosteroids
|
croup, epiglottitis, retropharyngeal abscess, bt/l tracheitis
|
|
|
|
VACTERL sequence
|
vertebral
anorectal cardiac tracheal esophageal renal limb |
|
|
|
croup - MCC, Si/Sx
|
parainfluenza virus, barking cough, steeple sign
|
|
|
|
epiglottitis - MCC, Si/Sx
|
S. pneumo
HiB tripod position, thumb sign |
|
|
|
tracheitis - MCC, Si/Sx
|
S. aureus
HiB rapidly progressive |
|
|
|
use ____ to stimulate gastric emtying
|
1. metocopromide
2. erythromycin - intestinal movement |
|
|
|
when should you give a febrile child with stridor corticosteroids
|
croup, epiglottitis, retropharyngeal abscess, bt/l tracheitis
|
|
|
|
VACTERL sequence
|
vertebral
anorectal cardiac tracheal esophageal renal limb |
|
|
|
croup - MCC, Si/Sx
|
parainfluenza virus, barking cough, steeple sign
|
|
|
|
epiglottitis - MCC, Si/Sx
|
S. pneumo
HiB tripod position, thumb sign |
|
|
|
tracheitis - MCC, Si/Sx
|
S. aureus
HiB rapidly progressive |
|
|
|
use ____ to stimulate gastric emtying
|
1. metocopromide
2. erythromycin - intestinal movement |
|
|
|
salter harris classification
|
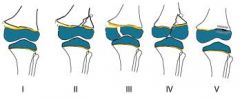
|
|
|
|
yellow fever
|
flavivirus, an arbovirus
transmitted by Aedes mosquito Sx: high fever, black vomiting, jaundice, Councilman bodies (acidophilic inclusions) may be seen in the liver. |
|
|
|
HIV immunity
|
CCR5: homozygous = immune (1% whites), heterozygous = slower course (20% whites).
CXCR1 - rapid progression to AIDS |
|
|
|
stress ulcers secondary to what?
|
sepsis, trauma (Cushings), burns (Curlings), dehydration, resp/card insufficiency, NSAIDS, steroids, H. pylori
|
|
|
|
when to give PPX for peptic ulcers
|
NPO, steroids
|
|
|
|
pyloric stenosis
|
3-5 moa, associated with erythromycine, eosinophila, gastroenteritis, epidermolysis, trisomy 18, turners.
"string sign" "shoulder sign" - bulge of pyloric mm into antrum. "double tract sign" - parallel streaks of barium in the narro channel |
|
|
|
benign neonatal familia convulsions
|
AD
brief, self limited. generlaized sz beginning in the first week of life and subsiding by 6 weeks. 10-15% chance of future epilepsy |
|
|
|
neuroblasoma
|
neural crest - small round blue cell.
MC neoplasm of infancy peak at 2 yoa sympathetis nervous tissue-abdomen, adrenal, retroperitoneal sympathetic ganglia. -30% cervical/thoracic may present with Horners. Opsoclonus - myoclonus (dancing eyes, dancing feet b/c paraneoplasti Ab" 95% inc HVA, VMA in urine; MIBG scan. stage 4s - infantile form is self limiting |
|
|
|
von Hippel-Lindau dz
|
neurocutaneous syndrome.
cerebellum, spinal cord, medulla, retina, kidneys, pancreas, epididymis. neuro: cerebellar hemaglioblasomas (adult with inc ICP). Retinal angiomata: small masses of thin walled capillaries in peripheral retina |
|
|
|
Agenesis of corpus callosum
|
with numerous syndromes and IEoM.
eg: lissencephaly, Dandy-Walker syndrome, Arnold Chiari type 2, Alcardi syndrome. CT: lat ventricles shifted laterally. |
|
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
|
AD
slowly progressive, dimnished facial movements, weakness of shoulder girdle. nl life span. |
|
|
|
HSV-1
|
gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, temporal lobe encephalitis, herpes labalis.
transmitted: respiratory secretions, saliva |
|
|
|
Opportunistic infxns in AIDS:
1. brain 2. eyes 3. mouth/throat 4. lungs |
1. cryptococcus, toxoplasmosis, CMV, PML (JC virus), AIDS dementia
2. CMV retinitis 3. thrush (Candida albicans), HSV, CMV, oral hair leukoplakia (EBV) 4. pneumocystitis carinii pneumonia (PJP), TB, histoplasmosis |
|
|
|
HSV-2
|
herpes genitalis, neonatal herpes
|
|
|
|
paramyxoviruses
|
ssRNA
RSV-ribavirus measles mumps |
|
|
|
AIDS opportunistic infections
1. GI 2. skin 3. genitals |
1. cryptosporidiosis, mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, CMV colitis, non-Hodgkins lymphoma (EBV)
2. shingles (VZV, Kaposi's sarcoma (HHV-8) 3. genital herpes, warts, cervical CA (HPV) |
|
|
|
HIV encephalitis
|
occurs late in the course of HIV infections, virus gains CNS access via infected macrophages, microglial nodules with multinucleated giant cells
|
|
|
|
paragonimas westermani
|
undercooked crab meat-inflammation and secondary bt'l infection of lung.
Tx: Praziquantel |
|
|
|
Enterobius vermicularis
|
food contaminated with eggs-intestinal infxn causes anal pruritis (scotch tape test)
Tx:mebendazole / pyrante pamoate |
|
|
|
strongyloides stercoralis
|
larvae in soil penetrate the skin, intestinal infxn
Tx: ivermectin/ thiabendazole |
|
|
|
Charge syndrome
|
coloboma
heart dz atresia choanae retarded growth genital anomalies ear involvement |
|
|
|
maple syrup urine disease
|
dec alanine, inc branched chain aa (leucine, isoleucine, valine)
-def of branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase - no decarboxylation. si/sx: poor feeding, emesis - letharfy, coma wthin first week; alternating hyperonicity and flaccidity, convulsions, dec glc (correcting does not improve sx), maple syrup odor or urine, sweat, and cerumen Tx: IV acute and nonbranched aa, diet |
|
|
|
1. transitory neonatal myasthenia
2. familial infantile myasthenia |
1. passive transfer of Ab from myasthenic female. self limited-generalized weakness and hypotonia for 1-2 months. Tx: supportive unless severe --> neostigmine or exchange transfusion
2. AR; seronegative d/o of NM jxn. response to edrophonium, long term tx: neostigmine or pyridostigmine; thymectomy and immunosuppressive care of no benefit. |
|
|
|
multiple CN palsies
think: |
botulism
|
|
|
|
MC 1st sign of infant botulism
|
no BM
|
|
|
|
gullain barre syndrome
|
postinfectious demyelinating neuropathy affecting predominantly motor neurons.
-classically 10 days s/p campylobacter jejuni or mycoplasma PNA -legs --> trunk, arms --> bulbar mm Tx: IVIG or plasmapharesis +/- intubation |
|
|
|
Ataxia-telangectasia
|
AR
MC degenerative ataxia, MC begins at 2 yoa --> cannot walk by adolescence. oculomotor apraxia is common. telangiectasea by teenage is prominent on bridge of nose, conjunctiva, and exposed surfaces of extremities. -50-100 x inc chance of brain tumors and lymphoid tumors |
|
|
|
6 yo male
2 wk hx of aggressive edema at various sites; hx of URI and yellow jacket sting Dx? |
serum sickness
|
|
|
|
male with acute onset monoarticular jt pain + b/l bells palsy
dx? cause? |
lyme dz
Ixodes tick |
|
|
|
fxns of T cells
|
cytotoxicity against virus infected cells
mediation of delayed type HS production of interleukin - 2 and lymphokines |
|
|
|
endogenous hypertriglyceridemia
|
inc VLDL
si/sx: obesity, glc intolerance, insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, hyperuridemia Tx: wt control, diet def: overproduction or dec clearance of VLDL |
|
|
|
maple syrup urine disease
|
dec alanine, inc branched chain aa (leucine, isoleucine, valine)
-def of branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase - no decarboxylation. si/sx: poor feeding, emesis - letharfy, coma wthin first week; alternating hyperonicity and flaccidity, convulsions, dec glc (correcting does not improve sx), maple syrup odor or urine, sweat, and cerumen Tx: IV acute and nonbranched aa, diet |
|
|
|
1. transitory neonatal myasthenia
2. familial infantile myasthenia |
1. passive transfer of Ab from myasthenic female. self limited-generalized weakness and hypotonia for 1-2 months. Tx: supportive unless severe --> neostigmine or exchange transfusion
2. AR; seronegative d/o of NM jxn. response to edrophonium, long term tx: neostigmine or pyridostigmine; thymectomy and immunosuppressive care of no benefit. |
|
|
|
multiple CN palsies
think: |
botulism
|
|
|
|
MC 1st sign of infant botulism
|
no BM
|
|
|
|
gullain barre syndrome
|
postinfectious demyelinating neuropathy affecting predominantly motor neurons.
-classically 10 days s/p campylobacter jejuni or mycoplasma PNA -legs --> trunk, arms --> bulbar mm Tx: IVIG or plasmapharesis +/- intubation |
|
|
|
Ataxia-telangectasia
|
AR
MC degenerative ataxia, MC begins at 2 yoa --> cannot walk by adolescence. oculomotor apraxia is common. telangiectasea by teenage is prominent on bridge of nose, conjunctiva, and exposed surfaces of extremities. -50-100 x inc chance of brain tumors and lymphoid tumors |
|
|
|
6 yo male
2 wk hx of aggressive edema at various sites; hx of URI and yellow jacket sting Dx? |
serum sickness
|
|
|
|
male with acute onset monoarticular jt pain + b/l bells palsy
dx? cause? |
lyme dz
Ixodes tick |
|
|
|
fxns of T cells
|
cytotoxicity against virus infected cells
mediation of delayed type HS production of interleukin - 2 and lymphokines |
|
|
|
endogenous hypertriglyceridemia
|
inc VLDL
si/sx: obesity, glc intolerance, insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, hyperuridemia Tx: wt control, diet def: overproduction or dec clearance of VLDL |
|
|
|
cutaneous mycoses
|
1. Tinea versicolor
2. Tinea nigra 3. TInea pedis/cruris/corporus/capitis |
|
|
|
tinea versicolor
|
Malassezia furfur - hot, humid weather. hypopigmented skin lesions
Tx: topical miconazole and selenium sulfide |
|
|
|
tinea nigra
|
Ctadosporum Werneckii
infects keratinized layer of skin --> brownish spots Tx: topical salicyclic acid |
|
|
|
trichinella spiralis
|
undercooked meat, usually pork; mm inflammation, periorbital edema.
Tx: thiabendazole |
|
|
|
Freidrick's ataxia
|
AR
MC: triplet expansion in X25 genes on chrom 9 which encodes mt'l protein - Frataxia degeneration of dorsal columns and rootlets, spinocerebellar tracts and to lesser extent pyrimadal tracts and cerebellar hemisphere. <10 yoa slow progression of lower limb --> upper profound hypotonia; peripheral nerve sensory deficit; + Rhomberg DTR dec or absent; associated with skeletal abnomalities, cardiomyopathy, optic atrophy. inc AFP |
|
|
|
Acute Cerebellar Ataxia
|
Dx of exclusion in kids (1-3 yoa) often follows virus by 2-3 weeks. ? autoimmune on cerebellum. sudden onset of severe truncal ataxia; often cannot sit or stand; 50% horizontal nystagmus; compete recovery within 2 months.
|
|
|
|
IQ scale
|
mild 55-70% 85%
mod 40-55% 10% severe 25-40% 3-5% profound <25% 1-2% |
|
|
|
causes of encephalopathy
|
1. mt'l
2. hepatic 3. HIV 4. lead - no correlation b/t sx severity and lead level 5. syndenham's chorea - MC in female, rare < 3 yoa 6. adrenoleukodystrophy 7. tourettes |
|
|
|
hepatic encephalopathy
|
MC related to fulminent viral hepatitis (50-75%).
mental status change; inc ammonia due to impaired hepatic failure; inc GABA may play a role; reversible with treatment. 75% mortality |
|
|
|
conjunctivitis types
|
1. allergic - IgE mediated, Tx: cold compression and antihistamine
2. viral- MC: adenovirus, also coxsachivirus - preauricular LN. Tx: supportive 3. Bt'l - H. influenzae and S. pneumo; mucopurulent d/c. Tx: topical Abx |
|
|
|
hutchinson's triad
|
congenital syphilis - manifests around 2 yoa
1. interstitial keratitis 2. peg shaped incisors 3. deafness (CN VIII) |
|
|
|
syringomyelia
|
slowly progressive cavity formation within brain or spinal cord. MC in cervical or lumbar regions.
incomplete closure of neural tube during 4th week of gestation. often develops post traumatically in setting of undiagnosed Chiari I or tethered cord. Sx: b/l imparied pain/temp sensation secondary to decussation of fibers near central canal |
|
|
|
morbidities of infants of DM mothers
|
1. caudal regression
2. double outlet R ventricle / truncus arteriosis 3. inc bili 4. HOCM 5. macrosomia/organomegally 6. polycythemia with hyperviscosity 7. shoulder dystocia 8. small left colon syndrome 9. dec glc, dec Ca, dec Mag |
|
|
|
dracunculus medinensis
|
in drinking water - skin inflammation and ulceration.
Tx: Niridazole |
|
|
|
aminoPCNS
|
Ampicillin (shigella)
Amoxicillin (better GI absorption) MoA: same as PCN, penicillinase sensitive. Tx: can penetrate outer membranes of some GNR (E. coli, Proteus, Haimophilus, Moraxella, Shigella, Salmonella, enterococci, Listeria, Pasteurella, Eikenella) Drug of choice for enterococci and listeria. toxic: HS rxn, amp rash, pseudomona colitis. |
|
|
|
Who is most susceptible to transient aplastic crises in patient's with parvo B 19?
|
pt's with chronic hemolysis: SCD, thalassemia, hereditary spherocytosis, pyruvate kinase deficiency
|
|
|
|
CD4 count less than ____ are at highes risk for atypical mycobt'l infections.
Tx? PPx? |
50
clarithromycin or azithromycine plus ethambutal, rifabutin, rifampin, cipro, or amikacin. rifabutin, clarithromycin, azithromycin |
|
|
|
Rifabutin
|
PPx for atypical mycobacteria
S.E. bright orange body fluids |
|
|
|
types of shock
|
hypovolemia
obstructive distributive/septic cardiogenic |
|
|
|
alprostadil
-when to give stat? |
ductal dependent congenital heart disease
|
|
|
|
rhythms associated with pulseless arrest
|
pulseless VT
VF asystole |
|
|
|
cardinal signs of instability with bradyarrythmias are _______
|
1. shock with hypotension
2. poor end organ perfustion 3. altered level of consciousness (+/- slow/absent ventilation) 4. sudden collapse |
|
|
|
MC coagulase negative staph that infect humans...
Tx: |
S. epidermidis, S saprophyticus
R to multiple antibiotics; therefore, treat with vanc, rifampin, cipro |
|
|
|
S.E. of continuous albuterol nebs
|
tremor, tachycardia, palpitations, transent dec in PaO2, prolonged QTc interval, arrhythmias, increased glc, dec mag, dec K
|
|
|
|
_____= MCC of limping and acute hip pain in kids 3-10 yoa
|
transient synovitis
|
|
|
|
2 week old neonate has jaundice, hepatomegaly, and positive urinary reducing substance.
Dx: |
galactosemia
|
|
|
|
familial dysautonomia
|
abnormal suck, feeding difficulties, pain and temp insensitivity, labile b/p, no tears, scoliosis
|
|
|
|
canavan disease
|
lethal CNS d/o, dev delay, hypotonia, seizures, blindness
AR - can't breakdown aspartic acid - myelination issues |
|
|
|
Tx for status epilepticus
|
1. Ativan - 0.1 mg/kg IV or Diazepam 0.3 mg/kg IV or 0.5 mg/kd PR
2. phenytoin 20 mg/kd IV (fosphenytoin (20 mg/kg) 3. phenytoin 10 mg/kg or phenobarb 20 mg/kg 4. ICU, more phenobarb/benzo |
|
|
|
unilateral dilated pupil, think:
|
uncal herniation
|
|
|
|
congenital scoliosis
|
errors in vertebral development during embryogenesis, > 50% have other malformations:
25% heart, 20% kidney, 40% spinal cord - therefore, get an MRI |
|
|
|
neonatal sz, think of what etiologies:
|
HIE, intraventricular hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, hypglycemia, hypocalcemia, intracranial infections, cerebral dysgenesis, drug withdrawal
|
|
|
|
how to treat syndenham chorea
|
haloperidol - a DA blocker
|
|
|
|
Reye's syndrome
|
Acute encephalopathy and fatty degeneration.
prodromal illness - URI, varicella - protracted emesis 5-7 days s/p illness onset +/- derlerium, combative behavior, stupor, sz, coma, death Dx: liver bx - yellow/white b/c increased TG content Tx: decreased ICP, supportive |
|
|
|
McArdle's disease
|
AR - glycogen stores in skeletal mm. def of glycogen phosphorylase.
Si/Sx: temporary weakness and cramping during and after exercise - no rise in blood lactate, get second wind with initiation of fatty acid metabolism. Dx: Asx during infancy. mm bx and assay--> def of enzymes; myoglobinuria, and increased CK at rest. tx: diet: inc fat and protein, sucrose prior to exercise and proper warm up period. |
|

