![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
324 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
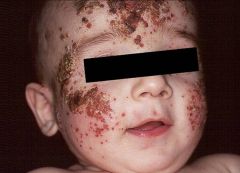
Eponym for Incontinentia Pigmentosa
|
Bloch-Sulzbuerger syndrome
|
|
|
Four phases of Incontinentia Pigmentosa
|
Phase 1: Vesicular (1-2wks old)
Phase 2: Verrucous (2-6wks) Phase 3: Hyperpigmentation Phase 4: Hypopigmentation (2nd - 3rd decade) |
|
|
Other Clinical Findings in Incontinentia Pigmentosa
|
Scarring Alopecia, Dystrophic changes in Nails, Anodontia or peg/conical teeth, strabismus, CNS - seizures, MR
|
|
|
Gene for Incontinentia Pigmentosa
|
NEMO, Xlinked.
Only females or Klinefelter's pts have seen to have this disorder. |
|
|
Conradi-Hunermann Syndrome Eponym?
|
Chondrodysplasia punctata
|
|
|
How many types of chondrodysplasia puntata are there?
|
Four -- base on inheritance patterns:
1. Conradi-Hunerman type is AD 2. Rhizomelic form is AR, dies in infancy, Arylsulfatase E gene 3. X-linked recessive, continguous gene deletion syndrome, Arylsulfatase E gene 4. X-linked dominant = EBP gene = Emopamil-binding protein on Xp11 |
|
|
Turner Syndrome Eponym
|
XO syndrome
Gonadal dysgenesis |
|
|
Noonan Syndrome Gene defect
|
AD
PTPN11 gene on Chromosome 12 encodes protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 (also in LEOPARD) |
|
|
LEOPARD Syndrome synonym
|
Multiple Lentigines Syndrome
|
|
|
Name the Dz:
retinal angiomas cerbellar medullary angioblastic tumors pancreatic cysts renal tumors and cysts cerebellar hemangioblastomas secondary polycythemia hypernephromas pheochromocytomas |
Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
|
|
|
Inheritance and gene mutation in Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
|
AD
germline mutation of a tumor suppressor gene on short arm of Chromosome 3 |
|
|
BLOOM SYNDROME
|
AR, RecQL3 gene
DNA helicase – important in DNA replication and repair Mutation: sister chromatid exchanges; chromosomal breaks/gaps |
|
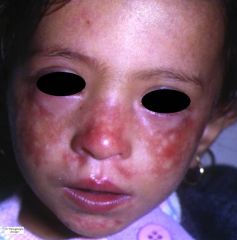
|
Bloom syndrome
Photodistributed erythema with telangiectasias in butterfly distribution Cheilitis CALMs |
|
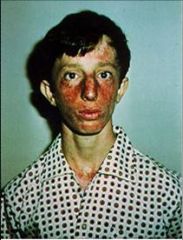
Dz & what other immune problems are assoc with it?
|
“triangle face” – long narrow face with prominent nose and small mandible
High pitched voice Low IgA, IgM Recurrent respiratory/GI infections Hypogonadism, Infertile males |
|
|
What Ig are low in Bloom Syndrome?
|
Low IgA, IgM -->
Recurrent respiratory/GI infections |
|
|
What syndrome has:
“triangle face” – long narrow face with prominent nose and small mandible High pitched voice Hypogonadism, Infertile males |
Bloom Syndrome
|
|
|
What neoplasms can be assoc with Bloom Syndrome?
|
Acute leukemia
Lymphoma GI adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Another name for Poikiloderma congenitale?
|
Rothmund-Thomson
|
|
|
Defect in Rothmund-Thomson
|
AKA: Poikiloderma congenitale
AR, RecQL4 gene (some cases) DNA helicase DNA repair Females > Males |
|
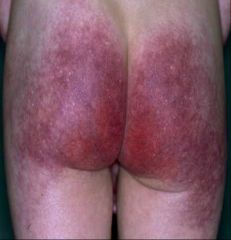
Name the Disease
|
Rothmund Thompson
Poikiloderma of face, buttocks, extensor surface |
|
|
What other findings assoc with Rothmund Thomson?
|
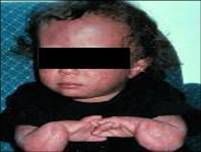
Alopecia
Dystrophic nails Juvenile cataracts (age 3-7) Hypogonadism Dental dysplasia Short with skeletal dysplasias Hypoplastic/absent radius or thumb Neoplasms Osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, SCC |
|
|
Neoplasms assoc with Rothmund-Thomson
|
Osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, SCC
|
|
|
Key Disease finding is Hypoplastic/absent radius or thumb?
|
Rothmund-Thomson
|
|
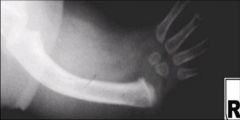
Disease?
|
Rothmund-Thomson
|
|
|
Defect in Cockayne Syndrome
|
AR
CSA: ERCC8 gene CSB: ERCC6 gene --> m/c Mutated DNA repair mechanism --> UV hypersensitivity & neurodegeneration |
|

|
Cockayne Syndrome:
Cachectic dwarfs w/ disproportionate long limbs Deafness Scaling erythematous plaques on malar cheeks, neck, hands Cachectic – subQ fat loss, sunken eyes Aged appearance “Mickey Mouse” facies Microcephaly, large ears |
|
|
What neurological changes or problems are seen in Cockayne Syndrome? Eye Changes?
|
Diffuse demyelination
progressive neurologic deterioration --> early death MR Intracranial calcification Retinitis pigmentosa “salt & pepper” retinal pigment, cataracts, optic atrophy [also seen in Refsum] XPB,D, G overlap |
|
|
Eponym for Trichothiodystrophy
|
Tay's Syndrome
or, PIBIDS |
|
|
PIBIDS stands for?
|
Photosensitivity
Ichthyosis Brittle hair Intellectual impairment Decreased fertility Short Stature |
|
|
Defect in Tay's Syndrome?
|
AR, ERCC2, same as XPD mutation
-- DNA repair defect |
|

|
Trichothiodystrophy:
Sulfur-deficient brittle hair Short, sparse Tiger-tail hairs (Trichoschisis) Of note: Photosensitive patients -- NO actinic damage, NO increased risk of skin cancers! |
|
|
Other findings in Trichotheodystrophy?
|
Ataxia
Cataract Hypogonadism |
|
|
Defect in Hartnup Disease?
|
AR
SLC6A19 gene Transporter neutral AA across the apical membrane in the kidney and intestine Defects = decreased absorption of tryptophan Tryptophan necessary for nicotinic acid production patients look like they have “pellagra” Tx: Nicotinic acid (Niacin) supplement |
|
|
Name the disease:
Lab abnormalties -- Massive aminoaciduria Tryptophan in urine CNS disturbance Cerebral ataxia Mild MR Psychiatric disturbance Emotional instability |
Hartnup Disease
Skin findings: Photodistributed erythema, scales Forehead, cheeks, extensor arms, dorsum of hands |
|
|
Name the three diseases with SLC mutations
|
Hartnup – SLC6A19
Zinc deficiency – SLC39A4 Citrullinemia type II – SLC25A13 [Type I – Argininosuccinic acid synthetase] |
|
|
Name the three diseases with RECQL mutations
|
WeBeR
Werner (2) Bloom (3) Rothmund Thomson (4) |
|
|
Defect in Chronic Granulomatous Disease
|
Deficient NADPH oxidase enzyme system:
gp91phox – encoded by CYBB gene (XLR) – m/c p47phox – 2nd m/c; AR p22phox p67phox |
|
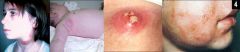
Disease?
|
Chronic Granulomatous Disease:
Lymphadenitis (cervical) Infections: Abscesses, Pyoderma, Periorificial dermatitis Epithelial linings (respiratory, GI) Hepatic abscesses, osteomyelitis, sepsis |
|
|
MC infection in Chronic Granulomatous Disease?
|
Staph aureus m/c bacterial infection
Aspergillus (fumigatus) m/c fungal infection Bronchopneumonia – most prevalent infection Female carriers: No increased infxns Recurrent stomatitis Lupus-like lesions on face w/ sun exposure |
|
|
What diagnostic tests are available to test for Chronic Granulomatous Disease?
|
Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test – WBC supposed to reduce dye into blue (not in CGD)
Oxidation of dihydrorhodamine to rhodamine w/ flow cytometry – quantitative test |
|
|
Gene defect in Wiscott Aldrich
|
XLR, WAS gene
Impaired T-cell activation and NK cell function Mutation causes problem with signal transduction & actin filament assembly |
|
|
What is the most common presenting symptom in Wiscott-Aldrich?
|
Presenting symptom:
1st few months of life --> bleeding problems |
|
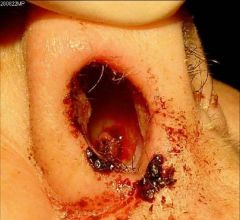
|
Wiscott-Aldrich:
Atopic dermatitis, Secondary bacterial infxns, Eczema herpeticum Thrombocytopenia bruising, bleeding |
|
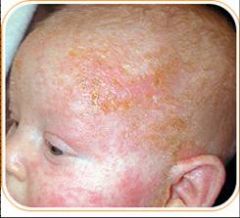
|
Atopic dermatitis, Secondary bacterial infxns, Eczema herpeticum
Thrombocytopenia bruising, bleeding |
|
Which recurrent infections are common?
Which Ig are low? high? |
Impaired immunity — cell-mediated, humoral
Recurrent infections: Encapsulated bacteria –m/c bacterial infection HSV, then HPV –m/c viral infection: - eczema herpeticum “minute mADE” Low IgM High IgA, D, E (ADE) |
|
|
What Ig are high vs low in Wiscott Aldrich?
|
minute mADE:
low IgM high IgA, D, E (ADE) |
|
|
MC assoc neoplasm in Wiscott Aldrich?
|
Lymphoreticular malignancy:
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma – m/c neoplasm |
|
|
MC cause of death in Wiskott aldrich?
|
Infxn > hemorrhage > malignancy – causes of death
|
|
|
Treatment for Wiscott-Aldrich?
|
Treatment:
BM transplant Splenectomy w/ abx prophylaxis |
|
|
Eponym for Hyper IgE syndrome
|
Job Syndrome or Buckley Syndrome
|
|
|
Defect in Hyper IgE Syndrome
|
AD STAT3
Basic deficiency: Impaired regulation of IgE function Deficient PMN chemotaxis |
|
|
Name the Disease:
Lab findings: IgE markedly increased IgD increased Peripheral eosinophilia |
Hyper IgE Syndrome
|
|
|
Describe clinical findings in Hyper IgE Syndrome
|
SKIN:
Eczematous dermatitis (flexures, postauricular, hairline) Excoriated papules on scalp, skin folds Infections – Staph aureus m/c OTHER FINDINGS: URI, respiratory infections coarse facies w/ broad nasal bridge osteopenia/fractures, scoliosis retained primary teeth; lack of secondary teeth Lab findings: IgE markedly increased IgD increased Peripheral eosinophilia |
|
|
MC of death in Hyper IgE Syndrome
|
Persistent lung infxn w/o bacterial prophylaxis—m/c cause of death
|
|
|
Treatment of Hyper IgE Syndrome
|
Treatment:
Cimetidine – immune modulation Interferon gamma – improve chemotaxis gamma globulin – decrease IgE levels |
|
|
Defect in Severe Combined Immunodeficiency
|
XLR
gamma chain (IL2 receptor) gene – m/c AR ADA (adenosine deaminase) gene – 20% JAK3 (Janus kinase 3 in WBCs) gene – chr19 Zap70 deficiency RAG1, RAG2 – Omenn’s Syndrome |
|
|
Name the disease:
SKIN: Cutaneous infections GVHD – in utero maternal WBCs, transfusion, BMT Morbilliform rash,SK like dermatitis, LP-like lesions,scleroderma-like lesions |
SCID
At risk for different types of infections: Staph, Strep, Candida Malabsorption due to chronic viral diarrhea Pneumonia—bacterial, Pneumocystis carinii Sepsis |
|
|
Name the disease:
Absent thymic shadow on CXR |
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency:
Treatment Death in 1 year without BMT Gene therapy |
|
|
Defect in Hereditary Angioedema
|
AD, C1INH gene
C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency or normal but defective |
|
|
Name the two forms of Hereditary Angioedema
|
Type I HAE – 85%
<35% of normal Type II HAE – 15% levels normal, but dysfunctional |
|
|
What are some causes of Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency?
|
Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency
Monoclonal B cell dz (lymphoma) Cryoglobulinemia Autoimmune d/o |
|
|
Clinical picture of Angioedema & pertinent negatives?
|
Angioedema
-- Laryngeal edema w/ obstruction -- 10-30% die of airway compromise Abdominal pain/vomiting/dysphagia NO urticaria, pruritus, pitting |
|
|
Lab findings & Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema?
|
Lab findings:
C2, C4 – decreased CH50, C3, C1 – normal Treatments: Danazol/Stanazol --> stimulate production of functional C1 est inh FFP/Epi/antihist/steroids --> flares |
|
|
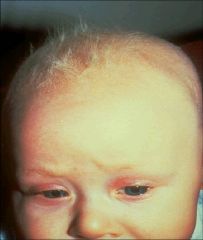
Defect in Menkes Syndrome?
|
XLR, MNK or ATP7A gene
Defective copper transport --> low serum copper Same gene in XLR Cutis Laxa XLR (CHAD’Z Lovely Kinky WIFE) |
|
|
MC hair change seen in Menkes?
|
HAIR
PILI TORTI – m/c Others: trichorrhexis nodosa, monilethrix |
|
|
Menkes Syndrome:
Scalp w/ short, steel-wool hair Hair broken off in eyebrows Eyelashes sparse |
|
|
What cause of death with Menkes?
|
Early death (2-3 y/o) from PNEUMONIA
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
SKIN: Hypopigmented doughy, lax skin Pudgy face; Upper lip like cupid’s bow CNS Tortuous arteries in brain Progressive decline—lethargy, seizures, MR MUSC-SKEL Frontal bossing Wormian bones in skull sutures Metaphyseal widening with spurs on long bones Fractures |
Menkes Syndrome
|
|
|
Lab findings in Menkes syndrome
|
Low serum copper and ceruloplasmin
|
|
|
Treatment Menkes Syndrome
|
Copper histidine – start very early!!!
Antiseizure Pamidronate – prevent fractures |
|
|
What is:
Occipital Horn Syndrome |
Variant of Menkes
Occipital horns (exostosis) @ insertion of trapezius and SCM Abnl facies, short flat clavicle, elbow deformities |
|
|
Defect in Bjornstad Syndrome
|
AR, Chr 2
BCS1L Gene encodes an ATPases necessary for assembly of complex III in the mitochondria |
|
|
Name the Syndrome:
Pili torti +/- alopecia Scalp involved NOT eyebrows, eyelashes Bilateral sensorineural deafness |
BJÖRNSTAD SYNDROME
|
|
|
CRANDALL SYNDROME
|
Bjornstad features + Hypogonadism
Crandall has cranberries for testicles… |
|
|
Causes of Pili Torti:
|
PILI TORTI
Bjornstad Crandall Bazex’s follicular atrophoderma Retinoid use Anorexia nervosa Trichothiodystrophy Menkes Citrullinemia |
|
|
ARGININOSUCCINIC ACIDURIA Defect
|
AR, argininosuccinate lyase deficiency
2nd m/c urea cycle defect |
|
|
What are some hair changes seen in Argninosuccinic Aciduria?
|
HAIR:
Trichorrhexis nodosa (50%) “broom-sticks” Increased in occiput |
|
|
Treatment for Argininosuccinic Aciduria
|
Tx:
Limit protein intake w/ arginine supplement Note: other findings -- Failure to thrive Hyperammonemia Vomiting, HSM CNS—lethargy, coma, severe MR, ataxia |
|
|
Name this finding:
Small white nodes at irregular intervals. Hairs fracture easily at nodes Ends resemble broom stick with bristles ends together |
TRICHORRHEXIS NODOSA
|
|
|
What diseases have:
TRICHORRHEXIS NODOSA |
Menkes (pili torti = m/c)
Isotretinoin (curly hairs) Trauma – m/c!!! proximal in blacks distal in Asians & whites Hypothyroidism |
|
|
MONILETHRIX Defect
|
AD, hHb1 & hHb6
Human basic type II hair keratin genes |
|

|
Monilethrix:
Elliptical nodes along shaft --> beaded appearance Undulating variation in diameter Breaks on internodes |
|
|
Name the disease that has the following findings:
OTHER FINDINGS: Keratosis pilaris –nape of neck, back, arms Teeth abnormalities Brittle nails Cataracts MR |
Monilethrix
|
|

|
TRICHOSCHISIS
Trichothiodystrophy (Tay’s, PIBIDS) Light bands = sulfur deficient |
|

|
Pili Annulati
Alternating bands (Not tiger tails!) Light bands = air-filled cavities that scatter light No assoc abnormalities |
|
|
Eponym and defect for:
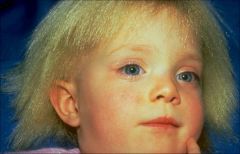
UNCOMBABLE HAIR SYNDROME |
AKA: Pili triangulate et canaliculi, Spun-glass hair
AD, sporadic; gene unknown |
|
|
HAIR
Dry, blond, shiny Scalp only Eyelashes, eyebrows NOT affected Uncombable KEY: NOT fragile (everything else in this section has fragile hair!) |
Uncombable Hair Syndrome
AKA: Pili triangulate et canaliculi, Spun-glass hair AD, sporadic; gene unknown |
|
|
Treatment for Uncombable Hair Syndrome
|
Tx:
Biotin 0.3 mg TID May improve with age |
|
|
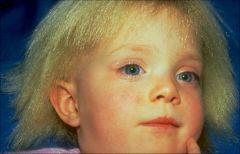
UNCOMBABLE HAIR SYNDROME
EM finding? Canal-like groove along shaft Triangular shaped |
|
|
Eponym for Hypohidrotic ED
|
AKA:
Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Christ-Siemens-Touraine Syndrome |
|
|
Defect in Hypohidrotic ED
|
Genetic mutations
X-linked—most common Ectodysplasin AD, AR EDAR (receptor) EDARADD (encodes protein that interacts with the receptor) All involved in NFKB signaling pathway |
|
|
Name the disease that has the following defects:
Ectodermal defects -- Hypotrichosis Anodontia/hypodontia Hypohidrosis/anhidrosis |
Hypohidrotic ED
|
|
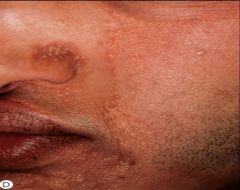
Other findings in Hypohidrotic ED?
|
Other cutaneous findings:
Skin smooth Effaced dermatoglyphics due to absence of sweat pores Eczema—2/3 of pts Sebaceous hyperplasia |
|
|
What are some of the systemic findings in Hypohidrotic ED?
|
Systemic findings:
Asthma & rhinitis Viscous nasal secretions Thick cerumen Bronchopulmonary infections |
|
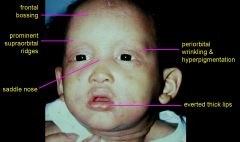
|
Hypohidrotic ED
|
|
|
Eponym for Hidrotic ED
|
aka Clouston's syndrome
|
|
|
Defect in Hidrotic ED
|
AD, Connexin 30 (GJB6) gene
PPK with transgrediens |
|
|
Clinical findings in Hidrotic ED or Clouston's syndrome?
|
AD, Connexin 30 (GJB6) gene
PPK with transgrediens Dystrophic, Paronychia Normal hair at birth, becomes sparse and brittle; absent in puberty Tufted terminal phalanges, Thickened skull |
|
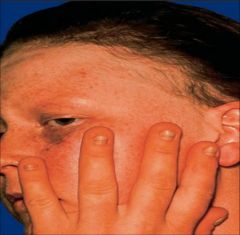
|
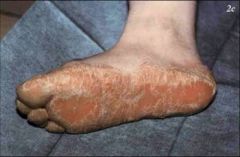
Hidrotic ED
|
|
|
What is EEC Syndrome
|
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal dysplasia-Cleft lip/palate syndrome
|
|
|
Inheritance and gene defect in EEC Syndrome?
|
AD, DNA binding domain of p63 gene
|
|
|
Clinical findings of EEC
|
Dry, scaly skin; Sparse hair; Dystrophic nails
Ectrodactyly—feet > hands Cleft palate +/- lip Chronic OM, Hydronephrosis, Lacrimal duct obstruction |
|
|
EEC Syndrome
|
|
|
AEC syndrome is aka as?
|
AKA:
Ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum-Ectodermal dysplasia-Cleft palate Hay-Wells Syndrome |
|
|
Defect in AEC syndrome
|
AD, Sterile alpha motif (SAM) of p63 gene
|
|
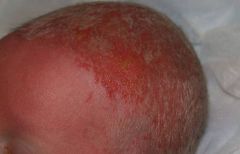
May present as:
Collodion baby Chronic erosive scalp dermatitis --> scarring alopecia |
AEC Syndrome
|
|
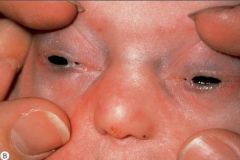
Defnining clinical feature for...?
|
AEC syndrome:
Ankyloblepharon adnatum filiforme—75% Lacrimal duct atresia --> conjunctivitis, blepharitis |
|
|
Name the four subtypes of Pachyonychia Congenita and assoc genes
|
4 subtypes:
PC1 = Jadassohn-Lewandowsky PC2 = Jackson-Lawler PC3 = Schafter-Branauer PC4 = Pachyonychia congenita tarda AD PC1 = K16, K6a genes PC2 = K17, K6b genes |
|
|
Name the Disease:
IDENTICAL SKIN FINDINGS “Omega nails” all 20 nails affected (fingers>toes) Thickened, subungual hyperkeratosis Pincer nails Focal symmetrical PPK, bullae Follicular hyperkeratosis on knees, elbows |
Pachyonychia Congenita
|
|
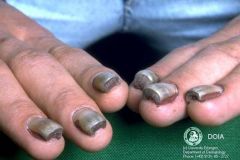
|
Omega Nails:
Pachyonychia congenita |
|
|
Defining feature:
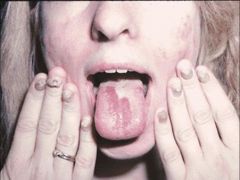
PC1 = oral leukokeratosis (NOT premalignant) |
|
|
Defining feature:
Natal teeth Cutaneous cysts: steatocystoma multiplex, epidermoid cysts, vellus hair cysts |
Pachyonychia congenita II
|
|
|
Defining Feature:
PC1 + corneal leukokeratosis |
PC3
|
|
|
Defining Feature:
late onset disease hyperpigmentation on flexural areas, buttocks and abdomen |
PC4
|
|
|
Eponym for Nail-Patella Syndrome
|
AKA:
Hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia Fong’s syndrome |
|
|
Gene defect in Nail Patella Syndrome
|
AD, LMX1B gene
In close proximity to Collagen V gene Collagen V is major part of glomerular BMZ --> see kidney problems |
|
|
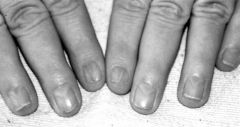
Findings:
Triangular lunulae --> pathognomonic Micronychia/hemionychia/anonychia Longitudinal fissures (thumb m/c) |
Nail Patella syndrome
|
|
|
Nail Patella Syndrome
|
|
|
Nail findings in Nail-Patella syndrome
|
Triangular lunulae pathognomonic
Micronychia/hemionychia/anonychia Longitudinal fissures (thumb m/c) |
|
|
Bone findings in Nail Patella syndrome/aka Fong's syndrome
|
BONES:
Absent or small patella --> pain, OA Posterior iliac horns Radial head subluxation, thick scapulae, scoliosis |
|
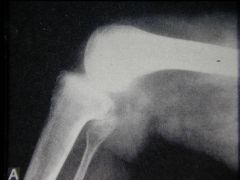
|
Nail-Patella syndrome
|
|
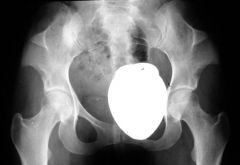
|
Nail Patella syndrome:
Posterior iliac horns |
|
|
Other findings in this syndrome include:
Glomerulonephritis, renal dysplasia/failure Lester iris – hyperpigmentation of pupillary margin of iris Heterochromia irides, cataracts, glaucoma |
Nail Patella syndrome / Fong's syndrome
|
|
|
What condition does Nail-Patella syndrome look similar too?
|
Trisomy 8:
Small nails Absent patella |
|
|
Alkaptonuria is aka? Gene Defect?
|
AKA: “Endogenous Ochronosis"
AR, HGO gene (chr 3) homogentisic acid oxidase deficiency accumulation of ochronotic pigment |
|
|
Common presentation of Alkaptonuria in children?
in adults? |
Black cerumen, underwear or diapers, sweat
Dark urine with high pH (>7.0) --> diapers turn black with NaOH ------------------- Adults --> “Blue man group” Facial blue-gray pigmentation Blue-gray pigmented cartilage & tendons (nose, ears, hands) Blue-gray sclera |
|
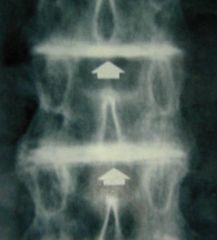
Disease?
Assoc findings? |
Adults:
Severe arthropathy of large joints Intervertebral disk calcification Mitral/aortic valvulitis --> increased risk of MI |
|
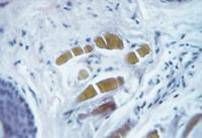
|
Banana body in Dermis:
Alkaptonuria |
|
|
Eponym and defect in Fabry Disease
|
AKA: Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum
XLR, -galactosidase-A (GLA) gene Glycosphingolipids accumulation in vascular endothelium --> heart, brain, kidneys XLR (CHADZ Lovely Kinky WIFE) |
|
|
What is the disease:
Acroparesthesias & paroxysmal acral painful crises with edema (kids dip their hands in toilet) Diphenylhydantoin, carbamazepine Acromegaly features |
Fabry Disease
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Maltese crosses in urine (birefringent lipid globules) |
Fabry Disease
|
|
|
What causes premature death in Fabry's disease?
|
Deposition leads to various problems:
Premature death due to: CVA, peripheral neuropathy MI/cardiac problems Progressive renal failure |
|
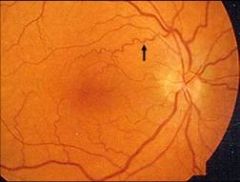
|
EYE—Cornea verticillata (whorled-like opacities) & torturous retinal vessels
see in Fabry's Disease |
|
|
Name the syndromes assoc with Angiokeratomas
|
Fabry’s
Fucosidosis (alpha-L-fucosidase deficiency) Sialidosis (defect: NEU1 gene) Beta-mannosidase deficiency Galactosialidosis GM1 gangliosidosis Kanzaki’s disease (alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency) |
|
|
What should you think of in a patient with acral paresthesias with no cutaneous findings and other systemic problems similar to Fabry’s?
|
MERCURY/HEAVY METAL POISONING
|
|
|
Defect in Gaucher disease
|
AR, Acid-ß-Glucocerebrosidase (GBA) gene
-- glucocerebroside accumulates in histiocytes in all types of organs |
|
|
Name the three types of Gaucher disease
|
3 Types:
Type I – adults; more common; Ashkenazi Type II – infantile Type III – juvenile |
|
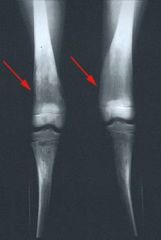
|
Erlenmyer flask deformity -- seen in Gaucher Disease, Type I
Type I—Adult form Hyperpigmentation of faces, neck & hands (bronze) Hepatomegaly with hypersplenism --> Petechiae, ecchymosis Enlarged lymph nodes Bone problems: - Pain - Fractures - Erlenmeyer flask deformity aseptic necrosis of femoral head - vertebral collapse |
|
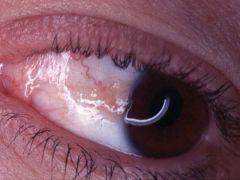
|
Pingueculae -- seen in type I adult form of Gaucher disease
|
|
|
Name the disease:
HSM CNS deterioration Hypertonic, rigid/spastic, catatonic Difficulty swallowing In adult form – there’s some neuronal glucocerebrosidase activity Aspiration pneumonia – death by age 1-2 |
Type II, infantile form of Gaucher disease
|
|
|
Cause of death in Type II, infantile form of Gaucher Disease
|
Aspiration pneumonia
|
|
|
How are type II and type III Gaucher disease different?
|
Type III Dz is the juvenile form and has the findings of type II PLUS bony involvement
|
|
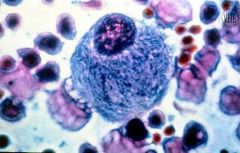
|
Gaucher Disease:
BM biopsy --> Gaucher’s cells (histiocytes filled with glucocerebroside ) |
|
|
Treatment of Gaucher Disease
|
Enzyme replacement
- Type I only - Does not cross BBB, not useful in types II & III - BM transplantation Supportive for II & III |
|
|
Name the main differences in the three types of Gaucher Disease
|
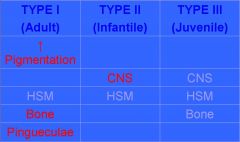
|
|
|
Defect in Niemann-Pick Disease
|
AR, Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase-1 (SMPD-1) gene
sphingomyelin accumulation in foam cells w/in all organs |
|
|
Name the different types of Niemann-Pick disease
|
Three types
Type A – infancy, m/c; Ashkenazi Jews Type B – infancy to childhood Type C – childhood; French-Canadians |
|
|
Name the Disease:
Xanthomas, JXG Cherry red spots in eyes Enlarged lymph nodes Pychomotor degeneration HSM Failure to thrive/emaciated Bronchopneumonia – m/c cause of death by age 2-3 |
Niemann-Pick Disease: type A
|
|
|
Describe type B and type C Niemann Pick Disease
|
TYPE B
Type A features minus CNS problems Have higher residual level of enzyme TYPE C Totally different gene – NPC gene DEFECT: cholesterol esterification, normal sphingomyelinase Developmental delay HSM Progressive psychomotor deterioration |
|
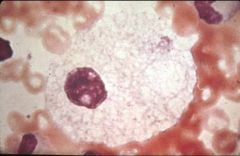
|
Niemann-Pick cell: “foamy blue histiocytes” with mulberry appearance
|
|
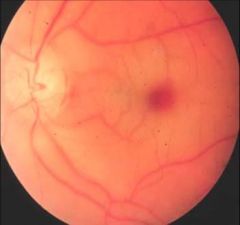
Differential Dx?
|
CHERRY RED SPOT
Niemann-Pick Tay-Sachs Sialidosis Sandhoff’s |
|
|
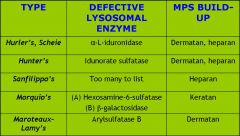
Name the Mucopolysaccharidoses and their defect
|
|
|
|
Name the disease:
COMMON FINDINGS—Short, thick & hairy |
MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSES
|
|
|
NAME THE MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSES THAT DOES NOT HAVE SHORT STATURE
|
Scheie
|
|
|
Name the Mucopolysaccharidoses that does not have corneal clouding?
|
Hunter’s, Sanfilippo’s
|
|
|
What are the common findings in mucopolysaccharidosis?
|
COMMON FINDINGS—Short, thick & hairy
Short (except Scheie), broad hands & short fingers, hernias, spinal derformity, short neck, joint laxity Corneal clouding (except Hunter’s, Sanfilippo’s) Heart problems HSM Bronchopneumonia—often end stage; sleep apnea with thickened narrow airway |
|
|
What is the only XLinked Mucopolysacharridoses?
|
HUNTER SYNDROME
|
|
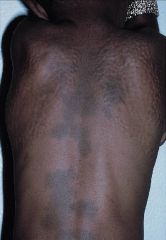
|
Hunter Syndrome
XLR – it’s the only one! Iduronate sulfatase deficiency Characteristic skin finding—Pebbling between angles of scapulae & posterior axillary line CNS = big problem |
|
|
Which of the mucopolysaccharisdoses has occipito-atlantic instability?
|
Hurler’s & Morquio’s
Occipito-atlantic instability --> quadraplegic |
|
|
Cause of death in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses?
|
Early death within 2nd decade (cardio-pulmonary decompensation)
EXCEPT: Scheie—normal lifespan |
|
|
Name the Disease:
Retention hyperkeratosis with normal epidermal proliferation Fine white scale, spares flexures & face Hyperlinear palms Atopic dermatitis in 50% Keratosis pilaris |
Ichthyosis Vulgaris
|
|
|
Inheritance and Defect in Ichthyosis Vulgaris?
|
Inheritance & gene defect?
AD with defect in profilaggrin synthesis |
|
|
What is the histo finding in Ichthyosis Vulgaris?
|
absent granular layer (best bx site is anterior shins)
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Brown scales on neck & extensors, relative sparing of flexures, palms, face Eye finding? Comma-shaped corneal opacities (asymptomatic) |
X-linked Ichthyosis
|
|
|
X-linked Ichthyosis: Inheritance/gene defect?
|
XLR with arylsulfatase-c gene defect
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Cryptorchidism- 20% Increased risk of testicular cancer & ALL Failure of labor: decreased placental sulfatase |
X-linked Ichthyosis
|
|
|
Name two syndromes that may result from contiguous gene deletions of the XLR arylsulfatase-c gene (XL Ichthyosis):
|
Kallman Syndrome
X-linked recessive chrondrodysplasia punctata (arylsulfatase E gene defective) |
|
|
Defect in Kallman syndrome?
|
XLR with defect in KAL1 (encodes anosmin)
|
|
|
Name the Disease:
Hypogonadism and cryptorchidism Mild feminization Micropenis Anosmia Renal agenesis |
Kallmann Syndrome
XLR with defect in KAL1 (encodes anosmin) |
|
|
Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis is aka?
|
Bullous CIE
|
|
|
Defect in Bullous CIE?
|
AD with defect in keratins 1 & 10
(aka Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis) |
|
|
How does a newborn present with Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis?
|
Newborn: widespread bulla and erythroderma, sepsis, H2O loss
|
|
|
How does an infant-adult with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis look like?
|
Infant-adulthood: generalized “corrugated” hyperkeratosis (dark warty scales with spiny ridges increased in flexural areas)
+/- palmoplantar keratoderma Malodorous, macerated intertriginous areas Post-puberty may localize to flexural areas |
|
|
Name the disease:
dark warty scales with spiny ridges increased in flexural areas +/- palmoplantar keratoderma Malodorous, macerated intertriginous areas Post-puberty may localize to flexural areas |
Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis
|
|
|
EM finding in EHK?
|
EM: clumped keratin filaments
|
|
|
What medication should you avoid in EHK?
|
Generally avoid systemic retinoids; some advocate short courses of systemic retinoids for adult flares
Avoid keratolytics --> denuded raw skin |
|
|
Parents with epidermal nevi with EHK features may have children with what?
|
Parents with Epidermal Nevi that have EHK features may pass on classic disease to their children due to gonadal mosaicism (“they” love to ask this on tests)
|
|
|
Ichthyosis Bullosa of Siemens
Inheritance/gene defect? |
AD defect in keratin 2e
|
|
|
Name the Disease:
Highly penetrant and evident from birth Fragile blisters early in life Later with hyperkeratotic plaques on the elbows and knees Rippled hyperpigmentation in flexural areas Superficial molting or peeling of the skin: 'Mauserung' phenomenon |
Ichthyosis Bullosa of Siemens
|
|
|
Gene Defect in Diffuse PPK (Unna-Thost/Vorner)
|
AD with defects in K9 and K1 (Vorner is K9>K1 and Unna-Thost is K1)
|
|
|
Gene Defect in Howel-Evans Syndrome
|
AD with defect in the TOC locus distal to K1 (envoplakin is not the defective gene within the TOC locus)---Tylosis & Oesophageal Cancer
|
|
|
Clinical presentation of Howel-Evans Syndrome
|
2nd decade: PPK, NO transgrediens
After 3rd decade: esophageal carcinoma Oral leukoplakia in one kindred |
|
|
Name the disease:
Pseudoainhum/autoamputation Starfish-shaped or linear keratoses on dorsal hands, feet, elbows, knees Scarring alopecia, HF hearing loss Retinoids may prevent auto-amputation |
Vohwinkel Syndrome
|
|
|
Defect in Vohwinkel Syndrome
|
AD with defect in GJB2 (connexin-26 classic form with deafness- same gene as KID) or loricrin (#1 component of cornified cell envelope)
Connexin-26 --> deafness Loricrin variant--> ichthyosis |
|
|
Defect in Mal de Meleda
|
AR with defect in SLURP-1 (proteins important in cell signaling and adhesion)
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Glove-stocking PPK WITH transgrediens Fissures, malodorous, pseudoainhum at DIP, hyperhidrosis Koilonychia and subungual hyperkeratosis Hyperkeratotic plaques on elbows/knees |
Mal de Meleda:
AR with defect in SLURP-1 (proteins important in cell signaling and adhesion) Island of Meleda in the Adriatic sea off Bosnia |
|
|
Defect in Mal de Meleda
|
AR with defect in SLURP-1 (proteins important in cell signaling and adhesion)
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Glove-stocking PPK WITH transgrediens Fissures, malodorous, pseudoainhum at DIP, hyperhidrosis Koilonychia and subungual hyperkeratosis Hyperkeratotic plaques on elbows/knees |
Mal de Meleda:
AR with defect in SLURP-1 (proteins important in cell signaling and adhesion) Island of Meleda in the Adriatic sea off Bosnia |
|
|
Defect in Mal de Meleda
|
AR with defect in SLURP-1 (proteins important in cell signaling and adhesion)
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Glove-stocking PPK WITH transgrediens Fissures, malodorous, pseudoainhum at DIP, hyperhidrosis Koilonychia and subungual hyperkeratosis Hyperkeratotic plaques on elbows/knees |
Mal de Meleda:
AR with defect in SLURP-1 (proteins important in cell signaling and adhesion) Island of Meleda in the Adriatic sea off Bosnia |
|
|
Defect in Ichthyosis Vulgaris
|
AD
FLG gene Defect in Profillagrin synthesis |
|
|
Defect in X-linked Ichthyosis
|
XLR
STS gene defect (arylsulfatase-c gene) Increased levels of cholesterol sulfate leads to decreased cholesterol and retention keratosis |
|
|
What two syndromes may result from continguous gene deletions in X-linked Ichthyosis?
|
Kallman Syndrome
X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata (arylsulfatase E gene defective) |
|
|
Defect in Kallman Syndrome
|
XLR -- defect in KAL1 (encodes anosmin)
|
|
|
hypogonadism and cryptoorchidism
mild feminization micropenis anosmia |
Kallman Syndrome
|
|
|
Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis is aka? Defect?
|
Bullous CIE
AD Defect in Keratins 1 and 10 |
|
|
Clinical Presentations:
Newborn -- widespread bulla and erythroderma Infant/Adult -- generalized hyperkeratosis maloderous, macerated intertriginous areas EM: clumped keratin filaments |
Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis
|
|
|
Patients with epidermal nevi that have EHK features may pass on what to their children?
|
Classic Epideromolytic Hyperkeratosis
|
|
|
May manifest as shedding in layers "Mauserung" (molting)
|
Ichthyosis Bullosa of Siemens
|
|
|
Defect in Ichthyosis Bullosa of Siemens?
|
AD defect in keratin 2e
Clinical: fragile blisters early in life, followed by hyperkeratotic plaques on the elbows and knees -- rippled hyperpigmentation in flexural areas |
|
|
Defect in Lamellar Ichthyosis
|
AR w/ TGM1 (keratinocyte transglutaminase gene defect)
|
|
|
Collodion Baby
Plate-like scales Hypohidrosis Scarring alopecia |
Lamellar Ichthyosis
|
|
|
Another name for Congenital Ichthyosiform Erythroderma (CIE)
|
Non-Bullous CIE
|
|
|
Defect in Non-Bullous CIE (Congenital Ichthyosiform Eryhtroderma)
|
AR
defects in TGM1 and Lipogenases: ALOX12B & ALOXE3 |
|
|
Collodion Baby
Erythroderma, fine white scale, flexures involved, plate-like scales on legs +/- PPK Cicatricial alopecia |
Congenital Ichthyosiform Erythroderma
|
|
|
Defect in Harlequin Fetus
|
AR
Suspected problem with profillagrin to fillagrin (candidate gene is ABCA12) |
|
|
What do you see on EM with harlequin fetus?
|
absence of lamellar bodies (massive hyperkeratotic plates)
|
|
|
Infancy: Ichthyosiform erythroderma & plates
Later: plate-like scales with no erythema and emphasized in flexures; pruritus MR, spastic di/paraplegia, scissor gait, speech difficulties “Glistening dot” retinal degeneration |
Sjogren-Larsson Syndrome
AR with defect in fatty aldehyde oxidoreductase (FALDH) gene (epidermal lipid synthesis); (ALDH3A2) |
|
|
increased phytanic acid - replaces NL fatty acids in skin and organs
Mild ichthyosis (skin not impressive) Ataxia, neuropathy Retinitis pigmentosa (salt & pepper) and sensironeural deafness Arrhythmias w/ heart block, CHF |
Refsum Syndrome
AR with defect in phytanoyl-CoA hydroxylase genes PAHX and PEX7 |
|
|
Name the key findings in Buschke-Ollendorf
|
AD dominant
dermal plaques/papules Osteopoikilosis on Xray Focal sclerotic densities in long bones, pelvis, and hands |
|
|
Name the Dz:
AD dominant dermal plaques/papules Osteopoikilosis on Xray Focal sclerotic densities in long bones, pelvis, and hands |
Buschke-Ollendorf
|
|
|
Name the Dz:
Numberous symmetric asymptomatic dermal nodules on back usu in mid to late teens Assoc with MEN type I may also see angiofibromas, cafe-au-lait macules and lipomas |
Familial cutaneous collagenomas
|
|
|
Describe familial cutaneous collagenomas
|
Name the Dz:
Numberous symmetric asymptomatic dermal nodules on back usu in mid to late teens Assoc with MEN type I may also see angiofibromas, cafe-au-lait macules and lipomas |
|
|
What are some associated skin findings with tuberous sclerosis?
|
Adenoma sebaceum
Periungual fibromas Ash-leaf macules |
|
|
Eruptive collagenomas has been associated with what dz?
|
syphillis
|
|
|
Gene defect in Non-bullous CIE aka "congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma"?
|
TGM1 defect
Presents as collodion baby in 90% of cases |
|
|
Gene defect in Bullous CIE (aka "epidermolytic hyperkeratosis")
|
K1 and K10
Presents as generalized erythema with superimposed superficial blisters and erosions |
|
|
Omenn syndrome defect
|
RAG1 and RAG2
AR form of severe combined immunodeficiency Exfoliative erythroderma with diffuse alopecia |
|
|
Inheritance? Gene Defect for Ataxia-Telangiectasia?
|
ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) gene
AR inheritance |
|
|
Normal function of the ATM gene, mutation causes what?
|
Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated gene:
Codes for Phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase-like protein: senses early damage to DNA, initiates apoptotic and cell cycle responses that allow DNA repair Mutation: Progressive neurologic deterioration -- defective DNA repair in nerve cells, leads to progressive depletion of Purkinje cells in the cerebellum (fails to cease DNA synthesis after UV radiation) |
|
|
MC cause of death in Ataxia Telangiectasia?
|
Bronchiectasis with respiratory failure
|
|
|
Lab findings in Ataxia-Telangiectasia?
|
Almost all have:
Elevated Alpha-Fetoprotein & CEA Decreased or absent: IgA2, IgG2 and IgG4, IgE Abnormally developed or absent thymus 14:14 seem to predict the development of lymphoma (female heterozygotes: also have a risk of breast CA) |
|
|
What is APECED? Gene defect?
|
APECED = Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy syndrome
AIRE gene defect: AutoImmune REgulator -- encodes DNA transcription factor |
|
|
Familial dysautonomia eponym?
|
Riley-Day
|
|
|
What group is seen to Riley-Day?
|
Ashkenazi Jews
|
|
|
Gene for Riley-Day? Describe the Syndrome?
|
IKBKAP (I Kan't Be KAPped)
Hallmark is insensitivity to pain Episodic hyperhidrosis Blotchy erythema of the face and trunk Deficient lacrimation Absense of fungiform papillai on the tongue Failure to thrive Mental retardation |
|
|
Ichthyosis Vulgaris
|
AD; PROFILLAGRIN
|
|
|
X-linked Ichthyosis (aka?)
|
Steroid sulfatase deficiency; Gene Xp22.32, X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis
|
aka Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma
aka Bullous ichthyosis 50% spontaneous mutation; keratin K1, K10 genes on Chromosome 12q, 17q respect |
|
|
Lamellar Ichthyosis
|
AR; transglutaminase 1 (TGM1) gene on 14q11
|
|
|
Congenital Ichthyosiform Erythroderma (CIE)
|
aka Nonbullous CIE
AR; TGM1 ALOX12B ALOXE3 |
|
|
Harlequin Fetus
|
AR most likely, genetic heterogeneity with recent description of de novo deletion of 18q21
|
|
|
Sjogren-Larsson Syndrome
|
AR; Fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase (FALDH) gene 17p11.2
|
|
|
Refsum Syndrome
|
aka Phytanic acid storage disease; Heredopathia atactica polyneuritiformis;
AR; PAHX gene on 10p and PEX7gene on 6q |
|
|
Conradi-Hunermann Syndrome
|
aka X-linked dominant chondrodysplasia puntata;
aka Conradi-Hunermann-Happle syndrome |
|
|
CHILD syndrome
|
Congential Hemidysplasia with Ichthyosiform erythroderma and Limb Defects (CHILD); aka Unilateral congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma
|
|
|
Netherton Syndrome
|
aka Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (ILC);
AR; SPINK5 gene on 5q32 |
|
|
Erythrokeratoderma Variabilis
|
aka Mendes da Costa syndrome;
AD; GJB3 gene on 1p35 |
|
|
KID Syndrome
|
Keratitis-Ichthyosis-Deafness syndrome;
AD and recessive transmission reported; GJB2 gene on 13q11-12 |
|
|
Diffuse Palmoplantar Keratoderma (PPK)
|
aka Vorner PPK or Epidermolytic PPK, Keratin genes 9 and 1 (on chromosome 17 and 12);
aka Unna-Thost PPK or Nonepidermolytic PPK (keratin 1 gene); AD transmission |
|
|
Howell-Evans Syndrome
|
AD; tylosis and esophageal cancer (TOC) gene locus on 17q25
|
|
|
Vohwinkel Syndrome
|
aka PPK mutilans;
aka Keratoderma herditaria mutilans; AD: classic form with deafness: GJB2 gene on 13q11-12 Loricrin-variant: loricrin gene on the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) on 1q21 |
|
|
Mal de Meleda
|
aka Keratoderma palmplantaris transgrediens;
AR; secreted Ly-6/uPar related protein 1 (SLURP1)gene on 8qter |
|
|
Papillon-Lefevre Syndrome
|
aka palmoplantar keratoderma with periodontosis; AR, CTSC gene on 11q14
|
|
|
Richner-Hanhart Syndrome
|
aka Tyrosinemia type II;
AR; tyrosine aminotransferase gene on 16q22.1-q22 |
|
|
Darier Disease
|
aka Darier-White Disease;
aka Keratosis follicularis; AD, ATP2A2 gene on 12q23-24 |
|
|
Epidermal Nevus Syndrome
|
aka Ichthyosis hystrix;
aka Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus (ILVEN); Linear sebaceous nevus syndrome; sporadic inheritance |
|
|
Oculocutaneous Albinism Type 1 (OCA1)
|
aka Tyrosinase-negative albinism;
AR, tyrosinase (TYR) gene on 11q14-q21 |
|
|
Buschke Ollendorf
|
LEMD3 or MAN1 gene
1. Dermatofibrosis lenticularis disseminata 2. Osteopoikilosis Normal lifespan |
|
|
McCune-Albright Syndrome
|
Rare
Post-zygotic somatic mutations activating the GNAS1 gene on Chr 20 "Coast of Maine" Cafe au Lait Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Hyperthyroidism and Precocious puberty |
|
|
Focal Dermal Hypoplasia eponym
|
Goltz syndrome
X-linked dominant Soft red-yellow nodules (fat herniations) in Blaschko's lines |
|
|
Menkes findings?
|
Xlinked recessive
MKN or ATP7A gene Pili torti, doughy skin, MR, metaphyseal widening with spurs in long bones |
|
|
Synonym for Alkaptonuria
|
Endogenous Ochronosis
|
|
|
Causes of exogenous achronosis?
|
Antimalarials, hydroquinone
|
|
|
Alkaptonuria Inheritance & Gene?
|
AR
HGO Gene: Homogentisic acid oxidase deficiency Results: accumulation of homgentisic acid in tissue Chr 3q21-q23 |
|
|
Key findings in Alkaptonuria
|
Blue-gray pigmentation on nose, cheeks, forehead, axillae; pigmented cartilage and tendons; pigmented sweat/cerumen; arthropathy; dark urine with pH above 7.0 -- discolors diapers after cleansing with alkaline soaps; mitral and aortic valvulitis (RISK OF MI INCREASED)
|
|
|
dark urine / discolored diapers
blue-gray pigmentation |
Alkaptonuria
|
|
|
Eponym for Fabry Disease
|
Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum
Anderson-Fabry Disease |
|
|
Enzyme Defect in Fabry Dz
|
X-linked Recessive
alpha-galactosidase A (GLA) gene Chr Xq21.33-q22 Accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids (ceramid trihexoside) which accumulate in vascular endothelium |
|
|
Incidence of Fabry and Dx?
|
1:40,000 males; heterozygote females have variable expression and c/b symptomatic.
Can dx with CVS sampling Enzyme assays Skin or BM Bx Urine Sediment |
|
|
Key features of Fabry's
|
The "A's"
Alpha-galactosidase-A Angiokeratomas Acroparesthesias & paroxysmal acral painful crises with edema (kids dipping hands in toilet) Anhidrosis - hypohidrosis Acromegaly features Angina: Acute MI, mitral insufficiency others: Kidney deterioration with "Maltese Cross" birefringent lipid globules; CVA, corneal opacities |
|
|
Tx of Fabry's
|
Enzyme replacement
|
|
|
Inheritance of Gaucher Dz, gene defect?
|
AR;
Acid-beta-glucocidase (ABG) gene Chr 1q21 Decreased glucocerebrosidase activity resulting in accumulation of glucocerebroside in histiocytes (Gaucher's cells) |
|
|
How many types of Gaucher's Dz?
|
Two types:
Type I (adult) - usu in later adulthood; ASHKENAZI Jews, NO CNS symptoms CNS Symptoms seen in: Type II (infantile) -- 2 to 3 months of life Type III -- rare, rapid deterioration like type II |
|
|
Key Features of Gaucher Dz
|
Type I
diffuse hyperpigmentation (bronze face) bone pain/fractures/fragile bones(erlenmyer flask deformity, aseptic necrosis of femoral head) hepatomegaly, hypersplenism Pingueculae Type II CNS deterioration, hypertonicity and neck rigidity, laryngeal spasm hepatosplenomegaly chronic aspiration - aspiration PNA, death by age 1-2 Type III -- hepatosplenomegaly, bone and slow neurodegeneration (basically type II with bone involvement) |
|
|
Lipid-engorged macrophage with "crumpled tissue paper" appearance
|
Gaucher cells
|
|
|
Gene defect in Niemann-Pick Disease
|
AR
sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase-1 SMPD-1 MN: "No Man Picks" his nose with his "Sphing"er accumulation of sphingomyelin in histiocytes w/in all organs |
|
|
Cherry red spots are found in what dzs?
|
Niemann-Pick (SMPD-1)
Tay-Sachs Generalized sialidosis Sandhoff's disease |
|
|
Name the mucopolysaccharidoses and their inheritance
|
Hurler, Scheie syndrome: 4
Hunter's syndrome: X Sanfilippo syndrome: several gene loci reported Morquio's (A): 16 Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome: 5 ALL autosomal recessive, EXCEPT Hunter's (X-linked) ALL have short stature, except Sanfilippo's. Common findings: Short, Thick & Hairy. Bone problems: short stature, dysostosis multiplex, broad hands with short fingers |
|
|
Name the Mucopolysaccharidoses and the gene defect
|
Hurler's, Scheie: alpha-L-iduronidase; dermatan, heparan sulfate
Hunter's: iduronate sulfatase; dermatan, heparan sulfate (cobblestone back) Sanfilippo's: (A)heparan-N-sulfatase, (B) alpha-N acetylglucosaminidase, (C) acetyl-CoA: alpha-glucosaminide acetyltransferase, (D) N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase; heparan sulfate Morquio's: (A) hexosamine 6-sulfatase (B) beta-galactosidase; keratan sulfate Maroteaux-Lamy: arylsulfatase B; dermatan sulfate |
|
|
Gene defect in:
Hurler's, Scheie |
alpha-L-iduronidase; dermatan, heparan sulfate
|
|
|
Gene defect in:
Hunter's |
iduronate sulfatase; dermatan, heparan sulfate (cobblestone back)
DOES NOT HAVE CORNEAL CLOUDING |
|
|
Gene defect in:
Sanfilippo's |
(A)heparan-N-sulfatase, (B) alpha-N acetylglucosaminidase, (C) acetyl-CoA: alpha-glucosaminide acetyltransferase, (D) N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase; heparan sulfate
DOES NOT HAVE CORNEAL CLOUDING |
|
|
Gene defect in:
Morquio's |
(A) hexosamine 6-sulfatase (B) beta-galactosidase; keratan sulfate
|
|
|
Gene defect in:
Maroteaux-Lamy |
arylsulfatase B; dermatan sulfate
|
|
|
Forms of Multiple Carboxylase Deficiency
|
Two forms: both AR
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency: HLCS gene, presents during 1st few days to months of life Biotinidase deficiency (BTD gene) - presents later in life |
|
|
Gene defect for multiple carboxylase deficiency
|
Holocarboxylase synthase deficiency: holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) gene
[Hypotonia, vomiting] Biotinidase deficiency: biotinidase (BTD) gene [optic atrophy, high-frequency hearing loss] Both have decreased biotin in serum -- leads to metabolic acidosis; hyper-ammonemia; Urine has organic aciduria -- 3-hydroxy-isovaleric acid |
|
|
Gene defect in Phenylketonuria
|
AR
Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency - accumulatiion of phenylalanine that competitively inhibits tyrosinase (hypopigmentation and toxic CNS effects) Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene Chr locus 12q24.1 think, "white mouse w/ eczema and scleroderma" (mousy urine, albinism, eczema, sclerodermoid changes) |
|
|
Eponym for hepatolenticular degeneration
|
Wilson's Disease
|
|
|
Gene defect in Wilson's Dz?
|
AR
ATB7B gene on Chr 13 (vs ATB7A in Menkes) encodes: adenosine triphosphatase CU2+ transporting polypeptide results in defect in biliary excretion of copper/copper transport |
|
|
Eye findings in Wilson's Dz?
|
Kaiser-Fleisher rings (copper deposits in Descemet's membrane)
|
|
|
Gene defect in acrodermatitis enteropathica
|
AR
SLC394A on Chr 8 gene encodes intestinal zinc-specific transporter protein, results in defective zinc absorption from the gut (also has low alk phos levels) |
|
|
Gene defect in hemochromatosis
|
AR
HFE gene hemochromotosis-HFE gene locus 6p21.3 increased intestinal iron absoroption and organ deposition |
|
|
What is the clinical triad of hemochromatosis?
|
Skin hyperpigmentation
Diabetes (aka 'bronze diabetes') Cirrhosis |
|
|
Gene defect in homocystinuria
|
AR
Cystathionine B-synthase (CBS) gene Chr 21q22.3 Mutation leads to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency which accumulates homocystine; leads to abnormal crosslinking of collagen |
|
|
Clinical features of homocystinuria
|
The "M's":
Malar rash Marphanoid body Mental Retardation Methionin levels elevated Musculoskeletal problems Myopia (Downward lens displacement vs upwartd lens displacement in Marfans) |
|
|
Gene inheritance of the hyperlipoproteinemia
|
Type I: AR
Type II: AD Type III: AR Type IV: AD Type V: AD |
|
|
Palmar Xanthomas are seen in which hyperlipoproteinemias?
|
III
|
|
|
CAD and CVAs are seen in which hyperlipoproteinemias?
|
II, III, IV
(II die from premature atherosclerosis!) |
|
|
Pancreatitis is seen in which hyperlipoproteinemias?
|
I, V
|
|
|
DM is seen in which hyperlipoproteinemias?
|
III, IV, V
|
|
|
HSM is seen in which hyperlipoproteinemias?
|
I, V
|
|
|
Dz's associated with angiokeratomas
|
Fabry’s
β-Galactosidase deficiency Fucosidosis (α-L-fucosidase deficiency) Sialidosis (defect: NEU1 gene) β-mannosidase deficiency Galactosialidosis GM1 gangliosidosis Kanzaki’s disease (alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase deficiency) |
|
|
What is Cornea Verticillata?
|
Whorled-like opacities and tortuous retinal vessels seen in FABRY's
|
|
|
Describe the four types of Neimann-pick Dz?
|
Type A – infancy, M/C type; Ashkenazi Jews, CNS Sx
Type B – infancy to childhood, NO CNS Sx (Type A without CNS involvement) Type C – childhood; French-Canadians, CNS Sx (Different Gene -- NPC gene; defect in cholesterol esterification, normal sphingomyelinase) Type D – As per Andrews Type C&D: assoc cholesterol metabolism defects |
|
|
Diagnosis of PKU
|
Serum: elevated phenyl-alanine
Urine: elevated phenyl-pyruvic acid (add ferric acid, urine becomes a deep green) |
|
|
Wilson's Disease clinical findings
|
MN: ABCD
Asterixis Basal ganglia degeneration Blue (Azure) lunulae Copper ↑ Ceruloplasmin ↓ Cirrhosis -- Liver CA Corneal deposits (Kayser-Fleischer ring) Choreiform movements Dementia |
|
|
Gene defect in Citrullinemia
|
SLC25A13
(vs SLC39A4 in Acrodermatitis Enteropathica) |
|
|
Name the different types of Citrullinemia
|
2 Types:
Type I – Argininosuccinic acid synthetase deficiency (inborn error of urea synthesis) Citrulline & aspartic acid conversion to argininosuccinic acid is defective -- Keratin is 16% arginine -- Hair: pili torti, Trichorrhexis Nodosa, atrophic hair bulbs Skin: defect leads to acrodermatitis enteropathica like dermatitis Type II – SLC25A13 (adult onset), affects only liver -- Exclusively seen in adult Japanese |
|

This is seen in what disorders?
|
Trichorrhexis Nodosa:
1. Genetic AD Form, normal hair at birth, then develops TN in months, no assoc problems 2. Arginosuccinic aciduria 3. Menkes syndrome 4. Citrullinemia |
|
|
Describe the characteristic skin findings in hyperlipoproteinemias and which type they are found in.
|
Eruptive xanthomas – I, III, IV
Xanthelasma – II,III Xanthoma striata palmaris – III Tendinous xanthoma – II Tuberous xanthomas at pressure points – II, III Planar xanthoma – II |
|
|
Eponym for Juvenile Gout?
|
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
|
|
|
Defect in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome?
|
XLR
Hypoxanthine-Guanin-Phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) deficiency enzyme deficiency in purine metabolism |
|
|
Clinical findings in Lesch Nyan syndrome
|
Gout Sx
Orange Cyrstals in Diapers Self-mutilating behavior (head-banging, biting lips, and fingers) Kidney stones (uric acid) Severe CNS sx: progressive MR, choreoathetosis Tx: allopurinol |
|
|
Birth: erythroderma, dehydration
Infancy: Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa, atopic dermatitis, hypernatremia Trichorrhexis invaginata -- pili torti or trichorrhexis nodosa are also possible Anaphylactic food reactions with elevated IgE Greatly increased percutaneous absorption May improve at puberty |
Netherton Syndrome
|
|
|
Defect in Netherton Syndrome
|
AR w/ defect in SPINK-5
Serine-Protease inhibitor LEKT1 gene |
|
|
Defect in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome
|
AD
NIPBL mutation |
|
|
Describe Cornelia de Lange
|
hypertrichosis: forehead, lateral face, shoulders, back, low anterior hairline, synophrys, trichomegaly.
Distinctive facies, upper extremity anomalies, microencephaly, MR, "growling cry" |
|
|
Describe Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
|
Hypertrichosis: lateral face, shoulders, back, thick eyebrowns, trichomegaly
Midfacial vascular stains, kelods, pilomatricomas Broad thumbs/halluces, beaked nose, high arched palate, short stature, MR |
|
|
Defect in Rubinstein-Taybe syndrome
|
AD
CREBBP mutations |
|
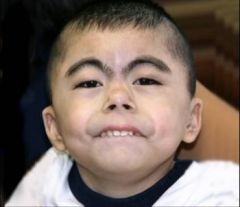
|
Cornelia de Lange syndrome
|
|
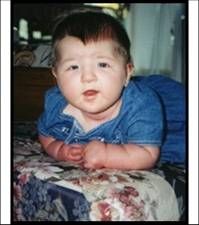
|
Rubenstein-Taybi syndrome
|
|
|
Eponym for POEMS syndrome?
|
Crow-Fukase
|
|
|
What does POEMS stand for?
|
Polyneuropathy, Organomegaly, Endocrinopathy, Monoclonal gammopathy and Skin changes
[a rare multisystemic disease in the setting of a plasma cell dyscrasia) |
|
|
Describe Setleis syndrome
|
AR, defect?
Bitemporal scar-like depressions Leonine facies Abnormalities of eyelashes, eyebrows and eyelids Flattening of nasal bridge Pursed lips Normal growth and development Puerto Rican ancestry |
|
|
Describe Lymphedema Distichiasis syndrome -- defect and clinical picture
|
AD, defect?
FOXC2 Variable penetrance Lymphedema Distichiasis Other disorder with FOXC2 defect? Meige syndrome (Late onset congenital lymphedema) |
|
|
Another name for Nail-Patella syndrome
|
Hereditary Osteo-Onychodysplasia (HOOD)
|
|
|
Gene defect for Nail-Patella Syndrome
|
AD inherited condition; assoc with mutations in the LMX1B gene (transcription factor that regulates collagen synthesis)
|
|
|
Name the two types of Pachyonychia Congenita
|
Type I = KRT6a and KRT16 defect, assoc with oral leukokeratosis
Type II = KRT6b and KRT 17 defect, assoc with premature dentition and pilosebaceous cysts |
|
|
another name for Darier dz and what nail finding
|
aka Follicular Dyskeratosis
red and white longitudinal streaks, V-shaped indentation of distal margin |
|
|
Types of Acanthosis Nigricans
|
Type I: assoc w/ malignancy;
Type II: familial Type III: asoc w/ Obesity & Endocrine (insulin resistance) |
|
|
Two Endocrine Syndromes with AN
|
Type A syndrome:
HAIR-AN syndrome -- characterized by hyperandrogenemia(HA), extreme insulin resistance (IR) and acanthosis nigricans (AN). Distinguished from type B from lack of antibodies to insulin receptor or other evidence of autoimmune disease. In Young Black Women. Type B - in older women w/ signs of autoimmune disease (circulating Ab to the insulin receptor). Pts w/ uncontrolled DM, acanthosis nigricans and ovarian hyperandrogenism |
|
|
Types of Primary Dyslipidemia
|
I - Chylomicrons (eruptive)
IIa - LDL (tendon&tuberous) IIb - VLDL & LDL (tendon&tuberous) III - IDL (palmar xanthomas) IV - VLDL (eruptive) V - Chylomicrons & VLDL (eruptive) |
|
|
Vogt Triad
|
epilepsy, angiofibromas (adenoma sebaceum), and mental retardation associated with tuberous sclerosis; affects 25% of patients
|

