![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Broad categories of ovarian neoplasms? |
Epithelial-stromal (benign, borderline, malignant) Germ cell tumors Sex chord-stroma Mets to ovaries
Borderline epithelial-stromal cell tumors have good prognosis
|
|
|
What are the germ cell tumors of the ovary? |
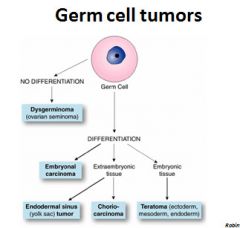
Germ cell tumors constitute approximately 20% to 30% of
Most germ cell tumors occur in children and |
|
|
____ ("___"): arise from post meiotic germ cell; mature fetal tissues; ____ is the most prevalent (skin, glial tissues)...also teeth, bone, adipose tissue, cartilage, respiratory and intestinal mucosa |
Mature cystic teratoma (dermoid cyst); ectoderm |
|
|
____: pre-meiotic oogonia; excellent prognosis; most common malignant germ cell tumor; age 20-30 year |
Germ cell tumor: dysgerminoma (biomarkers?) |
|
|
What makes up a immature teratoma? |
immature fetal tissue; mature + immature elements; primitive neuroepithelium; rapidly growing; peritoneal involvement; metastases |
|
|
____: pre-meiotic oogonia; excellent prognosis; most common malignant germ cell tumor; age 20-30 years |
Dysgerminoma (biomarkers?) |
|
|
*Sex cord-stromal tumors: primitive sex cord/____ origin; functioning tumor with low grade malignancy. What is it called in females and what does it secrete? |
Mesenchyme
Granulosa cell tumor. Activity leads to hyperestrogenism; bleeding, breast enlargement, endometrial hyperplasia/carcinoma; hemorrhage, rupture; |
|
|
Sex cord-stromal tumors: ____; a functioning tumor leading to androgenism; virilizing signs; abdominal symptoms; low or high grade malignancy |
sertoli-leydig cell tumor |

