![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
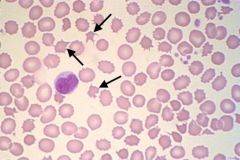
What is the cell called?
|
Acanthocyte (spiney cell)
|
|

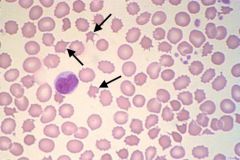
What type of stain is demonstrated in this image?
|
Acid Phosphatase
|
|
|
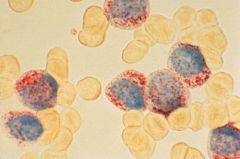
Agglutination
|
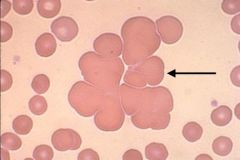
Describe the RBC morphology
|
|
|
Hurler's Syndrome. Alder's anomaly.
|
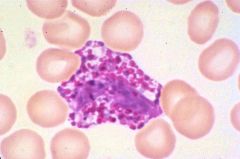
What disease or disorder is this cell characteristic of and what is the cell called?
|
|
|
Basophil
|
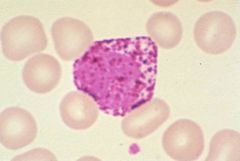
What type of cell is this?
|
|
|
Basophilic stippling
|

What is the RBC inclusions shown in this image?
|
|
|
Burr cell (echinocyte)
|
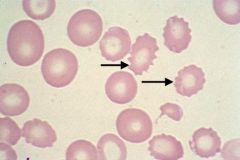
What is the name of this cell?
|
|
|
Remnant of the mitotic spindle
|
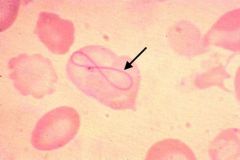
What is the cause of this RBC inclusion?
|
|
|
Chediak-Higashi cell is characteristic of Chediak-Higashi Syndrome. The giant lysosomal granules are caused by the fusion of the primary and secondary granules.
|
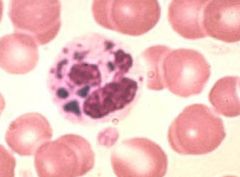
What type of cell is this, name the syndrome this cell is characteristic of, and explain the cause of the abnormality?
|
|
|
CML (CGL)
|
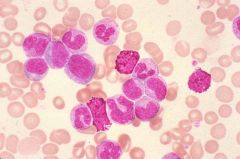
What type of leukemia is this?
|
|
|
The inclusion, a dohle bodie, consists of RNA around the periphery of the cell.
|
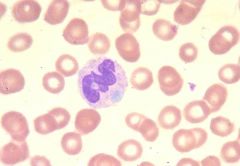
What is this WBC inclusion consist of?
|
|
|
Gaucher's Disease
|
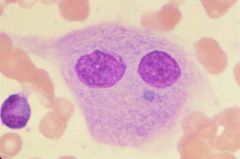
What disease is associated with this cell?
|
|
|
Hairy Cell Leukemia
|
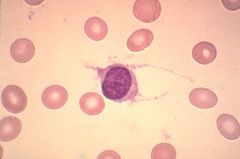
What leukemia is this cell associated with?
|
|
|
Activated neutrophils. LAP stain
|
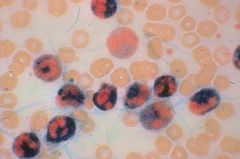
What cell is being stained positive in this image?
|
|
|
Hypersegmentation of a neutrophil
|
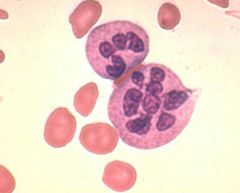
Describe the nuclear segmentation of this cell.
|
|
|
May-Hegglin
|
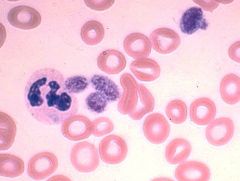
What disorder is characterized by this cell?
|
|
|
1. Neutrophilic myelocyte
2. Neutrophilic metamyelocyte 3. Neutrophilic band |
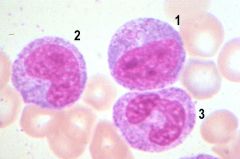
What are the three cell stages in the image (1, 2, 3)
|
|
|
Neutrophilia (shift to the left)
|
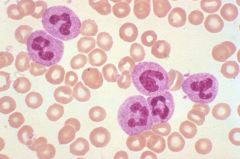
Describe the blood picture in this image?
|
|
|
Neutrophilic promyelocyte
|
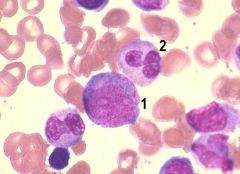
Name the stage of neutrophilic maturation.
|
|
|
1. Rubriblast
2. Prorubricyte 3. Rubricyte 4. Metarubricyte |
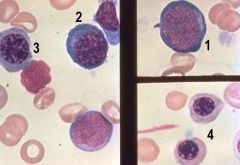
Name all four stages (1-4)
|
|
|
Reactive lymphocytes
|
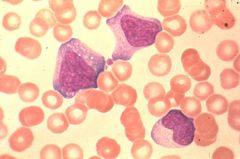
Describe the WBC's in this picture.
|
|
|
Specific esterase
|
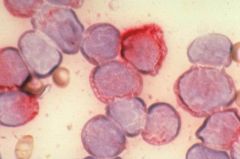
Name the stain.
|
|
|
Sea blue histiocyte
|
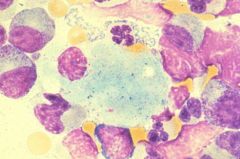
What is the cell type shown in this image?
|
|
|
Acute Erythroleukemia (AML M6)
|
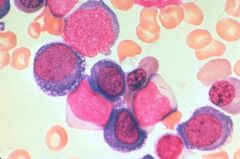
Name the disease state?
|
|
|
The deficiency in sphingomyelinase leads to the accumulation of sphingomyelin.
Neimann-Pick |
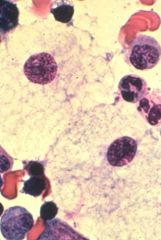
The enzyme deficiency in this cell causes an accumulation of what?
|
|
|
Toxic granulation of segmented neutrophils
|
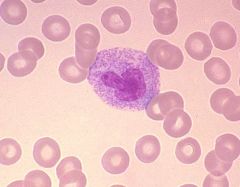
This reactive morphology occurs in what type of WBC?
|
|
|
Sudan Black B
|
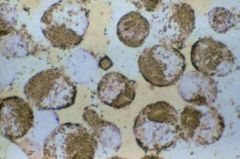
Name the stain
|
|
|
Eosinophilia
|
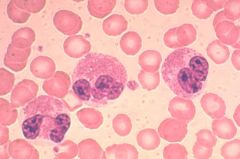
Describe the blood picture.
|
|
|
Megakaryocyte
|
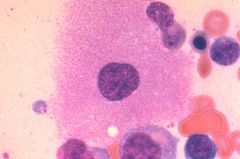
Name the cell type
|
|
|
Pelger-Huet
|
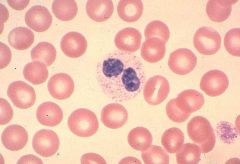
What disorder is associated with the hyposegmented segmented neutrophil?
|
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia- TRAP stain
|
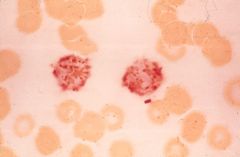
This stain is diagnostic of what disease?
|
|
|
Monocyte
|
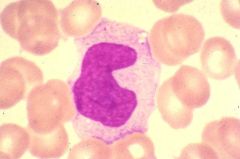
What is this cell?
|
|
|
Periodic Acid Schiff
|
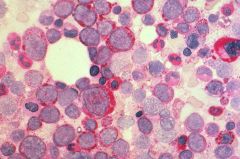
Name the stain
|
|
|
Plasma cell
|
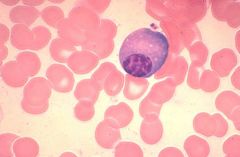
Name cell type in the image, not including the RBCs.
|
|
|
Blast
|
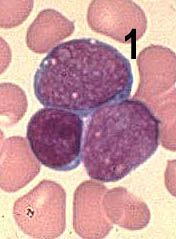
Describe the cell (1) in terms of stage of maturation...
|
|
|
With May-Hegglin you will observe thrombocytopenia due to the presence of giant platelets.
|
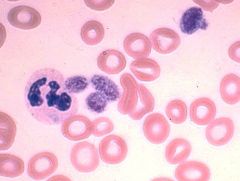
Quantify the platelets in relation to the disorder.
|
|
|
Gaucher cell. Deficiency in beta-glucocerebrosidase leads to the accumulation of the substrate, beta-glucocerebroside.
|
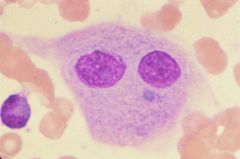
Name the cell and the cellular abnormality.
|
|
|
Non-specific esterase is specific for monocytes.
|
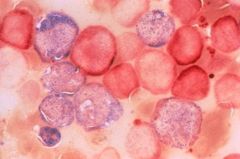
What is this "non-specific" stain specific for?
|

