![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endocrine Cell
|

|
|
|
4 main hormone types
|
1. peptides & proteins (insulin, FSH, GH)
synthesized by rER, stored in cytoplasmic granules and exocytosed when required 2. Steroids (oestrogens, glucocorticoids) derived from cholesterol synthesised in mitochondria & rER, not stored but released via diffusion 3.Tyrosine/amine-derived (dopamine, serotonin, epinephrine) synthesized from tyrosine stored in granules & released via exocytosis (thyroid hormones) stored extracellularly in colloid-filled cavities 4. Fatty acid derivatives (prostoglandins, leukotrienes) synthesized by rER stored in granules & released via exocytosis |
|
|
HYPOTHALAMO-HYPOPHYSEAL PORTAL CIRCULATION
|

Hypothalamus – neurosecretory neurons synthesize hormones which are transported to pituitary via vessels and axons
|
|
|
Anterior Pituitary Gland
- 3 parts |

derived from developing oral cavity
contains epithelial cells - sinusoidal cappilaries in pars intermedia |
|
|
POSTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND
|

neurohypothesus
1. stalk; infundibulum 2. pars.. |
|
|
Histology: LOW power
Pituitary |

|
|
|
BLOOD SUPPLY TO PITUITARY GLAND
|

|
|
|
pars distalis
|

•Cells arranged in clumps or cords
•Separated by fenestrated sinusoidal capillaries •Classified by their histochemical staining quality •Accurate differentiation requires immunocytochemical staining |
|

|
[pars distalis
|
|
|
Pars distalis
|

|
|
|
Pars Distalis = secretory cells and sinusoidal capillaries
- how to Dd b/w the secretory cells? |

|
|
|
electron microscope image of secretory cells in adenohypophysis
|

|
|

|
electron microscope image of sinusoidal capillary in the adenohypophysis
|
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
pars distalis - % cell types |

|
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS
pars intermedia |

Colloid-filled FOLLICLES
FOLLICLE CELLS (epithelial) - secrete MSH and endorphin |
|
|
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS pars tuberalis
|
•very VASCULAR region = VEINS
•CORDS of EPITHELIAL CELLS •small FOLLICLES lined with ACTH, FSH and LH cells |
|
|
NEUROHYPOPHYSIS
extension of the nervous system |

|
|
|
NEUROHYPOPHYSIS
|

1.Non-myelinated axons
2.Neurosecretory products (oxytocin, ADH) 3.Fenestrated sinusoidal capillaries 4.Glial cells (Pituicytes) |
|
|
Neurohypophysis hormones
|

|
|
|
NEUROHYPOPHYSIS pars nervosa
|

The axons are unique!
1.end in close proximity to capillaries 2. contain secretory vesicles in ALL parts of the neuron |
|
|
Herring Bodies
|

10-30nm Herring Bodies
Dilations of the axonal endings containing neurosecretory granules ADH & Oxytocin |
|
|
PITUICYTE
|

• glial cell
• branching cytoplasm • support function |
|
|
THYROID GLAND:
hormones |

|
|
|
THYROID FOLLICLE
|

cyst-like 0.2-1mm
lined with cuboidal epithelium = Follicular Cells filled with colloid = Thyroglobulin (glycoprotein) Extracellular storage |
|
|
EM: thyroid
|

|
|
|
Parafollicular cells (C cells)
|
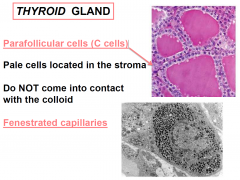
|
|
|
PARATHYROID GLAND
|
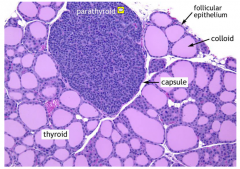
parathyroid gland is essential for life needs ot be conserved in thyroid cells
|
|
|
PTH Functions
|
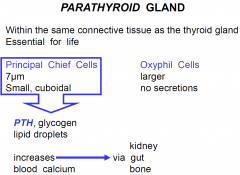
|
|
|
Parathyroid Gland Histology
|
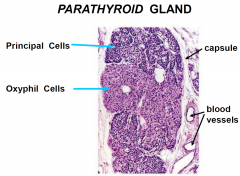
|
|
|
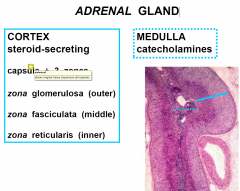
ADRENAL GLAND
|
|
|
|
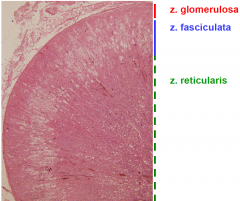
ADRENAL GLAND (CORTEX)
|
|
|
|
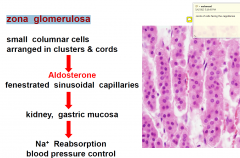
zona glomerulosa
|
|
|
|
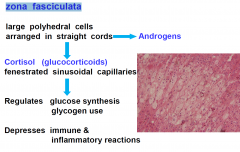
zona fasciculata
|
|
|
|
zona reticularis
|
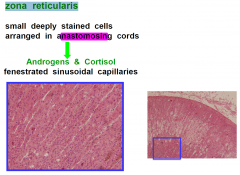
|
|
|
ADRENAL GLAND (MEDULLA)
|
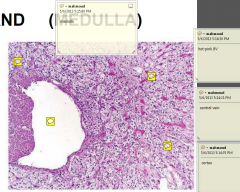
Chromaffin cells (modified neurons)
sinusoidal capillaries connective tissue Presynaptic sympathetic nerve fibres (axons) ganglion cells (modulate secretion) |
|
|
CHROMAFFIN CELLS
|
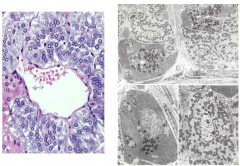
|
|
|
MEDULLA = sympathetic ganglion
|
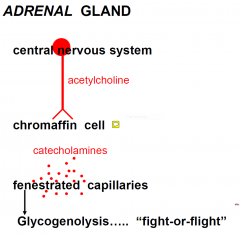
|

