![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
270 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
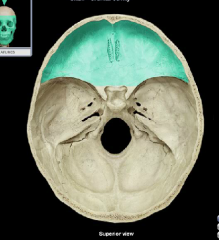
Anterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
|
|
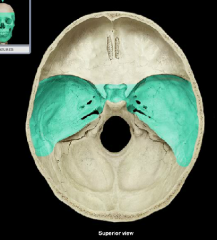
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
|
|
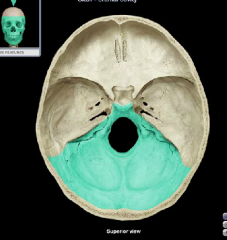
Posterior (cerebellar) cranial fossa
|
|
|
|
|
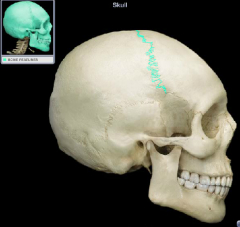
Coronal suture
|
|
|
|
|
Lambdoidal suture
|
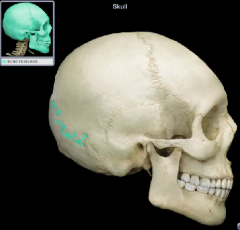
|
|
|
|
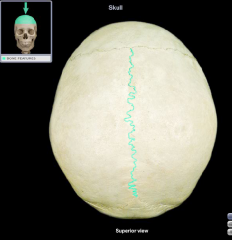
Sagittal Suture
|
|
|
|
Squamous suture
|
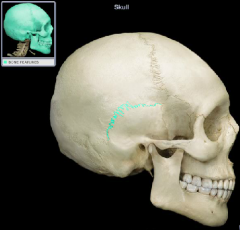
|
|
|
|
Superciliary arch
or Supraorbital Ridge |
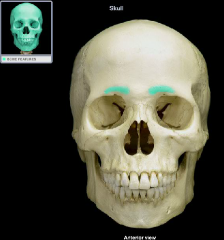
|
|
|
|
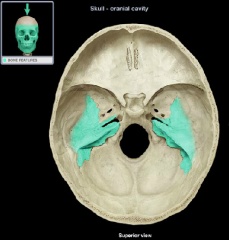
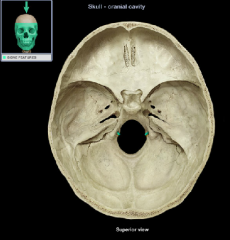
Petrous Part
|
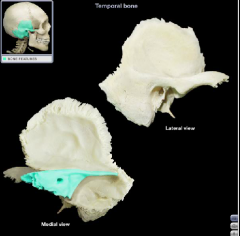
|
|
|
|
Petrous Part
|
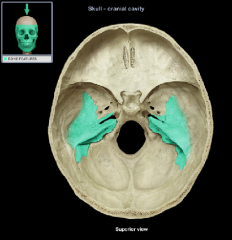
|
|
|
|
Mandibular Fossa
|
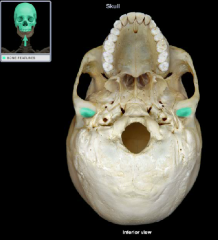
|
|
|
|
Mandibular fossa
|
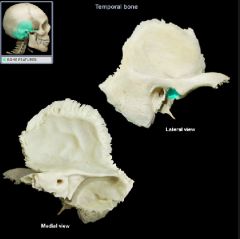
|
|
|
|
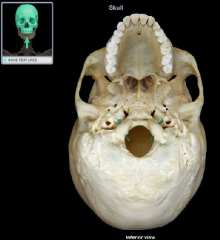
Carotid Canal
|
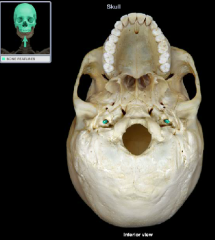
|
|
|
|
External Occipital Protuberance
|
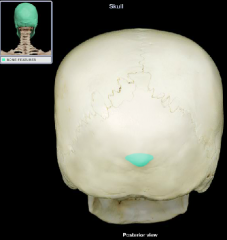
|
|
|
|
Occipital Condyle
|
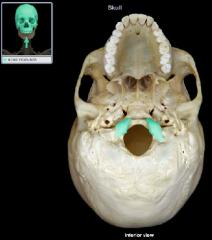
|
|
|
|
Hypoglossal canal
|
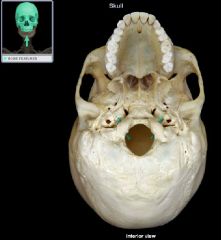
|
|
|
|
Hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
|
|
Hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
|
|
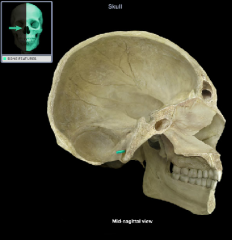
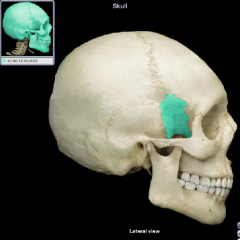
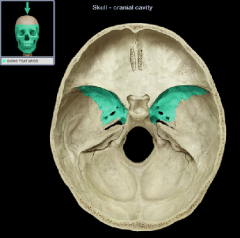
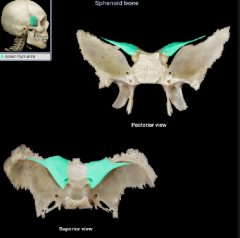
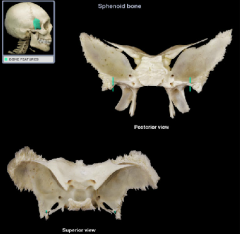
Greater Wing of the sphenoid bone
|
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
Greater Wing of the sphenoid bone
|
(name is back)
|
|
|
|
Greater Wing of the sphenoid bone
|
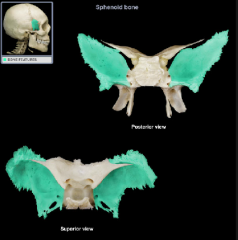
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone
|
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
Lesser Wing of the sphenoid bone
|
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
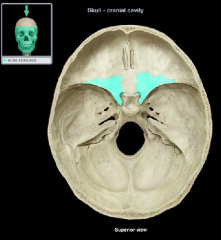
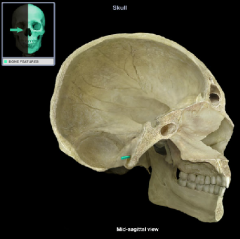
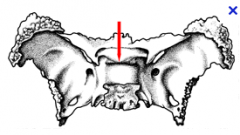
Sella turcica
|
|
|
|
|
Hypophysial Fossa of the sella turcica
|
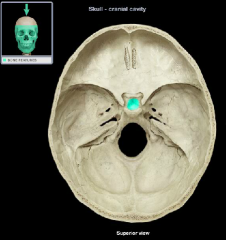
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
Dorsum sellae of the sella turcica
|
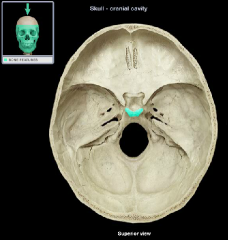
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
mental protuberance
|
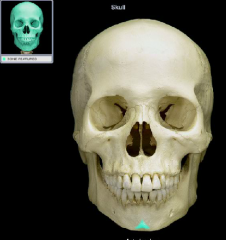
|
|
|
|
mandibular foramen
|
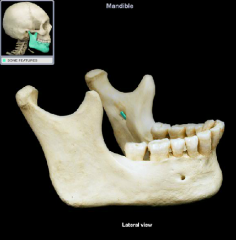
|
|
|
|
ramus of the mandible
|
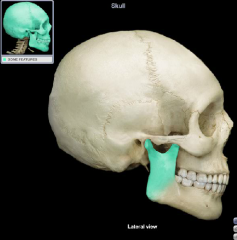
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
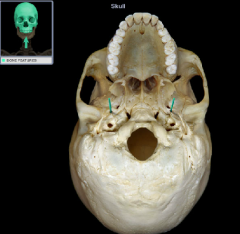
incisive fossa
|
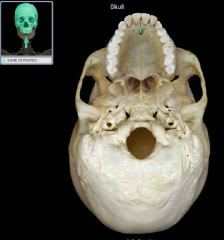
|
|
|
|
palatine process
|
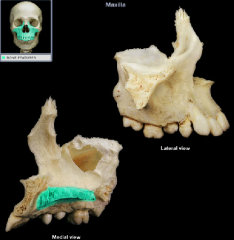
|
|
|
|
palatine process
|
|
|
|
|
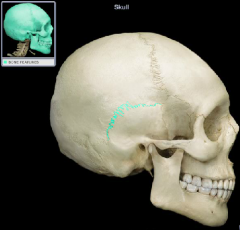
coronal suture
|
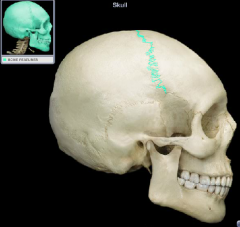
|
|
|
|
lambdoidal suture
|
|
|
|
|
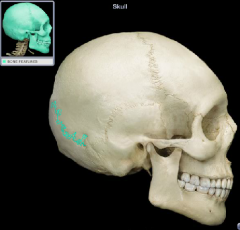
squamous suture
|
|
|
|
|
petrous part
|
|
|
|
|
petrous part
|
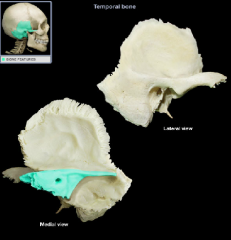
|
|
|
|
mandibular fossa
|
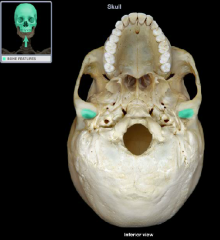
|
|
|
|
mandibular fossa
|
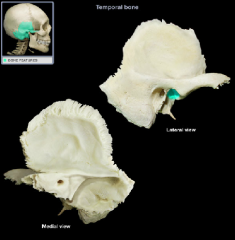
|
|
|
|
carotid canal
|
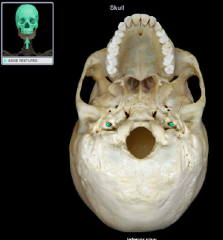
|
|
|
|
carotid canal
|
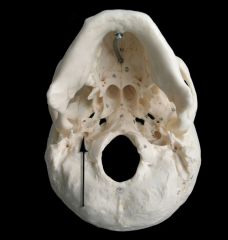
|
|
|
|
foramen rotundum
|
|
|
|
|
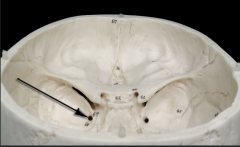
jugular foramen
|
|
|
|
|
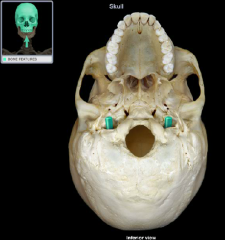
jugular foramen
|
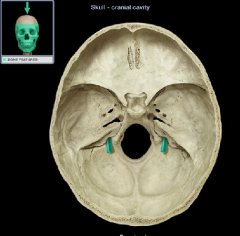
|
|
|
|
jugular foramen
|
Comment:
• Posterior to external opening of carotid canal • Traversed by internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), and accessory nerve (CN XI) |
|
|
|
external occipital protuberance
|
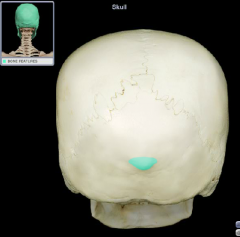
|
|
|
|
external occipital protuberance
|
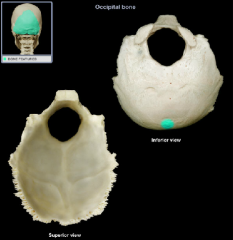
|
|
|
|
internal occipital protuberance
|
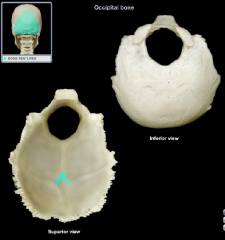
|
|
|
|
external occipital crest
|
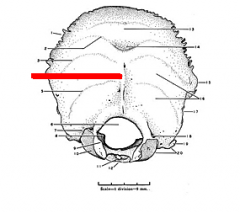
|
|
|
|
occipital condyle
|
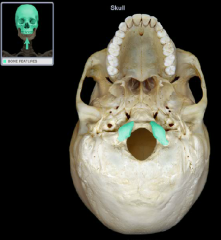
|
|
|
|
occipital condyle
|
|
|
|
|
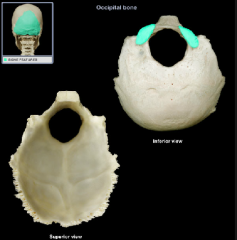
superior nuchal line
|
|
|
|
|
inferior nuchal line
|
|
|
|
|
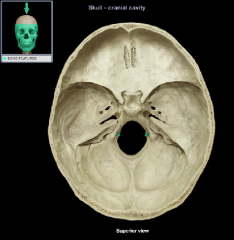
hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
|
|
hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
|
|
hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
|
|
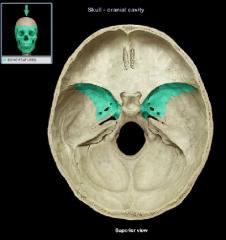
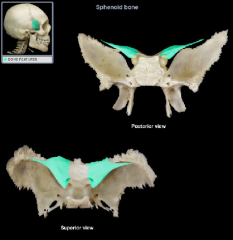
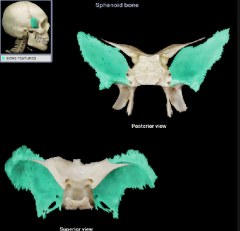
greater wing
|
|
|
|
|
greater wing
|
|
|
|
|
lesser wing
|
|
|
|
|
lesser wing
|
|
|
|
|
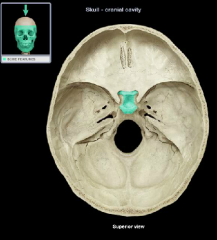
tuberculum sella(e) of the sella turcica
|
|
|
|
|
hypophysial fossa of the sella turcica
|
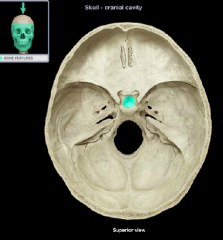
|
|
|
|
hypophysial fossa of the sella turcica
|
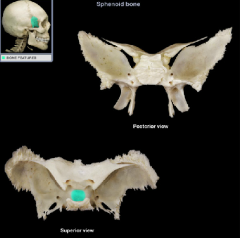
|
|
|
|
dorsum sellae of the sella turcica
|
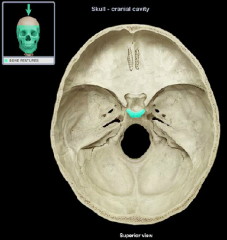
|
|
|
|
dorsum sella(e) of the sella turcica
|
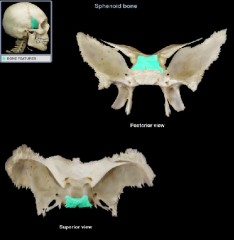
|
|
|
|
optic canal
|
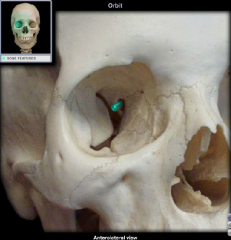
|
|
|
|
optic canal
|
|
|
|
|
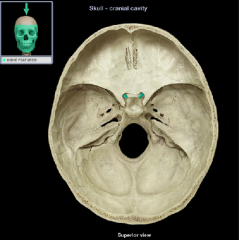
optic canal
|
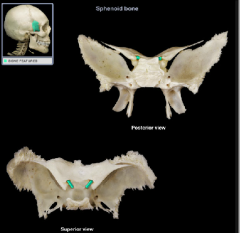
|
|
|
|
inferior oribital fissure
|
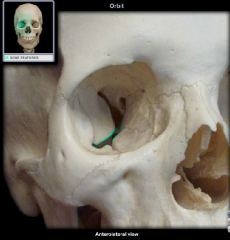
|
|
|
|
superior orbital fissure
|
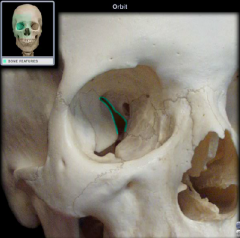
|
|
|
|
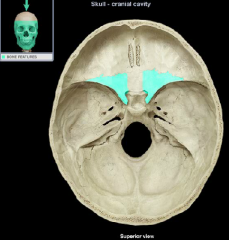
foramen rotundum
|
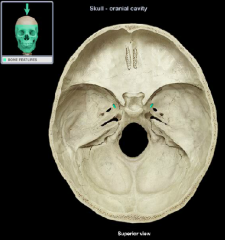
|
|
|
|
foramen rotundum
|
Location:
• Middle cranial fossa • Sphenoid bone (greater wing) • Just inferior to medial end of superior orbital fissure Description: • Horizontal canal • Connects middle cranial fossa with pterygopalatine fossa Comment: • Transmits maxillary (CN V2) nerve |
|
|
|
foramen rotundum
|
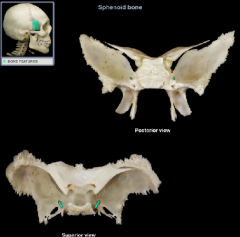
|
|
|
|
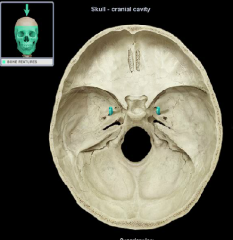
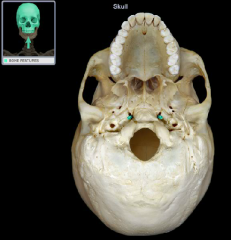
foramen ovale
|
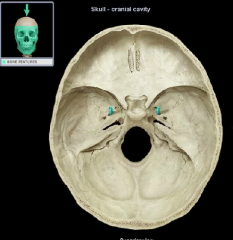
|
|
|
|
foramen ovale
|
|
|
|
|
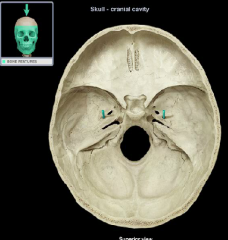
foramen spinosum
|
|
|
|
|
foramen ovale
|
Location:
• Sphenoid bone (greater wing) Description: • Oval-shaped hole • Superior opening in middle cranial fossa • Inferior opening in infratemporal fossa Comment: • Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (CN V3) passes through this opening |
|
|
|
foramen spinosum
|
Location:
• Sphenoid bone (greater wing) Description: • Round hole • Superior opening in middle cranial fossa • Inferior opening in infratemporal fossa Comment: • Middle meningeal artery passes through this opening |
|
|
|
foramen spinosum
|
|
|
|
|
foramen spinosum
|
|
|
|
|
foramen ovale
|
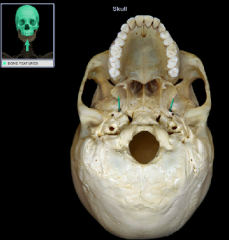
|
|
|
|
foramen ovale
|
|
|
|
|
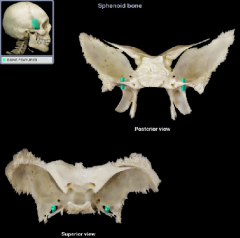
pterygoid process
|
|
|
|
|
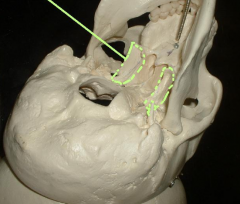
foramen lacerum
|
|
|
|
|
foramen lacerum
|
Location:
• Middle cranial fossa Description: • Irregularly shaped opening formed by sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones • Superior opening (middle cranial fossa) • Inferior opening (base of skull) Comment: • Inferior opening is closed in living subjects by fibrocartilage • Internal carotid artery enters posterior wall and ascends into middle cranial fossa |
|
|
|
foramen lacerum
|
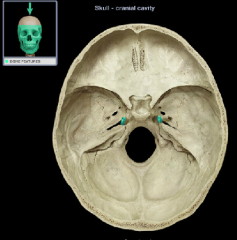
|
|
|
|
vomer
|
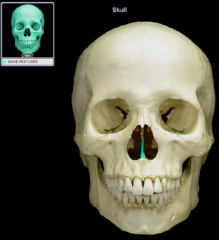
|
|
|
|
vomer
|
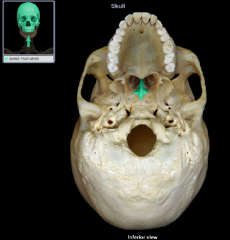
|
|
|
|
vomer
|
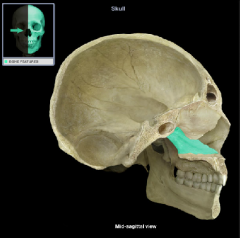
|
|
|
|
lacrimal bone
|
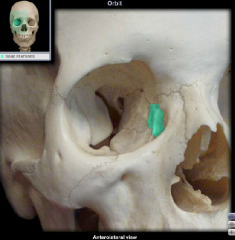
|
|
|
|
lacrimal bone
|
|
|
|
|
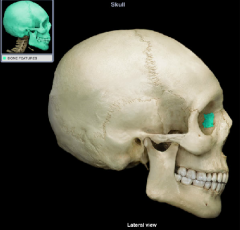
middle nasal concha
|
|
|
|
|
middle nasal concha
|
|
|
|
|
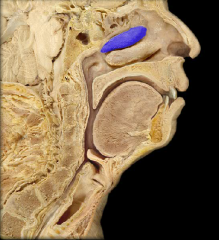
superior nasal concha
|
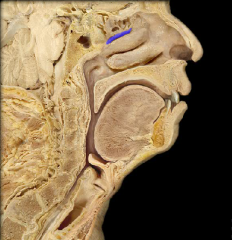
|
|
|
|
superior nasal concha
|
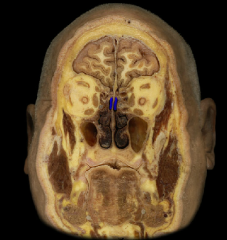
|
|
|
|
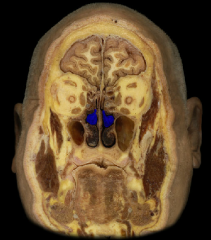
inferior nasal concha
|
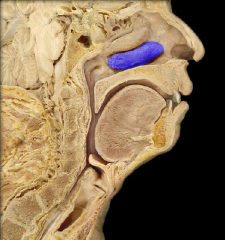
|
|
|
|
inferior nasal concha
|
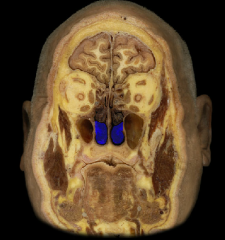
|
|
|
|
hyoid bone
|
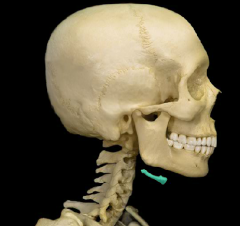
|
|
|
|
hyoid bone
|
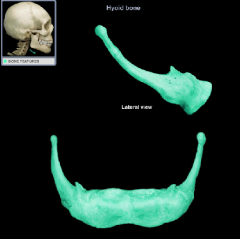
|
|
|
|
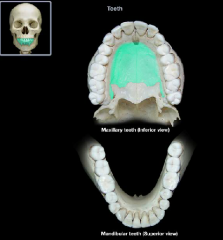
palatine process of the maxilla
|
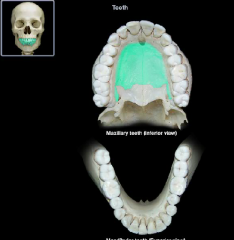
|
|
|
|
palatine process of the maxilla
|
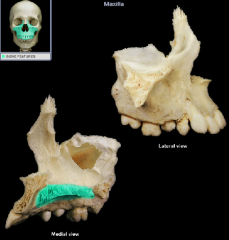
|
|
|
|
incisive fossa
|
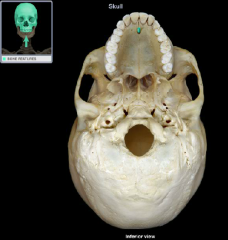
|
|
|
|
ramus of mandible
|
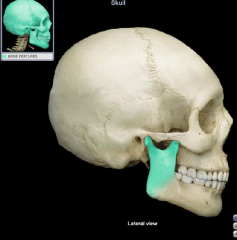
|
|
|
|
mental protuberance
|
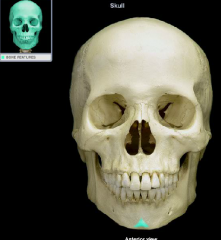
|
|
|
|
superior nasal concha
|
|
|
|
|
lacrimal bone
|
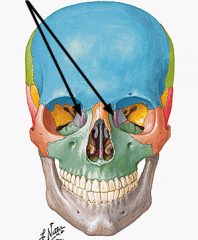
|
|
|
|
lacrimal foramen
|
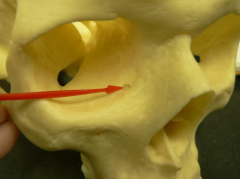
|
|
|
|
inferior nasal concha
|
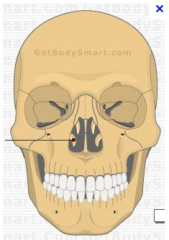
|
|
|
|
middle nasal concha
|
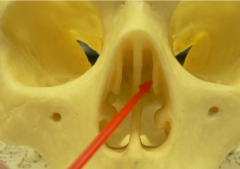
|
|
|
|
central canal
|
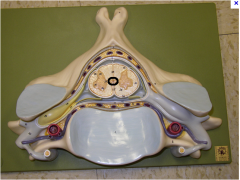
|
|
|
|
vertebral artery
|
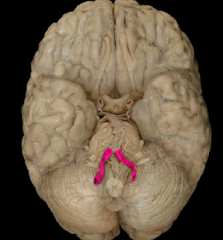
|
|
|
|
vertebral artery
|
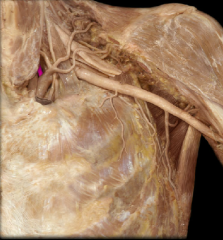
|
|
|
|
vertebral artery
|
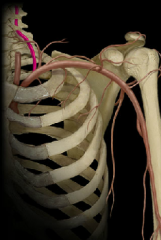
|
|
|
|
vertebral artery
|
Course:
• Paired vessel ascends through neck, via transverse foramina in cervical vertebrae • Enters cranial cavity via foramen magnum Distribution: • Brain • Spinal cord • Vertebral column Branches: • Posterior inferior cerebellar • Spinal arteries • Continues as basilar artery (formed by union of right and left vertebral arteries) Comment: • Large arteries do not by themselves supply structures, but do so through their branches |
|
|
|
basilar artery
|
Origin:
• Junction of paired vertebral arteries Course: • Unpaired (midline) vessel ascends on anterior (ventral) surface of pons Distribution: • Pons • Cerebellum Branches: • Pontine • Anterior inferior cerebellar • Superior cerebellar • Posterior cerebral |
|
|
|
posterior cerebral artery
|
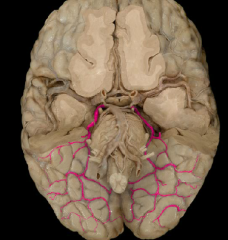
|
|
|
|
internal carotid artery
|
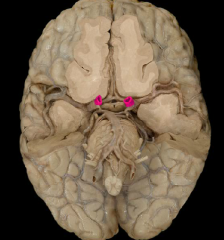
|
|
|
|
internal carotid artery
|
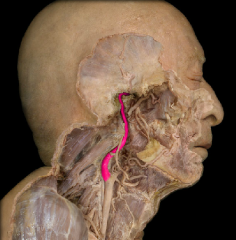
|
|
|
|
middle cerebral artery
|
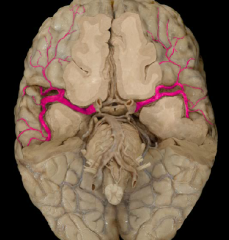
|
|
|
|
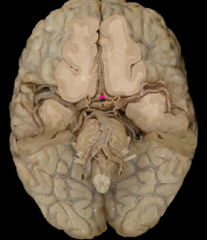
anterior cerebral artery
|
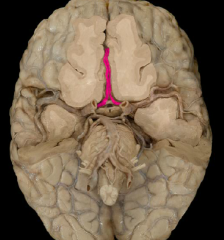
|
|
|
|
anterior cerebral artery
|
|
|
|
|
anterior communicating artery
|
|
|
|
|
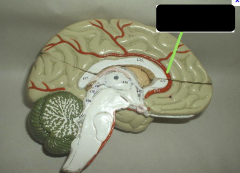
superior sagittal sinus
|
Comment:
• Unpaired, dural venous sinus • Contains arachnoid granulations for return of cerebrospinal fluid to venous circulation • Dural venous sinuses are endothelial-lined channels between layers of dura mater |
|
|
|
pineal body
|
|
|
|
|
superior colliculus
|
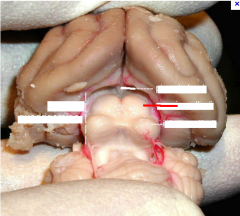
|
|
|
|
inferior colliculus
|
|
|
|
|
tuber cinerum
|
- hollow eminence of gray matter situated between the mammillary bodies and the optic chiasm
- part of hypothalamus |
|
|
|
infundibulum
|
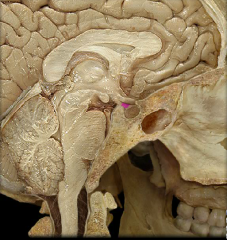
The connection between the hypothalamus and the pars nervosa hypophyseos (the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland)
|
|
|
|
infundibulum
Location, description, and function |
Location:
• Ventral surface of diencephalon (hypothalamus) at midline Description: • Contains hypothalamo-hypophysial tract • Contains hypothalamo-hypophysial portal vein that carries hypophysiotropic hormones to the anterior pituitary Function: • Transmits antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin through hypothalamo-hypophysial tract to posterior pituitary |
|
|
|
pituitary body
Location, description, and function |
Location:
• Midline of middle cranial fossa • Rests in hypophysial fossa of sphenoid bone Description: • Small, oval bilobed endocrine gland • Two functional lobes: anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis) • Connected by infundibulum to hypothalamus Function: • Anterior pituitary produces the following hormones: thyroid-stimulating (TSH), prolactin (PRL), adrenocorticotropic (ACTH), growth (GH), luteinizing (LH), melanocyte-stimulating (MSH), and follicle-stimulating (FSH) • Posterior ______ stores and releases: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) |
|
|
|
pineal gland
Location, description, and function |
Location:
• Diencephalon (epithalamus) Description: • Pea-sized endocrine gland • Attached to roof of third ventricle Function: • Secretes melatonin (involved in sleep/wake cycles) • Modified activity in endocrine organs (pituitary, pancreas, parathyroid, suprarenal, and gonads) |
|
|
|
bones that make up the orbit
|
Ethmoid
Frontal Lacrimal Maxilla Palatine Sphenoid Zygomatic |
|
|
|
posterior communicating artery
|
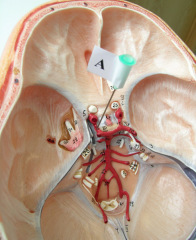
|
|
|
|
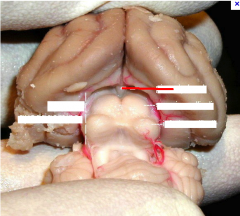
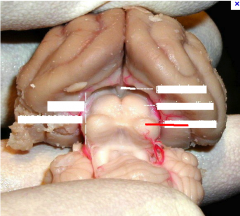
middle cerebellar peduncle
|
#1
|
|
|
|
superior cerebellar peduncle
|
#2
|
|
|
|
inferior cerebellar peduncle
|
#3
|
|
|
|
thalamus
|
|
|
|
|
mammilary body
|
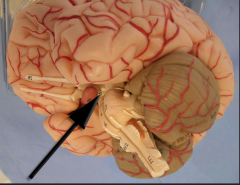
|
|
|
|
olive of the medulla oblongata
|
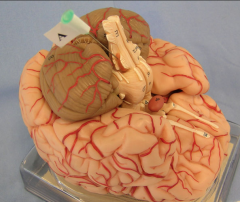
(name it back)
|
|
|
|
Occipital sinus
|
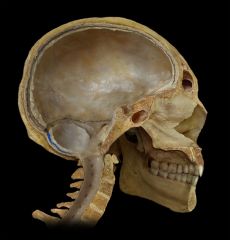
|
|
|
|
Insular lobe
|
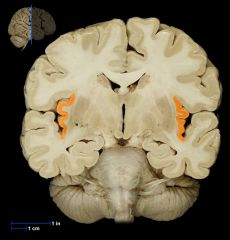
|
|
|
|
Superior orbital fissure
|
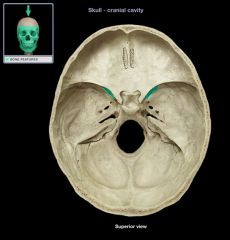
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
Autonomic reflex center; cardiovascular center; involved in respiratory control
|
|
|
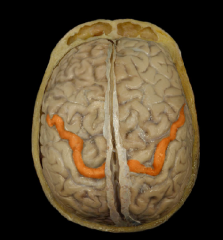
|
Precentral Gyrus
|
|
|
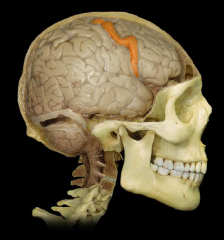
|
Precentral Gyrus
|
|
|
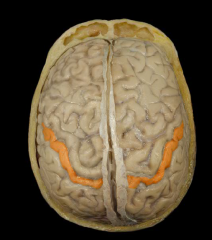
|
Postcentral Gyrus
|
|
|
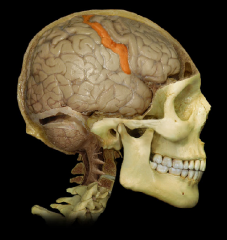
|
Postcentral Gyrus
|
|
|
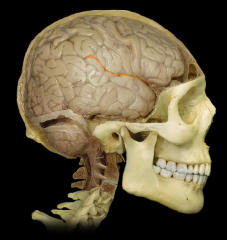
|
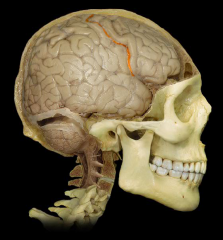
Lateral Sulcus
|
|
|
|
Lateral Sulcus
|
|
|
|
Central Sulcus
|
|
|
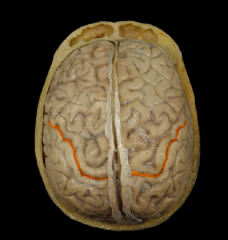
|
Central Sulcus
|
|
|
|
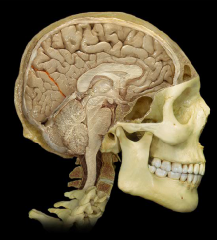
Parieto-occipital Sulcus
|
|
|
|
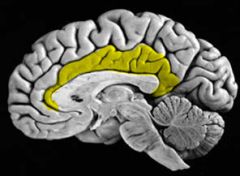
Cingulate (limbic) Gyrus
|
|
|
|
Cingulate (limbic) Gyrus
|
|
|
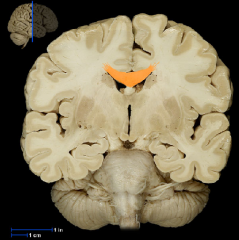
|
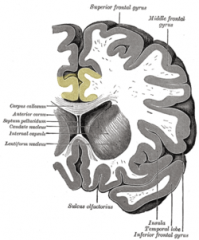
Corpus Callosum
|
|
|
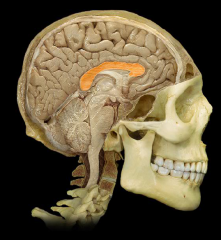
|
Corpus Callosum
|
|
|
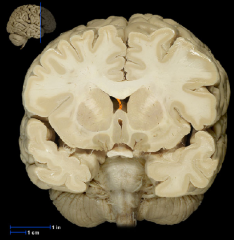
|
Septum Pellucidum
|
|
|
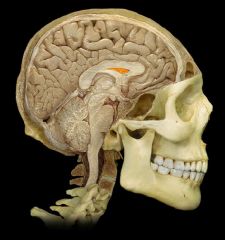
|
Septum Pellucidum
|
|
|
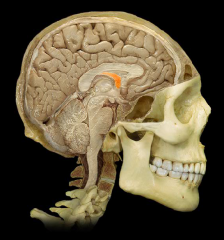
|
Fornix
|
|
|
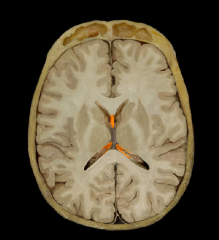
|
Fornix
|
|
|
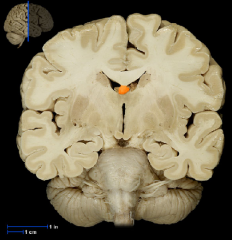
|
Fornix
|
|
|
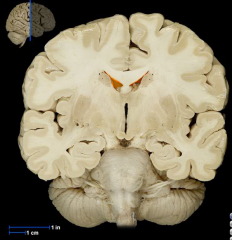
|
Lateral Ventricles
|
|
|
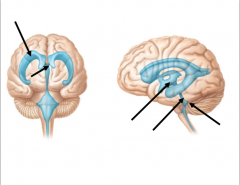
From left to right name the areas the arrows are pointing to
|
Lateral Ventricle
Interventricular Foramen Third Ventricle Cerebral Aqueduct Fourth Ventricle |
|
|
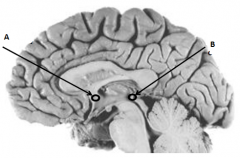
Name Arrow A
|
Anterior Commissure
|
|
|
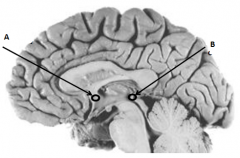
Name Arrow B
|
Posterior Commissure
|
|
|
|
Fourth Ventricle
|
|
|
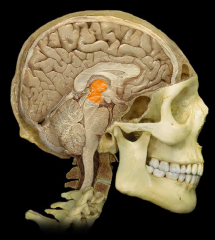
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
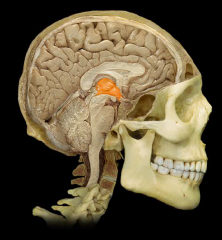
|
Third Ventricle
|
|
|
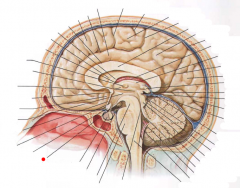
|
Tuber Cinereum
|
|
|
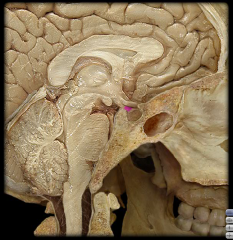
|
Infundibulum
|
|
|
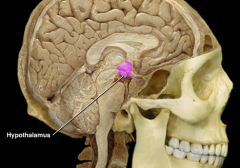
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
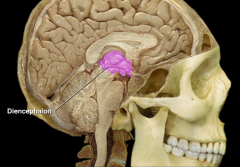
|
Diencephalon
|
|
|
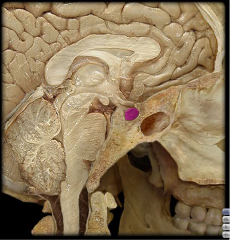
|
Pituitary Gland
|
|
|
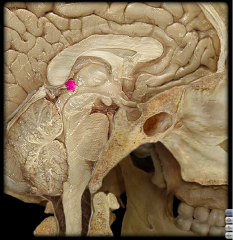
|
Pineal Gland (Body)
|
|
|
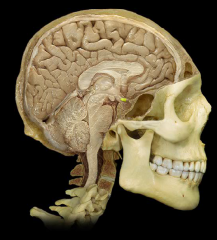
|
Optic Chiasm
|
|
|
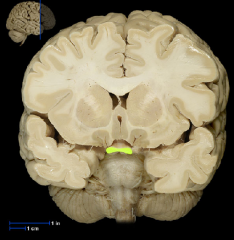
|
Optic Chiasm
|
|
|
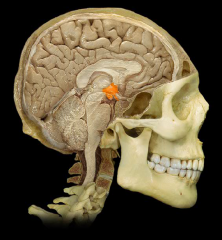
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
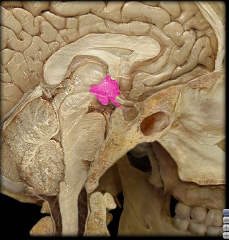
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
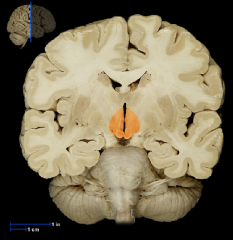
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
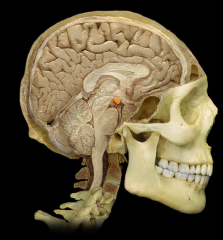
|
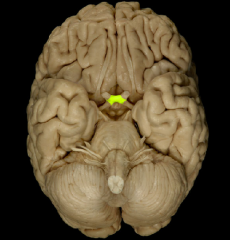
Mammillary Body
|
|
|
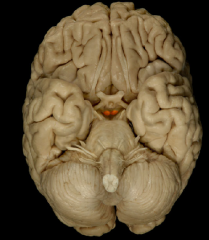
|
Mammillary Body
|
|
|
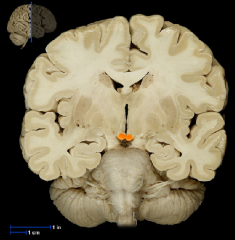
|
Mammillary Body
|
|
|
|
Optic Chiasm
|
|
|
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
|
|
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
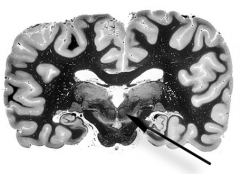
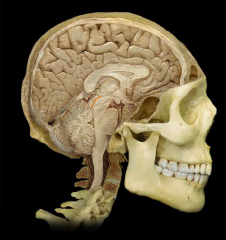
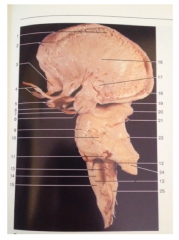
What is 17
|
Anterior Commissure
|
|
|
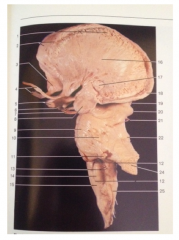
What is 9
|
Pons
|
|
|
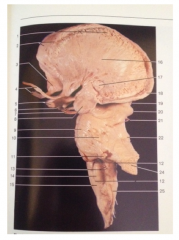
What is 14
|
Olive of the medulla oblongata
|
|
|
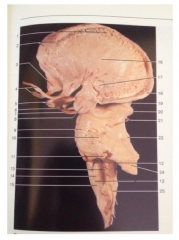
What is 15
What is its function |
Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata controls autonomic functions, and connects the higher levels of the brain to the spinal cord. It is also responsible for regulating several basic functions of the autonomic nervous system which include: Respiration – chemoreceptors Cardiac center – sympathetic, parasympathetic nervous system Vasomotor center – baroreceptors Reflex centers of vomiting, coughing, sneezing, and swallowing. These reflexes can be classified as "bulbar reflexes", including the, the pharyngeal reflex, the swallowing reflex (also known as the palatal reflex), and the masseter reflex. |
|
|
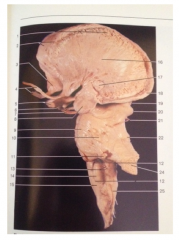
What is 19
|
Superior Colliculus
|
|
|
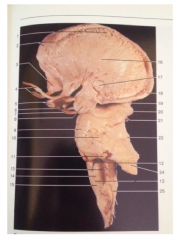
What is 20
|
Inferior Colliculus
|
|
|
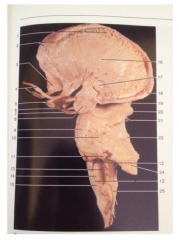
What is 22
|
Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
|
|
|
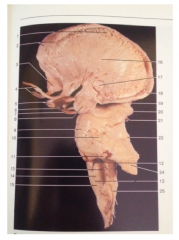
What is 24
|
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
|
|
|
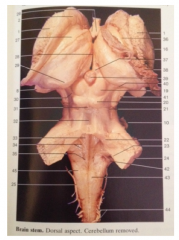
What is 19
|
Superior Colliculus
|
|
|
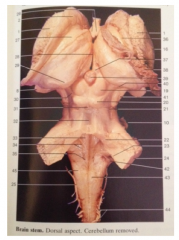
What is 20
|
Inferior Colliculus
|
|
|
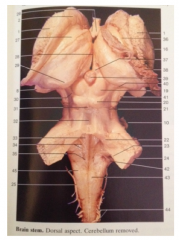
What is 41
|
Cerebral Peduncle
|
|
|
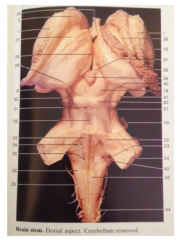
What is 22
|
Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
|
|
|
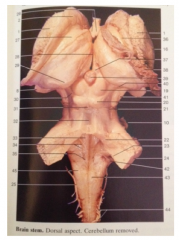
What is 24
|
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
|
|
|
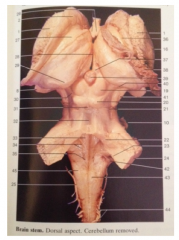
What is 23
|
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
|
|
|
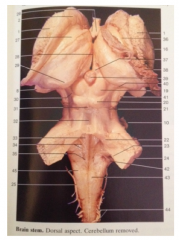
What is 39
|
Pineal Body
|
|
|
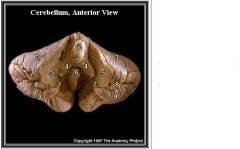
What is 1
|
Vermis of the Cerebellum
|
|
|
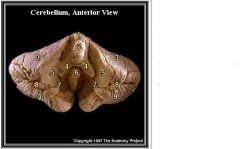
What is 8
|
Flocculus of the Cerebellum
|
|
|
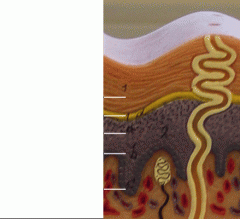
What is 1
|
Stratum Corneum
|
|
|
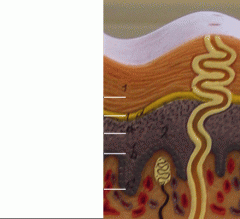
What is 1d
|
Stratum Lucidum
|
|
|
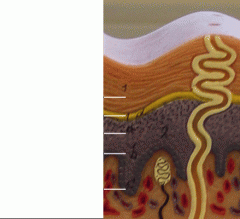
What is a
|
Stratum Granulosum
|
|
|
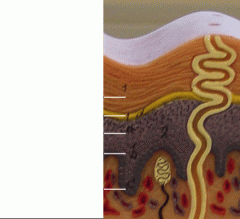
What is b
|
Stratum Spinosum
|
|
|
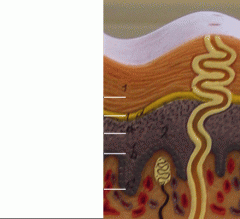
What is c
|
Stratum Basale
|
|
|
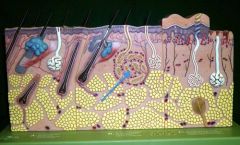
|
Apocrine Sweat Gland
|
|
|
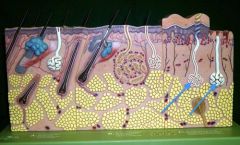
|
Eccrine Sweat Gland
|
|
|
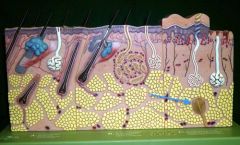
|
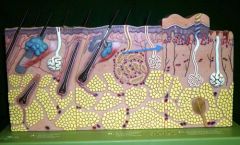
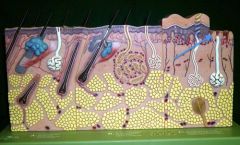
Pacinian Corpsucle
|
|
|
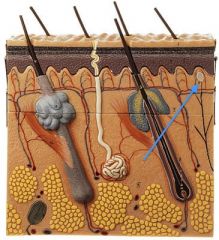
|
Meissner's Corpuscle
|
|
|
|
Dermal Papillae
|
|
|
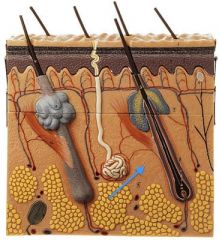
|
Meisner's Corpuscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Layer
|
|
|
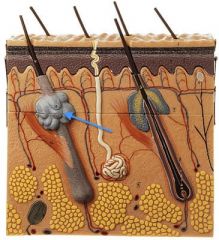
|
Sebaceous Gland
|
|
|
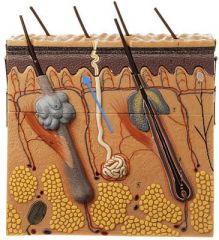
|
Dermal Papillae
|
|
|
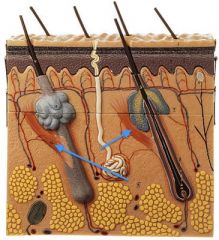
|
Arrector Pili Muscle
|
|
|
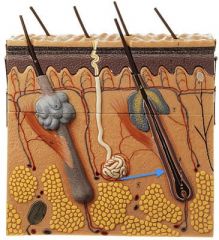
|
Hair Follicle
|
|
|
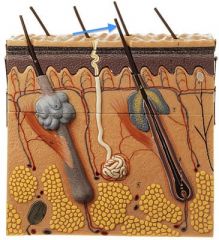
|
Hair Shaft
|
|
|
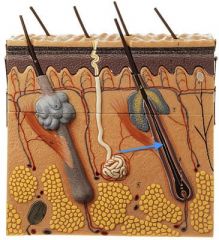
|
Hair Root
|
|
|
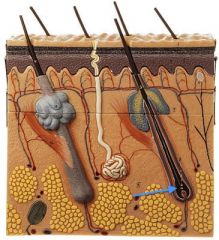
|
Hair Bulb
|
|
|
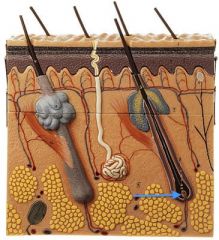
|
Hair Papilla
|
|
|
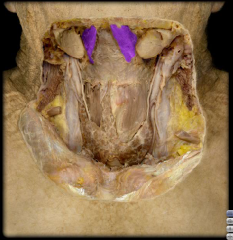
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Anterior Belly of Diagastric Muscle
Origin: Lower margin of the mandible Insertion: Hyoid Bone Function: Opens mouth, elevates hyoid Fibers run vertically |
|
|
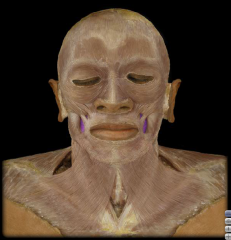
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Buccinator muscle
Origin: Lateral maxilla and mandible Insertion: blends with muscles at the angle of the mouth Function: Compression of cheek (e.g. inflating a balloon) |
|
|
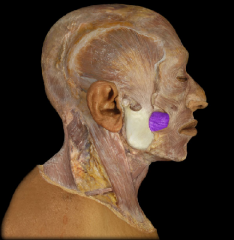
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Buccinator muscle
Origin: Lateral maxilla and mandible Insertion: blends with muscles at the angle of the mouth Function: Compression of cheek (e.g. inflating a balloon) |
|
|
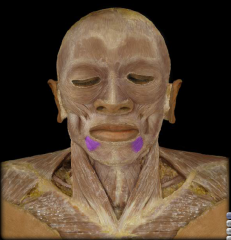
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Depressor anguli oris muscle
Origin: Mandible (body) Insertion: blends with muscles at the angle of the mouth Function: Depression of angle of mouth (grimace) |
|
|
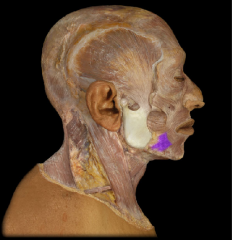
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Depressor anguli oris muscle
Origin: Mandible (body) Insertion: blends with muscles at the angle of the mouth Function: Depression of angle of mouth (grimace) |
|
|
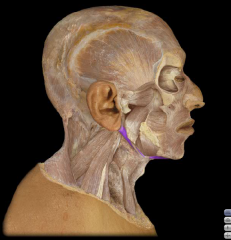
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Diagastric muscle (both anterior belly and posterior belly)
Origin: Anterior belly- Lower margin of the mandible. Posterior belly- Mastoid Process of temporal bone Insertion: Hyoid Bone Function: Opens mouth, elevates hyoid Anterior Belly Fibers run vertically |
Two muscles
|
|
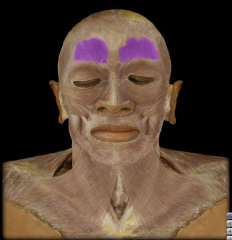
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Frontalis Muscle
Origin: Blends with orbicularis oculi muscle Insertion: Epicranialaponeurosis Function: Elevates eyebrows, creases skin of forehead |
|
|
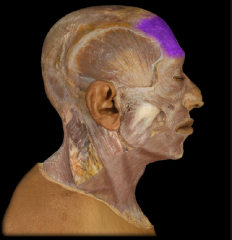
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Frontalis Muscle
Origin: Blends with orbicularis oculi muscle Insertion: Epicranialaponeurosis Function: Elevates eyebrows, creases skin of forehead |
|
|
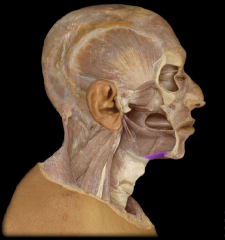
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Geniohyoid Muscle
Origin: Medial surface of the mandible Insertion: Hyoid Function: Elevation of Hyoid |
|
|
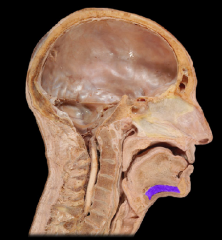
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Geniohyoid Muscle
Origin: Medial surface of the mandible Insertion: Hyoid Function: Elevation of Hyoid Geniohyoid Fibers run vertically |
|
|
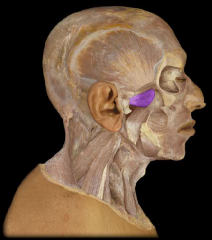
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Lateral (external) pterygoid Muscle
Origin: Greater wing of the sphenoid and lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid Insertion: Mandible (neck); Function: Protraction of mandible; side- to- side movement of mandible (chewing) |
|
|
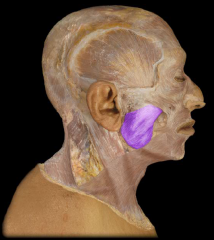
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Masseter Muscle
Origin: Zygomatic arch Insertion: Mandible (external surface of the angle and ramus) Function: Elevation of mandible (closing the mouth) |
|
|
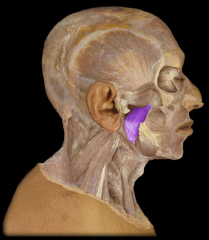
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Medial (internal) pterygoid muscle
Origin: lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid Insertion: Mandible (medial surface of the angle and ramus) Function:Elevation of mandible (closing the mouth); side- to- side movement of mandible (chewing); protrusion of mandible |
|
|
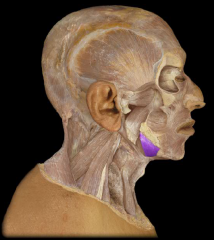
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Mylohyoid
Origin: Mandible (inner aspect of body) Insertion:Hyoid bone Function: Elevation of floor of mouth Mylohyoid Fibers run horizontally |
|
|
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Mylohyoid
Origin: Mandible (inner aspect of body) Insertion:Hyoid bone Function: Elevation of floor of mouth Mylohyoid Fibers run horizontally |
|
|
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Omohyoid Muscle
Origin: Scapular Insertion: Hyoid Function: Depression of the Hyoid |
|
|
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Omohyoid Muscle
Origin: Scapular Insertion: Hyoid Function: Depression of the Hyoid |
|
|
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Obicularis oculi
Origin: Frontal Bone, maxilla Insertion: fibers blend at lateral side of orbit Function: Closes eyelids |
|
|
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Obicularis oculi
Origin: Frontal Bone, maxilla Insertion: fibers blend at lateral side of orbit Function: Closes eyelids |
|
|
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Obicularis Oris
Origin: Skin around mouth Insertion: Lips Function: Closes lips, protrudes lips (pucker) |
|
|
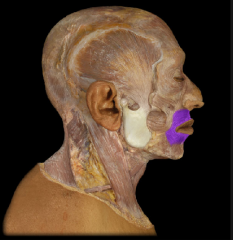
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Obicularis Oris
Origin: Skin around mouth Insertion: Lips Function: Closes lips, protrudes lips (pucker) |
|
|
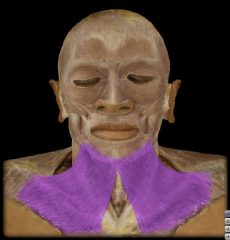
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Platysma
Origin: Upper thorax/ lower neck Insertion: Lower mandible Function: Elevates and creases the skin of the neck (expression of horror); Depression of lower lip/ angle of mouth |
|
|
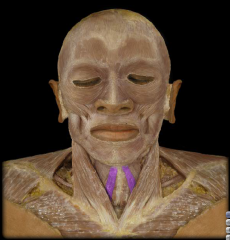
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Sternohyoid Muscle
Origin: Sternum, clavicle Insertion: Hyoid Function: Depression of Hyoid Bone |
|
|
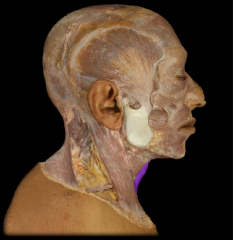
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Sternohyoid Muscle
Origin: Sternum, clavicle Insertion: Hyoid Function: Depression of Hyoid Bone |
|
|
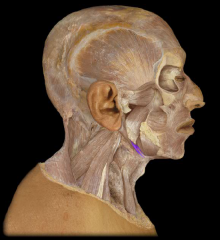
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Stylohyoid
Origin: Styloid process of temporal bone Insertion: Hyoid Function: Elevation of Hyoid bone |
|
|
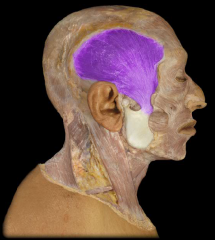
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Temporalis
Origin: Temporal bone Insertion: coronoid process and ramus of mandible Function: Elevation of mandible (closing mouth); retraction of mandible |
|
|
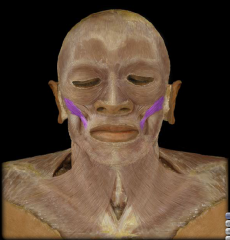
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Zygomaticus Major
Origin: Zygomatic bone Insertion: blends with muscles at the angle of the mouth Function: Elevation of the corner of the mouth (smile) |
|
|
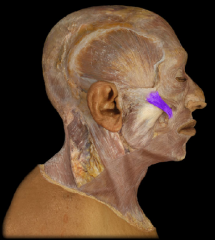
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Zygomaticus Major
Origin: Zygomatic bone Insertion: blends with muscles at the angle of the mouth Function: Elevation of the corner of the mouth (smile) |
|
|
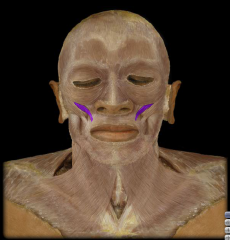
Name:
Origin: Insertion: Function: |
Name: Zygomaticus Minor
Origin: Zygomatic bone Insertion: Blends with obicularis oris muscle Function: Elevation of upper lip |
|
|
|
Order the muscles from deep to superficial:
Patysma Mylohyoid Geniohyoid Anterior belly of the diagastic |
Geniohyoid
Mylohyoid Anterior belly of the diagastic Patysma |
Germen
Men Deliver Packages |
|
|
What way do the muscle fibers run in these muscles:
Geniohyoid Mylohyoid Anterior belly of the diagastic |
Geniohyoid: Fibers run vertically
Mylohyoid: Fibers run horrizontally Anterior belly of the diagastic: Fibers run vertically |
|
|
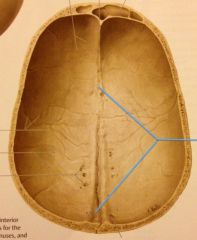
|
Superior Sagittal Groove
|
|
|
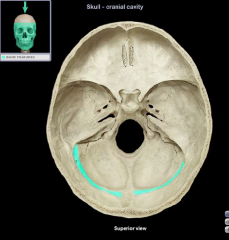
|
Transverse Groove
|
|
|
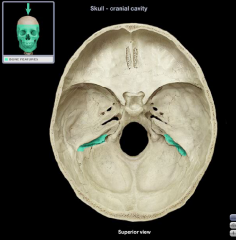
|
Sigmoid Sinus Groove
|
|
|
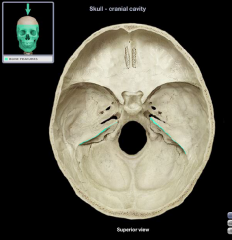
|
Superior Petrosal Groove
|
|
|
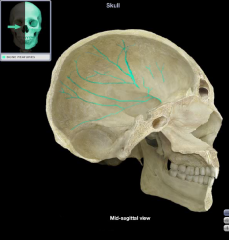
|
Meningeal (arterial) groove
|
|
|
|
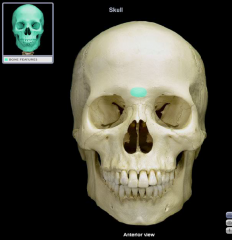
Glabella
|
|
|
|
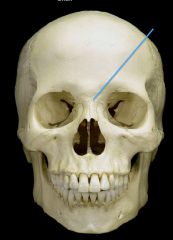
Nasion
the intersection of the frontal bone and two nasal bones of the human skull |
|
|
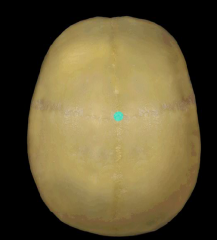
|
Bregma
intersection of coronal and sagittal sutures |
|
|
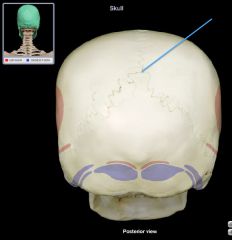
|
Lambda
Intersection of the lambdoid and sagittal sutures |
|
|
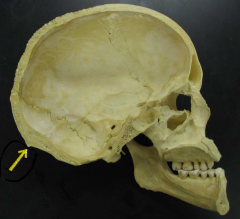
|
Inion
the term "inion" refers to the highest point of the external occipital protuberance |
|
|
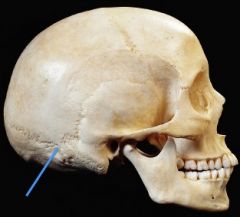
|
Asterion
Where the lambdoid, parieto-mastoid, and occipito-mastoid sutures meet |
|
|
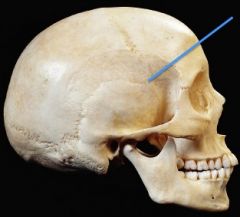
|
Pterion
the junction between three bones: the parietal bone the squamous part of temporal bone the greater wing of sphenoid bone |
|
|
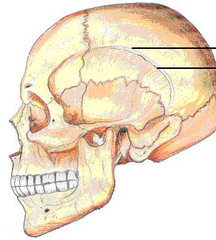
|
Superior temporal line of parietal bone
Inferior temporal line of parietal bone |
|
|
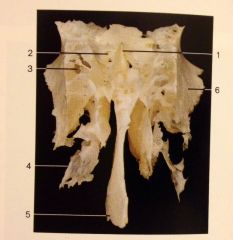
What is:
1,2,4,5 |
1. Crista galli
2. Cribriform Plate 4. Middle Nasal Concha 5. Perpendicular Plate |
|
|
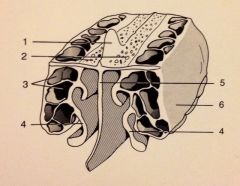
What is:
1,2,4,5 |
1. Crista galli
2. Cribriform Plate 4. Middle Nasal Concha 5. Perpendicular Plate |
|
|
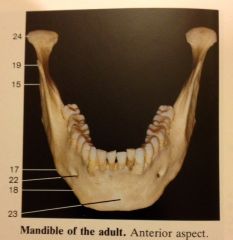
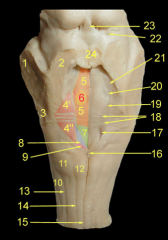
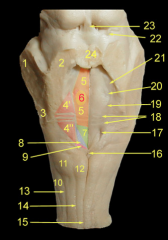
What is:
15 17 18 19 22 23 24 |
15 Ramus of the mandible
17 Angle of the mandible 18 Body of the mandible 19 Coronoid Process 22 Mental Foramen 23 Mental protuberance 24 Condylar Process |
|
|
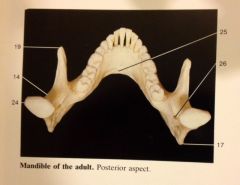
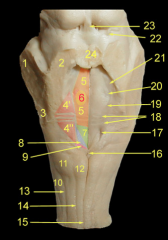
What is:
14, 19, 17, 24, 26 |
14 Mandibular notch
19 Coronoid Process 17 Angle of the mandible 24 Condylar Process 26 Mandubular Foramen |
|

