![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
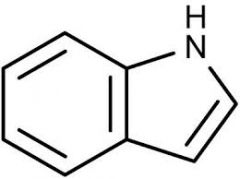
|
indole ring
|
|
|
Antacids
|
1. metal oxides/ hydroxides, carbonates, hydrogencarbonates
2. alginates 3. antifoaming agents (dimethicone) |
|
|
Analgesics
|
止痛藥
1. salicylic acid 2. morphine 3. codeine 4. heroin |
|
|
Salicylic acid
|
Mild analgesics
Aspirin/ paracetamol |
|
|
Depressants
|
鎮靜劑
1. ethanol 2. diazepam (Valium) 3. Nitrazepam (mogadon) 4. Fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac) |
|
|
Stimulants
|
Amphetamines
Epinephrine (adrenaline) Nicotine Caffeine |
|
|
Antibacterials
|
Penicillin
|
|
|
Mind-altering drugs
|
LSD
mescaline THC Cannabis |
|
|
Therapeutic window
|
range of a drug's conc in the blood between its therapeutic level and its toxic level
LD50/ED50 (lethal/ effective) Large: safe Small: easy to overdose |
|
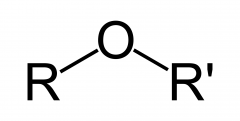
|
Ether
|
|
|
Narcotic
|
麻醉
|
|
|
Analgesic
Antipyretic reduce inflammation |
止痛
退燒 發炎 |
|
|
Reye's syndrome in children
|
Aspirin risk
|
|
|
Techniques for detection of ethanol in the breath, blood and urine
|
Breathalyser
absorption of infrared radiation/ fuel cell in intoximeter gas-liquid chromatography |
|
|
synergistic effect
|
actions of other drugs are enhanced by the presence of alcohol
|
|
|
Palpitations
Tremors |
心慌
震 |
|
|
Heterocyclic ring
|
a ring of atoms of more than one kind; especially a ring of carbon atoms containing at least one atom that is not carbon
|
|
|
Effects of medicines and drugs
|
alters physiological states
alters mood/ emotions alters incoming sensory sensations |
|
|
Analogues
lead compounds |
Research of new pharmaceutical products
|
|
|
Methods of administrating drugs
|
oral
rectal inhalation injections (intervenous, intermuscular, subcutaneous) |
|
|
Mild analgesics preventing pain
|
by intercepting the pain stimulus at the source, often by interfering with the production of substances that cause pain
non-narcotic |
|
|
Strong analgesics preventing pain
|
temporally bind to the receptors in the brain, preventing the transmission of pain impulses without depressing the CNS
narcotic |
|
|
Aspirin
|
GOOD: prevent heart attacks/ strokes, reduce inflammation
BAD: stomach ulcers/ bleeding, Reye |
|
|
Paracetamol
|
GOOD: very safe in correct dosage
BAD: does not reduce inflammation, blood disorder, kidney damage |
|
|
Antiseptic
|
Ethanol
preventing the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. |
|
|
Amphetamines and adrenaline
|
phenyl ethyl amine structure
|
|
|
Antiviral drugs works
|
1. alter the cell's DNA so that the virus cannot use it to multiply
2. blocking enzyme activity within the host cells 3. change cell membrane that prevent the entry of the virus into the cells |
|
|
Cisplatin
|
anticancer drug
bind to the nucleic base guanine prevent replication of damaged DNA of a cancer cell trans is useless (not correct orientation to bind) |
|
|
increased potency of diamorphine than morphine
|
Morphine: polar hydroxyl group
Diamorphine: non-polar ester groups, facilitate transport into the non-polar environment of the CNS> opoid receptors, preventing the brain from receiving pain signals |

