![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
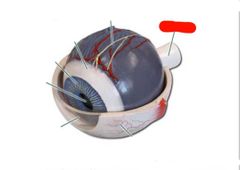
|
Optic nerve |
|
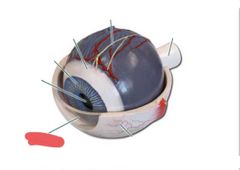
|
Cornea |
|
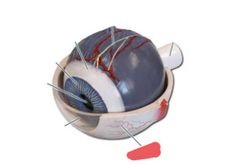
|
Sclera |
|

|
Iris |
|

|
Pupil |
|
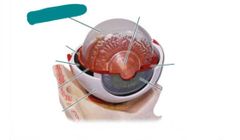
|
Vitreous humor |
|
|
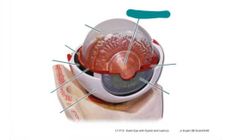
Lens |
|
|
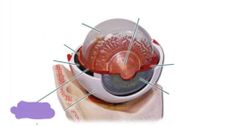
Ciliary body |
|
|
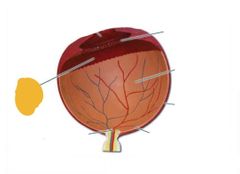
Ciliary body |
|
|
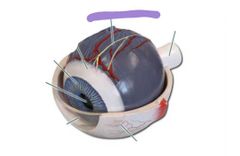
Choroid |
|
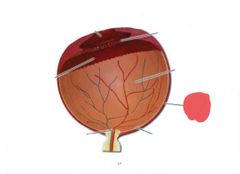
|
Choroid |
|
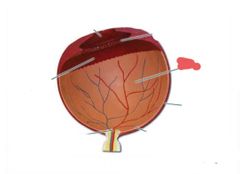
|
Retina |
|

|
Auricle of external ear |
|

What is this tube? |
External auditory meatus |
|

What is at the end of the external auditory meatus that separates the external and middle ear |
The tympanic membrane |
|

|
Tympanic cavity |
|
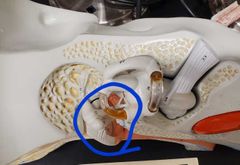
What are we? |
Auditory ossicles |
|

Name the ossicles |
Blue: malleus Purple: incus Pink: stapes |
|

What tube am I |
Auditory tube |
|
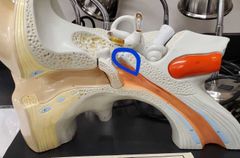
|
Tensor tympani |
|
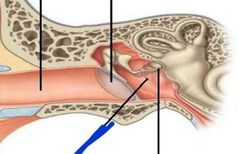
|
Stapedius |
|
|
Muscles of the inner ear |
Tensor tympani Stapedius |
|
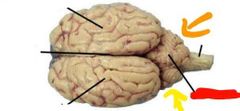
|
Red: vermis Orange: left hemisphere of the cerebellum Yellow: right hemisphere of the cerebellum |
|
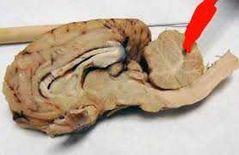
|
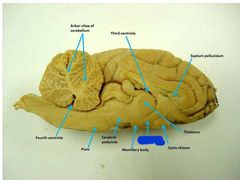
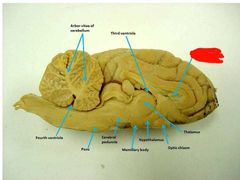
Arbor vitae of the cerebellum |
|
|
What is the cerebellar cortex? |
Outer layer of the cerebellum |
|

|
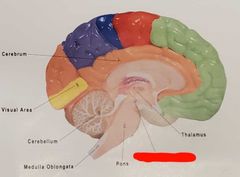
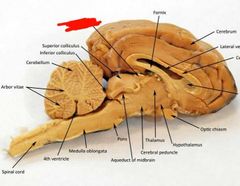
Medulla oblongata |
|
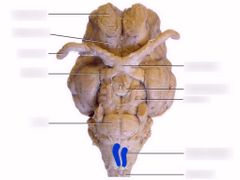
What are these called? |
Pyramids of the medulla oblongata |
|

|
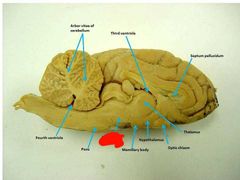
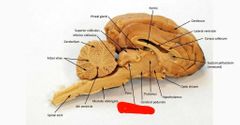
Pons |
|
|
Cerebral peduncles |
|
|
Cerebral peduncles |
|

|
Cerebral aqueduct |
|
|
Cerebral aqueduct |
|
|
Tegmentum |
|
|
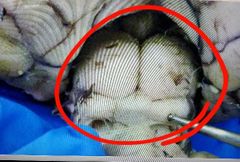
Corpora quadrigemina |
|

|
Superior colliculi |
|

|
Inferior colliculi |
|
|
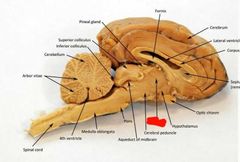
Thalamus |
|
|
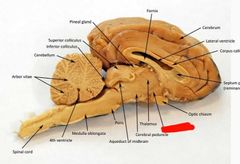
Hypothalamus |
|
|
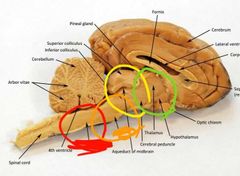
Red: medulla oblongata Orange: pons Yellow: midbrain Green: diencephalon |
|
|
Pineal gland |
|

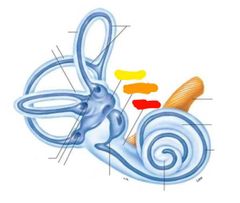
Outer layer of cochlea and semicircular canals |
Bony labyrinth |
|

Blue layer? |
Membranous labyrinth |
|

|
Semicircular canals |
|

|
Semicircular ducts |
|

|
Cochlea |
|

|
Vestibule |
|
|
Red: vestibule Orange: saccule Yellow: utricle |
|
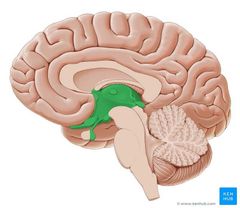
|
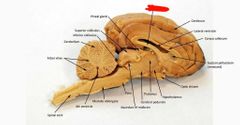
Diencephalon |
|
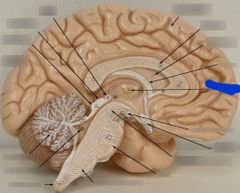
|
Intermediate mass |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
|
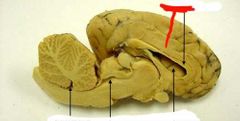
|
Pituitary gland |
|
|
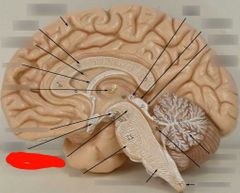
Cingulate gyrus |
|
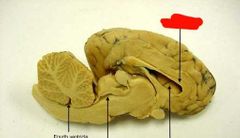
|
Corpus callosum |
|
|
Septum pellucidum |
|
|
Fornix |
|
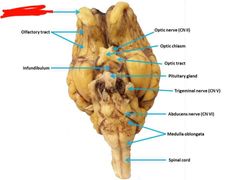
|
Olfactory tract |
|
|
Olfactory bulb |
|
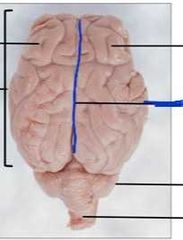
|
Longitudinal fissure |
|
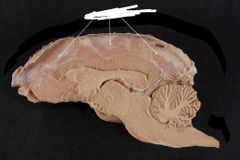
|
Falx cerebri Mater between hemispheres of brain |
|
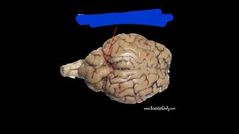
|
Transverse fissure |
|
|
Layer of mater in the transverse fissure that separates the cerebellum and cerebrum |
Tentorium cerebri |
|
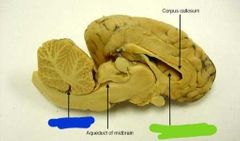
|
Blue: 4th ventricle Green: lateral ventricle |
|

|
4th ventricle |
|

|
Lateral ventricle |
|
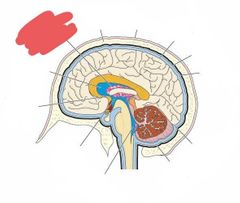
|
Choroid plexus |
|
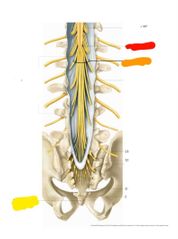
|
Red: conus medullaris Orange: cauda equina Yellow: filum terminale |
|
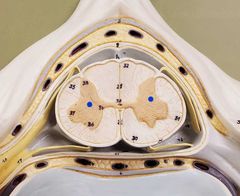
|
Gray matter |
|
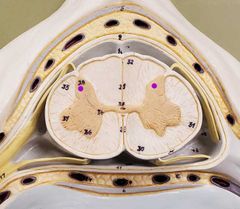
|
Posterior horns |
|
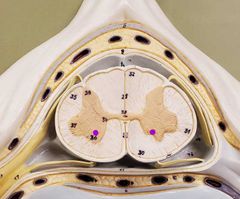
|
Anterior horns |
|
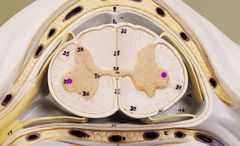
|
Lateral horns |
|
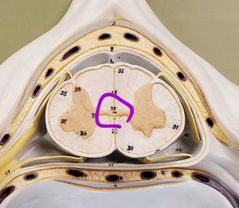
The hole |
Central canal |
|
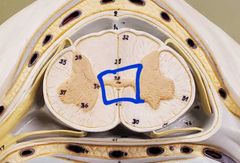
The tissue around the hole |
Gray commissure |
|
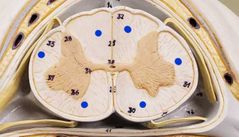
|
White matter |
|
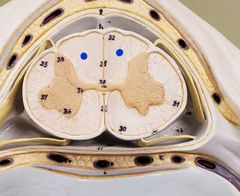
|
Posterior column |
|
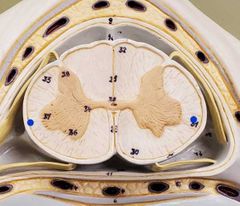
|
Lateral columns |
|

|
Anterior columns |
|
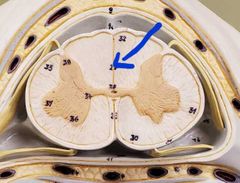
Whats this line |
Posterior median sulcus |
|
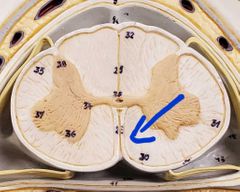
What is this line |
Anterior median fissure |
|

|
Subarachnoid space |
|
|
What flows through the subarachnoid space? |
Cerebrospinal fluid |
|

|
Epidural space |
|

|
Dura mater |
|

|
Arachnoid mater |
|

|
Pia mater |
|
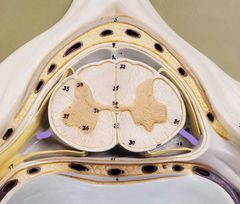
|
Denticulate ligaments |
|
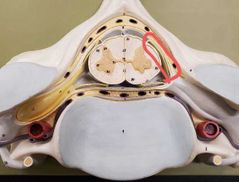
|
Dorsal root |
|
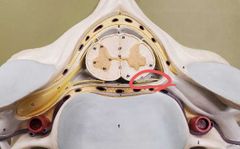
|
Ventral root |
|
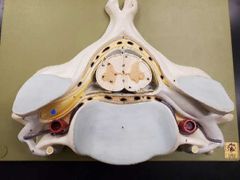
|
Dorsal root ganglion |
|
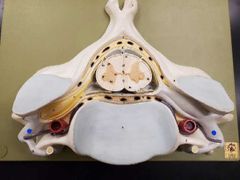
|
Ventral ramus |
|
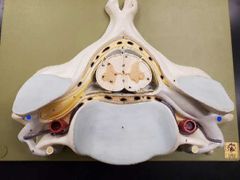
|
Dorsal ramus |
|
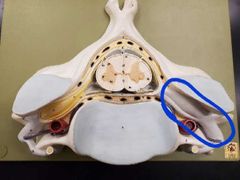
This whole thing is a... |
Spinal nerve |
|
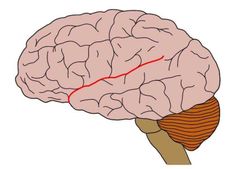
|
Lateral sulcus |
|
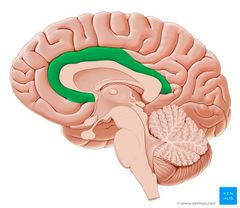
|
Cingulate gyrus |
|

|
3rd ventricle |
|
|
Monosynaptic reflex |
-sensory receptor sends sensory info up sensory neuron -neuron goes through dorsal root ganglion -to dorsal root -to anterior horn -synapses with motor neuron in anterior horn -motor response goes down motor neuron through ventral root |
|
|
How many muscles respond to monosynaptic reflexes? |
1 |
|
|
Polysynaptic reflex |
-sensory receptor sends info up sensory neuron -through dorsal root ganglion -to dorsal root -to posterior gray horn -then synapses with interneuron -interneuron goes to anterior gray horn and synapses with motor neuron which then travels down ventral root to multiple muscles to respond |
|
|
How many muscles do polysynaptic reflexes deal with |
2 |
|
|
Whats the main difference between monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes |
Polysynaptic reflexes have an interneuron that sends info from sensory neuron to motor neuron and monosynaptic does not |
|
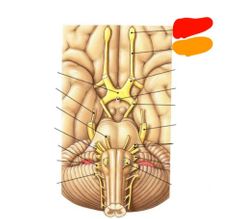
|
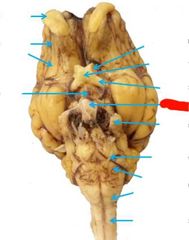
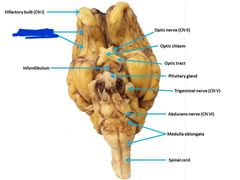
Olfactory bulb Olfactory tract (CN I) Smell |
|
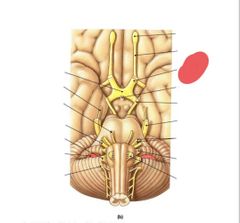
|
Optic nerve (II) Vision |
|
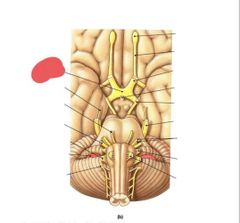
|
Optic chiasm |
|
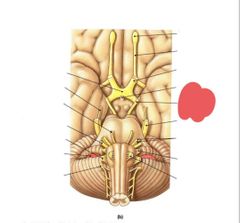
|
Oculomotor nerve (III) eye movement and pupil contriction |
|
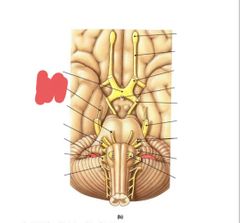
|
Trochlear nerve (IV) eye movement |
|
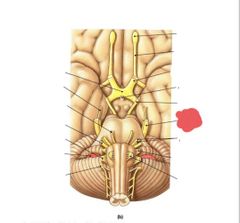
|
Trigeminal nerve (V) Chewing and somatosensory from face and head |
|
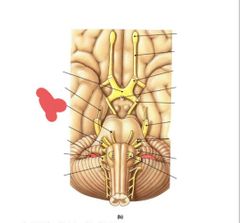
|
Abducens (VI) Eye movement |
|
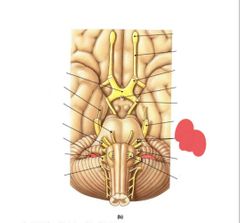
|
Facial nerve (VII) taste, somatosensory info from ear, and faciel expressions |
|
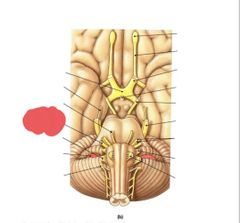
|
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) hearing and balance |
|
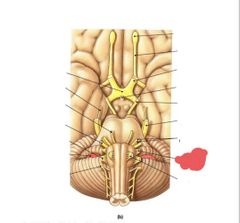
|
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) taste, somatosensory info from tongue and pharynx, swallowing |
|
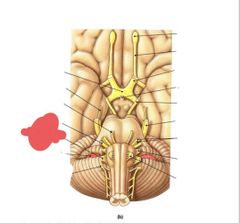
|
Vagus nerve (X) Regulates internal organ function |
|
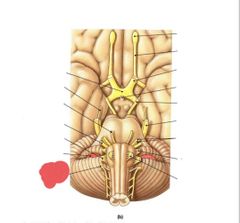
|
Accessory nerve (XI) Muscles for Head movement |
|
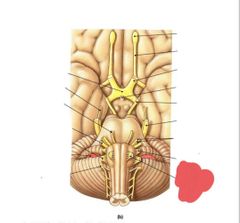
|
Hypoglossal nerve (XII) tongue muscles |

