![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where to dispose glass test tubes? |
In the disinfectant basin |
|
|
Where to dispose of used glass slides? |
Disposed in disinfectant basin |
|
|
Where to dispose of broken glass? |
- notify your instructor - don’t attempt to pick up broken glass due to cuts happening - place in a broken glass bin by door of class room |
|
|
Dispose of used gloves? |
Remove gloves inside out and place in autoclave bags at end of tables. |
|
|
Dispose of paper towels used in bench disinfection? |
Dispose in regular trash bin |
|
|
Where to dispose of uncontaminated trash. |
In trash cans on floor at end of table. |
|
|
Where to dispose of contaminated Petri plates? |
In autoclave bags at end of each table. |
|
|
Where to dispose of cotton swabs used to clean microscopes? |
In autoclave bags at end of table. |
|

What is this and it’s function? |
Ocular Allows to view |
|
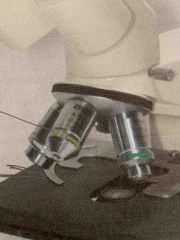
What is this and it’s function? |
Objective Magnifies what’s on the slide |
|

What is this and it’s function? |
Condenser Concentrate the light beam onto the specimen |
|

What is this and it’s function? |
Course focus knob Allows for a clear view |
|

#5 What is this and it’s function? |
Iris diaphragm Adjust the light of the condenser |
|

#6 What is this and it’s function? |
Mechanical stage Holds the slide |
|

#7 What is this and it’s function? |
Mechanical stage (x-y - stage) knobs Will adjust the stage |
|

#8 What is this and it’s function? |
Condenser height adjustment knob Adjust brightness of light |
|
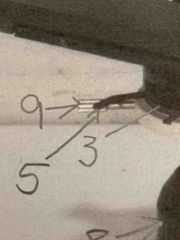
#9 |
Condenser centering screws |
|

#11 |
Rheostat |
|

#12 |
Base diaphragm |
|

What is this and it’s function? |
Fine focus knob Allows for clear viewing |
|

#14 What is this and it’s function? |
Stage clip Hold slide still for viewing |
|
|
Name two things a microscopic does? |
1- magnifies 2- |
|
|
How do you calculate the total magnification? |
Magnification= ocular * objective |
|
|
Name the two terms that influence resolution |
1- magnification 2- resolving power |
|
|
Explain how to clean a microscope? |
Clean ocular with q-tip and alcohol Make sure stage is clean and no slide is left on it Roll up cord to plug in microscope make sure stage is lowered Have the 4X in first position |
|
|
Explain how to use a microscope correctly? |
After setting up microscope place slide on stage with stage clip securing it. Start at 4X objective. Use course focus knob and fine focus knob to view. Then you can go higher on the objective. |
|
|
Explain the purpose of immersion oil pan using 100X objective. |
Used to increase resolution Power of a microscope. |
|
|
What are the proper steps for handwashing? |
1- wet hands with soap and water and lather 2- wash entire hands front, back and underneath fingernails 3- using a rotational movement wash both wrist 4- make sure handwashing is 20 seconds 5- Rinse hands 6- thoroughly dry your hands were disposable paper towel 7- turn off the Fossett using the paper towel |
|
|
What percentage of infections is transmitted by dirty hands? |
80% of infections are transmitted by hands |
|
|
When is it necessary to wash hands with soap and water instead of using a hand sanitizer? |
When hands are visibly soiled |
|
|
What type of hand hygiene is more affective method of removing or in activating microbes? |
Soap and water |
|
|
Define ubiquitous |
Present, appearing, or found everywhere |
|
|
Define pure culture |
A culture that contains a Single species of microbe |
|
|
Define colony |
When each cell reproduces many times and gives rise |
|
|
Define turbidity |
Cloudiness which indicates growth |
|
|
Define media |
Nutrient material stable for cultivation of microorganisms |
|
|
Define inoculum |
Sampling a pure culture to a new sterile media |
|
|
Define aseptic technique |
Using practice and procedures to prevent contamination |
|
|
Explain the portance of allowing the loop to cool before obtaining your bacterial sample? |
So you don’t kill the bacteria you’re trying to obtain |
|
|
Explain the importance of holding the test tube With your little finger while taking your bacterial sample? |
To help prevent spills and it’s easier to obtain your bacterial sample |
|
|
Explain the importance of obtaining a pinpoint amount of sample as you’re inoculum? |
If you use too large of a sample you will not have a significant area on the plate to achieve the dilution needed for separation of one cell from another |
|
|
After dipping your loop in the bacteria place on Algar plate |
obtain sample on sterile Q-tip from broth. Lift the lid on the petri plate and swab largest section of the agar. Dispose of swap and autoclave bag. Use loop to complete rest of the procedure. Sterilize your loop. Place the loop in center of first section and gently drag the loop one time into the second section. Lately drag the tip of the loop from side to side and a back-and-forth motion to fill the second section. In between sections sterilize loop. Place loop in center of the second section and gently drag loop one time into third section lightly drag the tip of the loop from side to side in a back-and-forth motion to spread the bacteria to fill the third section. Place the plate lid and sterilize the loop. Stack Algar plates upside down in the class tray to be incubated. |
|
|
Explain why the agar plates are labeled on the bottom and inverted when incubated |
If labeled on top of lid we will not know sections and zones of where we started the bacteria. They are inverted due to it being easier to pick up plates instead of lid being on top because it will spill |
|
|
State the criteria used to describe the physical characteristics of a bacterial colonies |
Form, evaluation, margin, size, or color |
|
|
List in order the reagents used in the traditional Gram stain procedure |
Crystal violet, grams Iodine, acetone, safranin |
|
|
State the function of each reagent used in the Gram stain procedure |
Crystal violet- primary stain Grams iodine- mordant that combines with crystal violet in the cell Acetone- The decolorizer Safranin - counter stain for secondary stain
|
|
|
Explain the mechanism of the Gram stain (why Graham negative cells lose the primary died during decolorization) |
Will dissolve the lipids in the outer membrane of gram-negative cell walls |
|
|
Explain the difference between simple stain and differential stain |
Simple stain is when only one dye is used Differential stain is when 2 dyes are used |
|
|
Name one of the genera that are identified using the acid-fast stain |
Mycobacterium |
|
|
List the diseases caused by acid fast bacteria |
Novartis Asteroids- pulmonary disease Cryptosporidium- diarrheal disease Mycobacterium- Hansen’s disease Mycobacterium- TB |
|
|
During acid fast staining how is the primary stain forced into acid-fast bacteria |
Carbon fuchsin is lipid soluble and contains phenol which helps the stain penetrate the cell wall |
|
|
Explain why certain organisms are acid fast |
Like mycobacterium contain large amounts of lipid substance within their cell walls called mycolic acids. These acids resist standing by ordinary methods such as Gram stain |
|
|
What decolorizer is used in acid-fast stain and the Gram stain |
Gram stain uses acetone alcohol (3-5 seconds) Acid fast uses acid-alcohol decolorizer (15-30 seconds) |
|
|
State in order to three reagents used in the acid fast stain |
Carbolfuchsin dye Acid-alcohol decolorizer Methylene blue counterstain |
|
|
Name to medically important genre of bacteria that produce endospores |
Bacillus anthracis- anthrax Clostridium botulinum- botulism Clostridium perfringens- gas gangrene Clostridium tatami- tetanus Clostridium difficult- toxic enterocolitis and pseudomembranous colitis |
|
|
Name two medically important genre of bacteria that produce endospores |
Bacillus anthracis- anthrax Clostridium botulinum- botulism Clostridium perfringens- gas gangrene Clostridium tatami- tetanus Clostridium difficult- toxic enterocolitis and pseudomembranous colitis |
|
|
Describe the process used to stain the relatively impermeable endospore |
Prepare slide and allow slide to air dry then place the slide on a warmer. while slide is on warmer put a small piece of film paper on top of the slide and add malachite green to paper. Keep adding dye as it starts to dry out after five minutes on warmer transfer slide to stain rack for another five minutes remove filter paper from the side rinse the slide with Deionized water shake off excess water add Gram safranin to the slide for two minutes rinse the smear with the ionized water and blot dry with bibulous paper or paper towel observe then observe results with oil immersion lens of microscope |
|
|
What color is negative stain in a positive stain |
Positive stain is purple Negative stain is pink |
|
|
Explain why it is necessary to use a negative stain instead of a positive stain to visualize a capsule |
The negative stain will stain everything except what you want to see. Thus the organism will stand out as a transparent or refractive structure against a contrastingly dark background |
|
|
Identify a bacterial capsule in a negative stain |
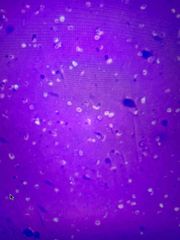
The clear dots that has a spot in it |
|
|
Identify a bacterial capsule in a negative stain |
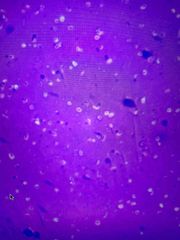
The clear dots that has a spot in it |
|
|
Describe the three genes located in the pGLO plasmid |
BLA gene GFP Ara-C |
|
|
Describe the three proteins encoded by the gene found in the pGLO plasmid |
Beta- lactamase Repressor Fluorescent protein |
|
|
Define competent |
Are E. coli cells that have been specially treated to transform efficiently |
|
|
Describe two methods used to make the E. coli component |
Heat shock Electroporation |
|
|
Explain the regulation mechanism of the green fluorescent protein gene expression |
The repressor protein and will not be transcribed without the addition of the sugar Arabinose to the cells nutrient medium |
|
|
Describe the different plates used and The expected results (growth & color) for each |
1 Lucia agar plate with ampicillin and arabinose - prediction of glow is yes 2 luria agar plates with ampicillin- prediction ofof glow is no 1 plain luria agar plate- Prediction of glow is no |
|
|
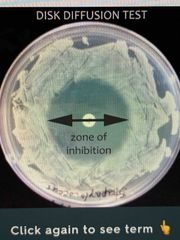
Compare the Kirby-Bauer test with the minimal inhibitory concentration test |
Kirby-Bauer- Characteristics as the stability of the antibiotic, the rate of diffusion of the antibiotic, the bacteria being tested the pH of the culture medium, the depth of the culture medium, the inoculum density, The incubation time, the incubation temperature, and the concentration of the anabiotic can affect the results The minimal inhibitory concentration test- this method determines the lowest concentration of an antibiotic that can inhibit the growth of a test organism |
|
|
State the principle of the beta lactamase test and interpret test results |
To rapidly test isolated colonies for the prediction of beta lactamase; a positive beta-lactamase test will show yellow around the disc, A negative beta -lactamase test will show an orange/pink result |
|
|
State the media used for the antibiotic sensitivity test |
Mueller Hinton agar |
|
|
Given an antibiotic sensitivity chart and Kirby-Bauer test measure the zone size of inhibition in millimeters and interpret the results |
Back (Definition) |

