![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
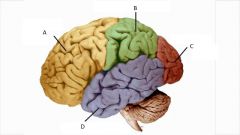
Identify the Lobes of the Cerebral cortex |
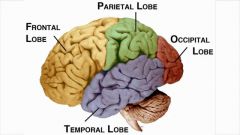
A - Frontal B - Parietal C - Occipital D - Temporal |
|
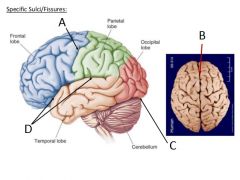
Identify the fissures and sulci of the cerebral cortex |
A - Central Sulcus B - Longitudinal Fissure C - Transverse Fissure D - Lateral Sulcus |
|
|
Diagram showing grey matter and white matter |
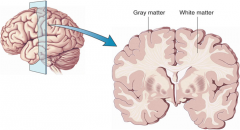
|
|
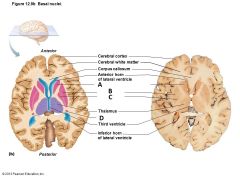
Identify the structures of the basal nuclei |
A) Head of Caudate Nucleus B) Putamen C) Globus Pallidus D) Tail of Caudate Nucleus |
|
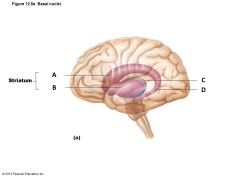
Identify the structures of the basal nuclei |
A) Caudate Nucleus B) Putamen C) Thalamus D) Tail of Caudate Nucleus |
|
|
Diagram showing the corpus callosum |
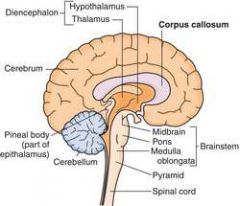
Corpus callosum - white matter that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres |
|
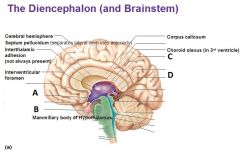
Identify the indicated structures of the diencephalon What is the structure that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus? |
A - Hypothalamus B - Pituitary gland C - Thalamus D - Pineal gland of Epithalamus - The Infundibulum |
|
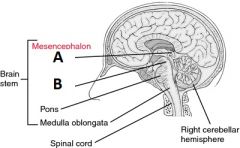
Identify the structures of the mesencephalon |
A - Corpora quadrigemina B - Cerebral Peduncle Note: the substantia nigra is also part of mesencephalon, but cannot be seen on a whole or sagittal section of the brain |
|
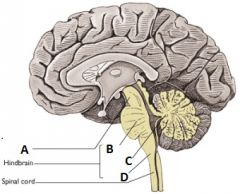
Identify the structures of the Rhombencephalon |
A - Midbrain (not technically part of rhombencephalon B - Pons C - Cerebellum D - Medulla |
|
|
Ventral view of the brain with the Medulla, Pons, and Cerebellum |
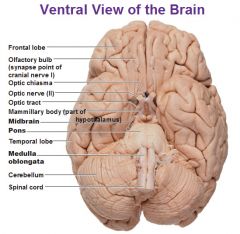
|
|
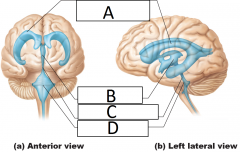
Identify the indicated structures |
A - Lateral ventricles B - Third ventricle C - Cerebral aqueduct D - Fourth ventricle |
|
|
Diagram showing the meninges |
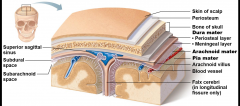
Note that the pia mater clings tightly to the surface of the brain Note that the subarachnoid space contains the CSF |
|
|
How many cranial nerves are there? What are the first 6? |
12 cranial nerves CN I) Olfactory CN II) Optic CN III) Oculomotor CN IV) Trochlear CN V) Trigeminal CN VI) Abducens |
|
|
What are the cranial nerves 7-12? |
CN VII) Facial CN VIII) Vestibulocochlear CN IX) Glossopharyngeal CN X) Vagus CN XI) Accessory CN XII) Hypoglossal |
|
|
Diagram of the cranial nerves |
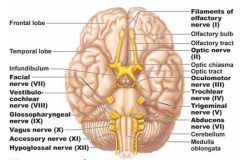
|
|
|
Diagram showing the flow of blood from the heart though the aortic arch |

|
|
|
flowchart showing blood flow from the heart |
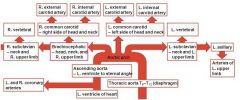
|
|
|
Diagram showing arteries of the head |
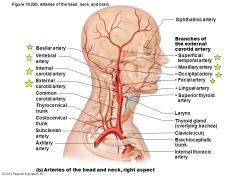
|
|
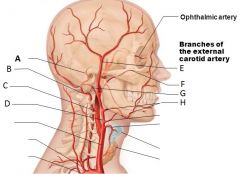
Identify the indicated arteries |
a) Basilar artery b) Vertebral artery c) Internal carotid artery d) External carotid artery e) Superficial temporal artery f) Maxillary artery g) Occipital artery h) Facial artery |
|
|
What areas of the head get their blood supply from the external carotid artery? |
It supplies most areas of the head except the brain and orbit supplies: - thyroid gland - larynx - tongue - skin and muscles - posterior scalp - upper and lower jaws |
|
|
What areas of the head get their blood supply from the vertebral arteries? |
supply: - cervical spinal cord - vertebrae - deep structures of neck the left & right vertebral arteries join together to form the basilar artery (supplies brainstem, cerebellum, posterior part of brain) |
|
|
What is the Circle of Willis? Why is it important? |
Cerebral arterial circle - a circulatory anastomosis (joins the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries, the internal carotids, and basilar artery) - avoids ischemia by allowing blood flow if one path is blocked - supplies the brain and surrounding structures |
|
|
What areas of the head get their blood supply from the internal carotid arteries? |
- the orbits - over 80% of the cerebrum |
|
|
flowchart of veins to the heart |
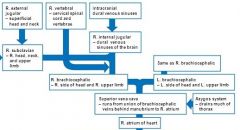
|
|
|
Major veins of the head |
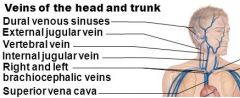
|
|
|
Major veins of the head, right superficial aspect |
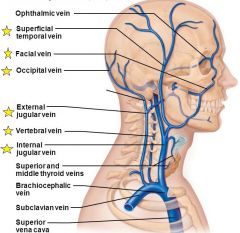
|
|
|
Which parts of the head are drained by the external jugular vein? |
- superficial scalp and face structures, which are served by the external carotid arteries |
|
|
Diagram showing the venous sinuses of the head |
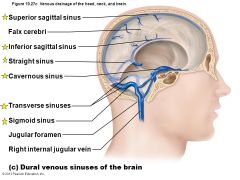
|
|
|
What is a venous sinus? |
Dural venous sinuses - venous channels found between layers of dura mater in the brain |
|
|
What vein do the venous sinuses drain into as blood returns to the heart? |
The internal jugular veins - these veins then join with the subclavian veins on each side to form brachiocephalic veins, which then unite to form the superior vena cava |

