![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the pelvic cavity contain?
|
The rectum and urethra in males and females.
In the female, the vagina and the vestibule are in the pelvic cavity and the in male, it's the prostate. |
|
|
What fascia is the pelvic cavity lined by?
|
Transversalis fascia and peritoneum.
|
|
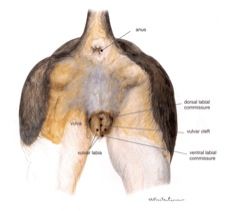
Sex this animal!
|
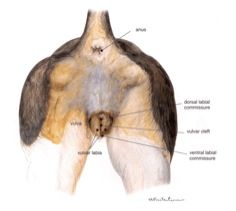
Female dog.
|
|
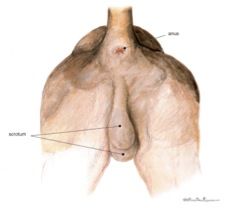
Sex this animal!
|
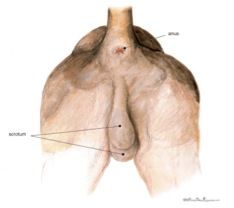
Male dog
|
|
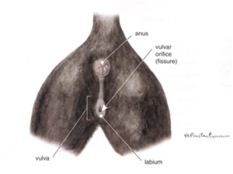
Sex this animal!
|
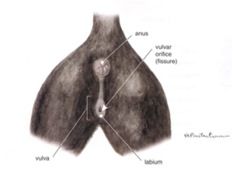
Female cat
|
|
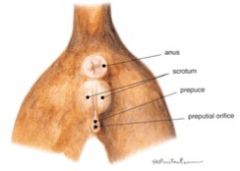
Sex this animal!
|
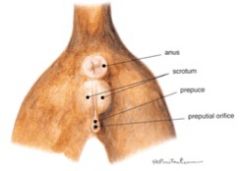
Male cat
|
|
Sex these kittens!
|
It's a female on the left and a male on the right.
|
|
|
Why are the ischiorectal fossa important clinically?
|
They are filled with fat in obese animals.
|
|
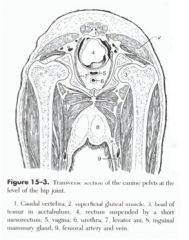
What is the function of the pelvic diaphragm?
And while we're down there, what's 4, 5, 6, and 7? |
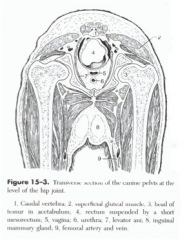
The function is to retain pelvic viscera in place, depress the tail, and aid in expelling pelvic contents (feces and fetuses).
4 is the rectum 5 the vagina 6 the urethra 7 the levator ani |
|
|
What fibers do hypogastric nerves contain?
What do they innervate? |
They contain sympathetic fibers from the caudal mesenteric ganglion and innervate the pelvic viscera.
|
|
|
Is the pelvic nerve sympathetic or parasympathetic? Where does it originate from? What does it innervate?
|
It carries parasympathetic axons from the ventral branches of S1, S2, and S3.
It innervates the descending colon, rectum, and urogenital organs. |
|
|
What does the pelvic plexus contain sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers from?
|
It contains sympathetic fibers from the hypogastric nerve and parasympathetic fibers from the pelvic nerve and visceral afferent fibers.
|
|
|
Where does the pudendal n. originate from? What is is sensory to?
What branches should we be able to locate grossly? |
It originates from the ventral branches of S1, S2, and S2 and is sensory to the rectum, the internal and external reproductive organs, and perineal skin.
It's motor to the perineal mm. And branches to the superficial perineal branch, deep perineal n., caudal rectal nerves, and continues as the dorsal nerve of the penis/clitoris. |
|
|
Where do the external and internal iliac arteries and the median sacral artery supply blood to?
|
The external iliac artery supplies the pelvic limb.
The internal iliac artery supplies the pelvic cavity and pelvic limbs. The median sacral artery supplies blood to the sacrum and then becomes the median caudal artery which supplies the caudal (coccygeal) vertebrae. |
|
|
What does the caudal gluteal artery supply blood to?
|
To muscles outside of the pelvis and in the caudal thigh region.
|
|
|
What does the internal pudendal artery supply blood to?
|
It supplies blood to the pelvic viscera.
|
|
|
What is the main arterial supply to the pelvic viscera in the male and female dog?
|
The prostatic artery in the male and vaginal artery in the female.
The vaginal artery supplies the vagina, uterus (horns, body, cervix), urinary bladder, urethra, ureter, and rectum. The prostatic artery supplies the prostate, ductus deferens, epididymis, urinary bladder, pelvic urethra, ureter and rectum. |
|
|
What innervates the bladder sympathetically, parasympathetically and sensory? Why is this a good test question?
|
The bladder is innervated sympathetically by the hypogastric n., parasympathetically by the pelvic n., and sensory from the pudendal n.
This is a good test question (per Dr. Clark) because the innervations involve knowing three diffferent types of nerve. |
|
|
Is the bulbourethral gland present in cats or dogs?
|
Cats
|
|
|
What are the four functions of accessory genital glands?
|
1. adds volume to the ejaculate to provide a vehicle for sperm.
2. provides a source of energy for sperm. 3. acts as a buffer by neutralizing the ph in urine and the co2 produced by sperm. 4. production of prostaglandins that cause smooth muscle contraction in the female reproductive tract. |
|
|
What are all the possible accessory sex glands?
Which belong to the male dog and the male cat? |
The prostate, ampullary glands, bulbourethral glands, and vesicular glands.
The male dog has the prostate and ampullary glands and the male cat has the prostate and bulbourethral glands. |
|
|
Where are the ampullary glands of the male dog located?
|
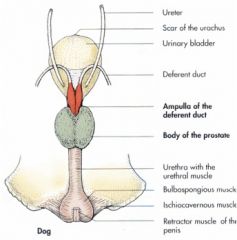
They are located in the wall of the terminal portion of the ductus deferens. (in orange)
|
|
|
Does the dog or cat have a short or long pre-prostatic urethra?
|
The dog has a short pre-prostatic and the cat a long one.
|
|
|
Where in the cat is the bulbourethral gland located?
|
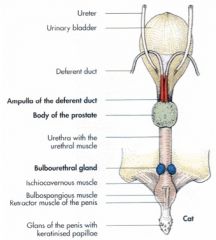
Located dorsally near the ischial arch, just cranial to the attachment of the penis to the ischium. It's in blue.
|
|
|
Where does the rectum begin? The anal canal?
|
The rectum is the continuation of ttehe descending colon within the pelvic cavity. It begins at the Ca2-Ca3 vertebrae.
The anal canal is ventral to Ca4 vertebra. |
|
|
What are the three anal canals?
|
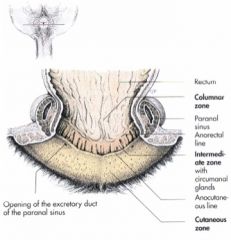
The columnar, intermediate, and cutaneous zone.
The columnar zone is the rectal mucosa in the longitudinal folds. The intermediate zone is the anocutaneous line. The cutaneous zone is the location of the openings of the paranal sinuses (anal sacs). |
|
|
Which of the anal sphincters is striated muscle and which is smooth?
|
The external sphincter is striated and the internal sphincter is smooth muscle.
The external sphincter is located superficial to the anal sacs and is innervated by the caudal rectal nerve. The internal sphincter is located deep to the anal sacs. |
|
|
Is the rectococcygeus muscle striated muscle or smooth muscle?
|
Smooth.
It aids in smooooooth defecation. |
|
|
What are the abdominal lymph nodes?
|
The lumbar lymph center, celiac lymphocenter, cranial mesenteric lymphocenter, and caudal mesenteric lymphocenter.
|
|
|
What lymph nodes are a part of the lumber lymph center?
|
The lumbar aortic lnn. and renal lnn.
|
|
|
What lymph nodes are a part of the celiac lymphocenter?
|
The splenci, gastric, hepatic, and pancreaticoduodenal lnn.
|
|
|
What lymph nodes are a part of the cranial mesenteric lymphocenter?
|
The cranial mesenteric, jejunal, cecal, and colic lnn.
|
|
|
What lymph nodes are a part of the caudal mesenteric lymphocenter?
|
The caudal mesenteric lnn.
|
|
|
What do the lumbar aortic lnn. drain generally?
|
the aorta, mediastinum, pleura, and diaphragm
|
|
|
What do the renal lnn. drain? Where do they drain to?
|
They receive afferent lymph from the kidneys and drain into the lumbar aortic nodes or lumbar lymphatic vessels.
|
|
|
What do the hepatic lymph nodes drain?
|
The stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and liver.
|
|
|
What do the splenic lymph nodes drain?
|
They drain the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, omentum and diaphragm.
|
|
|
What do the pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes drain?
|
They drain the duodenum, pancreas, and omentum.
|
|
|
What do the jejunal lymph nodes drain? What are they known for? Where are they located?
|
They drain the jejunum, ileum, and pancreas. They are the largest lymph nodes. They are located along the cranial mesenteric artery.
|
|
|
The colic lymph nodes drain what?
Where do they drain to? |
They drain the ileum, cecum and colon.
They drain to the medial iliac or lumbar lymph nodes. |
|
|
Where do the caudal mesenteric lymph nodes drain from and into?
|
They drain from the colon and drain to the medial iliac lnn or the cisterna chyli.
|
|
|
Where is the medial iliac lnn. located?
|
It is located between the deep circumflex iliac and the external iliac.
|
|
|
Where is the internal iliac or hypogastric lnn. located?
|
They are located between the internal iliac and median sacral arteries.
|
|
|
Where is the sacral lymph node located?
In what percent of dogs are they located? |
They are located near the median sacral artery in ~50% of dogs.
|
|
|
Where does the medial iliac (or external iliac) lnn. drain from?
|
Bascially, the colon, rectum, anus, vagina, vulva, testis, epididymis, speramatic cord, vaginal process, cremaster muscle, prostatem, ureter, bladder.
Collects lymph from the superficial inguinal, left colic, sacral, and hypogastric lnn. |
|
|
Where do the internal iliac or hypogastric lnn. drain from?
|
They drain from the pelvic muscles, tail muscles, pelvis, femur, lumbar, colon, rectum, anus, uterus, vagina, vestibule, vulva, clitoris, testis, epididymis, prostate, penis, ureters, bladder, urethra
(just know generally) |
|
|
Where do the sacral lymph nodes drain from?
|
The pelvic limb mm., the muscles of the tail, pelvic bones, femur, sacrum, uterus, vagina, vestibule, vulva, clitoris, prostate, penis, urethra.
(just know generally) |

