![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lymph is most similar to: A. water B. saliva C. interstitial fluid D. blood plasma |
interstitial fluid (C) |
|
|
Once collected, lymph is returned to: A. arterial circulation B. venous circulation C. the kidneys for filtration D. the liver for detoxification |
venous circulation (B) |
|
|
Which of the following is a role of lymph nodes? A. They filter lymph B. They produce red blood cells C. They produce lymph D. They return lymph to circulation |
They filter lymph (A) |
|
|
Which lymphoid organ serves in immune surveillance and in filtering lymph? A. the spleen B. the thymus C. lymph nodes D. tonsils |
lymph nodes (C) |
|
|
Which lymphoid organ serves as the site where T lymphocytes become immunocompetent T cells? A. thymus gland B. tonsils C. thyroid gland D. spleen |
thymus gland (A) |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue)? A. lymph nodes B. appendix C. Peyer's patches D. tonsils |
lymph nodes (A) |
|
|
Lymphedema may be treated by all EXCEPT which of the following? A. manual compression of the affected area B. movements of the affected area C. treatments that promote growth of lymphatic vessels D. bed rest to allow enhanced blood flow and therefore healing the affected area |
bed rest to allow enhanced blood flow and therefore healing the affected area (D) |
|
|
After surgical removal of the spleen (i.e., a splenectomy), some other organs take over most of its functions. Which of the following spleen functions in the adult can not be performed by bone marrow? A. immune surveillance B. erythropoiesis C. removal of aged and damaged red blood cells from the blood D. storage of platelets |
removal of aged and damaged red blood cells from the blood (C) |
|
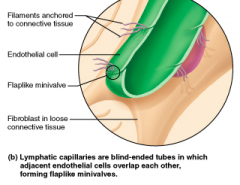
What is the main function of the lymphatic system? A. The lymphatic system makes blood cells through a process known as hematopoiesis B. The lymphatic system regulates blood pressure through the renin angiotensin aldosterone mechanisms C. Returns leaked fluid and plasma proteins that escape from the bloodstream to the blood D. Pumps and transports blood throughout the body |
Returns leaked fluid and plasma proteins that escape from the bloodstream to the blood (C) |
|
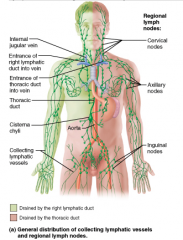
Lymph from what regions of the body is drained into the right lymphatic duct? A. right upper limb; right side of the head and thorax B. right upper limb, right side of the head and thorax, and the right lower limb C. digestive organs and lower limbs D. left upper limb, left side of the head and thorax, and both lower limbs |
right upper limb, right side of the head and thorax (A) |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of the lymphatic system? A lymph nodes B. blood vessels C. lymph D. lymphatic vessels |
blood vessels (B) |
|
|
Large clusters of lymph nodes occur in all of the following locations except the ________. A. lower extremities B. inguinal region C. axillary region D. cervical region |
lower extremities (A) |
|
|
Which of the following is not a normal component of lymph? A. water B. plasma proteins C. red blood cells D. ions |
red blood cells (C) |
|
|
What type of tissue is commonly found in all lymphoid organs and tissues (except the thymus)? A. elastic connective tissue B. reticular connective tissue C. areolar connective tissue D. elastic cartilage connective tissue |
reticular connective tissue (B) |
|
|
What is the role of the B lymphocytes (B cells) in lymphoid tissue? A. produce plasma cells that secrete antibodies B. phagocytize foreign substances C. capture antigens and bring them back to the lymph nodes D. manage the immune response |
produce plasma cells that secrete antibodies (A) |
|
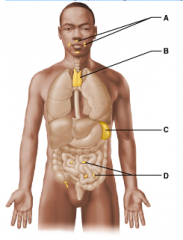
Which of these lymphoid organs is the thymus? Select from letters A-D. |
B |
|
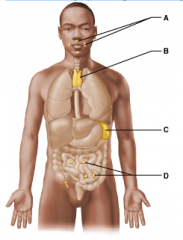
Which lymphoid organ is primarily active during the early years of life? Select from letters A-D. |
B |
|
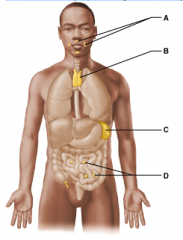
Which of these lymphoid organs is a part of collection of tissues called the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT) and removes pathogens entering the pharynx (throat)? Select from letters A-D. |
A |
|
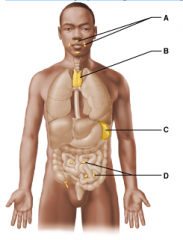
Which lymphoid organ extracts aged and defective blood cells and platelets from the blood in addition to storing some of the breakdown products for later reuse? Select from letters A-D. |
C |
|
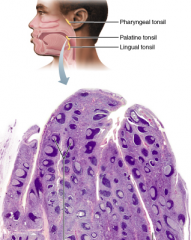
Which tonsil is located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx and is referred to as the adenoids if it is enlarged? A. palatine tonsils B. tubal tonsils C. pharyngeal tonsil D. lingual tonsil |
pharyngeal tonsil (C) |
|
|
Peyer's patches are located __________. A. in the wall of the small intestine B. in the liver C. in the wall of the colon D. in the spleen |
in the wall of the small intestine (A) |
|
|
Which of the following would not be classified as a lymphatic structure? A. pancreas B. spleen C. Peyer's patches of the intestine D. tonsils |
pancreas (A) |
|
|
Which cells become immunocompetent due to thymic hormones? A. monocytes B. lymphocytes C. basophils D. macrophages |
lymphocytes (B) |
|
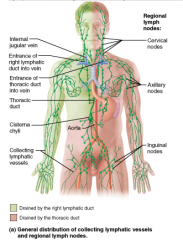
Lymph from the right leg ultimately is delivered to which duct in the thoracic region? A. subclavian trunk B. thoracic duct C. right lymphatic duct D. jugular trunk |
thoracic duct (B) |
|
|
Which of the following lacks lymph capillaries? A. small intestine B. bones and teeth C. skin D. loose connective tissue |
bones and teeth (B) |
|
|
The lymphatic capillaries function to absorb the excess protein-containing interstitial fluid and return it to the bloodstream (T/F) |
True |
|
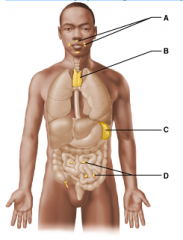
Which of these lymphoid organs destroys bacteria before it can breach the intestinal wall and generates "memory" lymphocytes for long-term memory? Select from letters A-D. |
D |
|
|
Which of the following lymphoid cells secrete antibodies? A. macrophages B. plasma cells C. dendritic cells D. T lymphocytes |
plasma cells (B) |
|
|
Which of the following are functions of lymphoid tissue? A. furnish an ideal surveillance vantage point for lymphocytes and macrophages B. house and provide a proliferation site for neutrophils C. house and provide a proliferation site for lymphocytes D. A and C |
A and C (D) |
|
|
Where is the spleen located? A. forming a ring of lymphoid around the entrance to the pharynx B. inferior neck and extending into the superior thorax, partially overlying the heart deep to the sternum C. left side of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm and curled around the anterior aspect of the stomach D. clusters of lymphoid follicles located in the wall of the distal portion of the small intestine |
left side of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm and curled around the anterior aspect of the stomach (C) |
|
|
Where are Peyer's patches located? A. proximal portion of the small intestine B. large intestine C. appendix D. distal portion of the small intestine |
distal portion of the small intestine (D) |

