![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Eukaryotes have three (major) different RNA polymerases that are recruited to three different types of promoters. Name 'em and describe what each polymerase recognizes.
|
Pol I : recognizes rRNA genes and synthesizes what is called pre-ribosomal RNA, or pre-rRNA.
Pol II : recognizes mRNA genes and special "snurp" RNA genes Pol III : recognizes small RNA genes like tRNA and 5S rRNA genes. |
|
|
What ingredients are needed for the RNA synthetic reaction to occur?
|
+1 start site
RNA polymerase a template strand NTPs (4) as substrates metals and other things like Mg2+ and Zn2+ for enzyme |
|
|
Describe how the first two NTPs join in RNA biosynthesis.
|
the alpha phosphate of the 2nd nucleotide does a nucleophilic attack on the 3' OH of the 1st nucleotide, releasing pyrophosphate and creating the first phosphodiesterase bond in the chain.
|
|
|
In transcription, a driving force is that _________ is an excellent leaving group due to the large negative delta G.
|
pyrophosphate (PPi)
|
|
|
How do primary transcripts of RNA become "mature RNAs"?
|
they undergo post-transcriptional processing (nucleolytic trimming and base modification)
|
|
|
In a eukaryote, what part of the cell are ribosomes made? With which Pol?
|
Ribosome parts are made in the nucleolus with pol I.
note: final maturation of ribosomes occurs outside the nucleus. |
|
|
What are the bacterial ribosome subunits and what rRNAs are they composed of?
|
Bacterial ribosome assembled is 70S. Its units are 50S and 30S. 50S is made of 5S, 23S and lotsa (36) proteins. 30S is made of 16S rRNA and lotsa (21) proteins.
|
|
|
What are the eukaryotic ribosome subunits and what rRNAs are they composed of?
|
The assembled eukaryotic ribosome is 80S. It's components are 60S and 40S. The 60S is made of 5S rRNA, 28S rRNA, 5.85S rRNA and lotsa (49) proteins. the 40S is made of 18S rRNA and 33 proteins.
|
|
|
What are the bacterial ribosome subunits and what type of rRNA is each made of? What about the eukaryotic ribosome subunits?
|
50S : 5S rRNA , 23S rRNA, lotsa proteins
30S: 16S rRNA and proteins 60S: 5S rRNA, 28S rRNA, 5.85S rRNA and proteins 40S: 18S rRNA and proteins |
|
|
The pre-rRNA transcript for eukaryotes is the ___S.
|
45S
remember, this pre-transcript iswhere the 28S, 5.85S and 18S that partially make up the 40S and 60S subunits that make the eukaryotic ribosome. |
|
|
What has to occur in order for pre-rRNA to become mature rRNA?
|
snoRNPs mehtylate the keeper regions (the 18S, 5.85S, 28S areas) then cleave off the rest.
|
|
|
In a eukaryotic cell, the rRNA components of the subunit assembles in the ________ ; subunits themselves are put together in the _______.
|
rRNA subunit components assemble into their respective 40S and 60S subunit in the nucleolus. (Yes, the 5S made by Pol III in the nucleus gets transported into the nucleolus by an unknown mechanism.) These subunits don't actually assemble into the 80S until they are in the cytosol.
|
|
|
Contrast the differences in rRNA processing for prokaryotes and eukaryotes with regards to:
a) where processing occurs b) the pre-rRNA transcript name c) what "clips"/ cleaves |
a) for prok: cytosol since no nucleolus. for euk: nucleolus
b) prok: 30S euk: 45S c) prok: nucleases euk: snoRNPs |
|
|
True or False: In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, a step towards rRNA maturation is methylation.
|
True. Methylation is a way to signal "keepers".
|
|
|
tRNAs go through significant post-transcriptional modifications such as ______, _______ and ________. Sometimes also _______.
|
3' and 5' end "trimming" , 3' CCA extension, base modifications.
Sometimes also intron splicing. |
|
|
What are the arms of a tRNA?
|
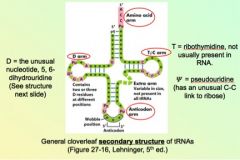
|
|
|
How is thymidine incorporated into tRNA? (as _______)
|
as ribothymidine. note the "ribo" emphasizes it is part of tRNA since RNA usually doesn't have thymidine.
|
|
|
Which of the following common modified bases in tRNAs are responsible for permitting differences in 3D structures because of different hydrogen bonding that it promotes?
a) ribothymidine b) pseudouridine c) dihydrouridine |
b) pseudouridine permits for differences in 3D structure
|

