![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Economic Growth as an Objective |
In emerging and developing economies, governments might aim to increase economic development before economic growth, which will improve living standards, increase life expectancy and improve literacy rates. |
|
|
Low Unemployment as an Objective. |
Governments aim to have as near to full employment as possible. They account for frictional unemployment by aiming for an unemployment rate of around 3%. |
|
|
Low Inflation as an Objective. |
In the UK, the government target is 2%, measured by CPI. This aims to provide price stability for firms and consumers and will help them make decisions for the long run. |
|
|
Environmental Protection as an Objective |
This aims to provide long run environmental stability. It ensures resources used are not exploited, such as oil and natural gas, and that they are used sustainably. |
|
|
Expansionary policy |
Expansionary policy is aimed at increasing AD to bring about growth. |
|
|
Deflationary policy |
Deflationary policy attempts to decrease AD to control inflation. |
|
|
Monetary policy |
Monetary policy is where the central bank or regulatory authority attempts to control the level of AD by altering base interest rates or the amount of money in the economy. |
|
|
Fiscal policy |
Fiscal policy is use of borrowing, government spending and taxation to manipulate the level of aggregate demand and improve macroeconomic performance. |
|
|
Causes of the great depression. |
Loss of consumer and business confidence, Banks had lent too much which had created an unsustainable boom, Protectionism may also have reduced world trade which decreased AD and lowered confidence. |
|
|
Market based policies (Supply-side) |
Market based policies are policies which are designed to remove anything that prevents the free market system working efficiently, causing lower output and higher prices. |
|
|
Interventionist based policies (Supply-side) |
Interventionist policies are policies designed to correct market failure, for example the free market under provides education and so the government provides it. |
|
|
Economic growth vs protection of the environment. |
As the economy grows, we expect more resources to be used. As we use resources and produce goods, we produce pollution and noise and destroy habitats. |
|
|
Economic growth vs Balance of Payments. |
Some countries such as India have seen rapid economic growth leading to balance of payments problems. The country is so large that its industry is largely producing goods for its own people and the wealth of the people has led to increased demand for imported goods. |
|
|
Unemployment vs Inflation- Short run Phillips curve. |
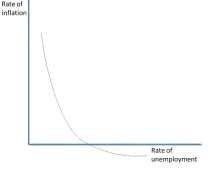
A. W. Phillips found a trade-off between inflation and unemployment, called the Phillips curve. He found the existence of an empirical regularity, which said that the rate of change in money wages increased as the rate of unemployment fell. This was then generalised into a relationship between unemployment and inflation, by arguing that firms pass on increases in wages to the customer in increased prices. |
|
|
Quantitative Easing (QE) |
A type of monetary policy in which a nations central bank tries to increase the liquidity in its financial system by purchasing government bonds from the nations largest banks. This often stimulates economic growth and encourages more free lending from banks. |

