![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ceramics type of bond |
Ionic and Covalent |
|
|
Ceramic Structure: 2 parts |
Cations (+) Anion (-) |
|
|
crystalline are more....bond type |
ionic |
|
|
amorphous are more....bond type |
covalent |
|
|
Ceramic structure types (3) |
Ax (NaCl) AmXp (CaFl2) AmBnZp (BaTiO3) |
|
|
Packing factor is function of.... |
size of A, B and x and electrically neutral. Charged ions make it difficult to pack close |
|
|
2 Ceramic Groups |
Traditional & Modern |
|
|
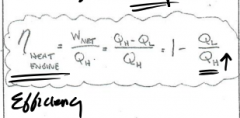
The highest Tmp (equaTion) |
|
|
|
Ceramics |
Pro: Very high specific properties, corrosion resistant, high use temper, the hardest, formable Con: no toughness, lowest Kic, porosity, $$$, low impact resistance, difficult to machine |
|
|
Ax has how many atoms? |
2 |
|
|
structure for CaF2 |
ax2 |
|
|
BaTiO3 ceramic structure |
AmBnXf |
|
|
4 Ceramic defects |
Point, Line, Surface, Volume |
|
|
Point Defects |
vacancy, interstitial, substitutional |
|
|
Line Defects |
Edge, screw |
|
|
Surface Defects |
desire small grains, increase grain boundary |
|
|
Volume Defects |
porosity |
|
|
Advanced Ceramics (4) |
Heat Engine, Optical Fiber, Ceramic Ball Bearings, Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) |
|
|
Advanced Ceramic: Optical Fiber |
High purity silica, very clean, no scattering of light |
|
|
What is a polymer? |
Large organic chains or molecules Examples: rubber, wood, oild |
|
|
What does it mean? "Poly" "mer" |
Many repeating unit |
|
|
Isomerism |
Same compound but with a different structure |
|
|
Type of chains and type of bonding of Polymer |
Linear: covalent & vander waal Branched: covalent & vander waal Crosslinked: covalent |
|
|
Polymerization |
joining mers via current, heat, pressure, etc |
|
|
Addition |
Thermoplastics, same mers,sequential linear, fast, spontaneous |
|
|
Condensation |
Thermosets, different mers, slow, by product, cross-linked polymers |
|
|
Degree of polymerization "n" |
average # of mers in a chain n=Molecular weight (given)/total molecular weight of atoms |
|
|
True or False. As chain extend in length does Tmp ^, Sy^, hardness ^ and E^? |
True |
|
|
Crystallinity |
chain alignment "ribbons" or crystals |
|
|
Why do we want crystallinity? |
Chains become closer together and vander wall bond strength is increased, easiest for long chains, linear to form crystals, slow cooling from melt |
|
|
Polymers |
Pro: low density, cheap, strong eough, low tmp, recycle Con: poor mechanical properties, weak, creep, embrittle, low Tmp, low impact resistance, temp sensitive, UV sensitive |
|
|
Thermoplastics |
liquify/melt, linear chains, copoymer, addition polymerization, viscoelastic Properties: melt, ductile, low Sy and E, formable |
|
|
Thermosets |
permanently set, do not melt, char or burn, network, covalent bonds, retationally rigit, brittle, condensation plymerization, elastomers Properties: brittle, high Sy, E, low Kic |
|
|
Traditional Ceramics |
Clay based, brick, tile, glasses, silicate, High temper, abrasives |
|
|
Modern Ceramics |
High purity powder, controlled micro structure, C, graphite, diamond, strengthening mech? sw, sss, gs, ds |
|
|
Polymer molecules can be characterized by: |
Size, Shape, Structure |
|
|
Saturated bonds |
Uses up all bonding |
|
|
Unsaturated bonds |
Double bonds or greater were used |
|
|
Monomers |
Double unsaturated structure |
|
|
Thermosets have what kind of molecular configuration? |
Crosslinked |
|
|
Thermoplastics have what kind of molecular configuration? |
Linear and Branched |
|
|
What are the 3 major polymer molecular configurations? |
isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic |
|
|
Isotactic are groups of the... |
same side of chain |
|
|
Syndiotactics are groups of the... |
alternate sides |
|
|
Atactic are groups of the... |
randomly positioned |
|
|
Viscoelastic: As strain rates increases |
brittle behavior, chain have no time to slide |
|
|
Viscoelastic: As strain rates decreases |
ductile behavior |
|
|
Glass Transition Temperature |
Temp where the material goes from rubber to brittle |
|
|
Additive types |
Pigments, stabilizers, plasticize, reinforcement, antistatic, flame retardants |
|
|
Polymer properties affected by |
degree of polymerization, bond type, chain structure, e, temp, environment, additives |
|
|
Copolymer |
two or more monomers polymerized together |
|
|
Elastic Region |
The amorphous region is unkinking, elongation of the chains, crystallites thicken due bonding and stretching |
|
|
Plastic Region at yield |
Necking, tilting of crystallites/chain folds, crystalline region aligning, vander waals breaking |
|
|
Plastic Region #3 |
Crystalline blcok segments separate from lamellae, vander waals breaking |
|
|
Plastic Region #4 |
Continued block sliding and separation, tie chains are aligned with load, fibrillar structure, vander waals and covalent bonds break |
|
|
Particle reinforced |
large particle, dispersion strengthened |
|
|
Fiber reinforced |
continuous(aligned) and discontinuous (short), fiber types whiskers, fibers, wires |
|
|
Structural |
Laminates, sandwich panels |
|
|
Composites are |
two or more materials that synergistically combine to give optimum properties that neither material count provide alone |
|
|
Matrix |
soft, ductile, adhere to fiber/ppt, transfer shear stress |
|
|
Fiber |
Hard, tough, strong, stiff, corrosion resistant, low density, $$ |
|
|
Composites |
Pros: low density, high E, the highest specific properties, fatigue resistance, tailorable Cons: low damage tolerance, toxic, moisture absorption, $$$, difficult to process, |
|
|
Cite the overall mechanism common to all 4 strengthening mechanisms |
stopping of slowing dislocation motion |
|
|
What is the mechanism of plastic deformation |
dislocation motion |
|
|
What is the mechanism of elastic deformation |
bond stretching |
|
|
What are 3 steps in precipitation hardening and describe |
Solution treat: heat up allow to 100% alpha Quench: rapidly cool below solidus Age: at room temp or below solidus |
|
|
One requirement for age hardening to occur |
decreasing solubility with temp |
|
|
Vulcanization |
is a chemical process for converting natural rubber or related polymers into more durable materials by the addition of sulfur or other equivalent curatives or accelerators |

