![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
streptococcal pharyngitis (caused by S. pyogenes) |
|
|
streptococcal pharyngitis (caused by S. pyogenes) |
|
|
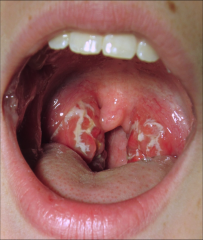
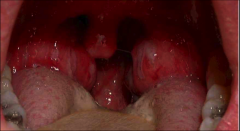
Streptococcal Pharyngitis |
caused by microbe Streptococcus pyogenes(underline, S. pyogenes). common name: strep throat. resistant to phagocytosis, diagnosed by enzyme immunoassay (EIA). Complication: scarlet fever |
|
|
streptococcal pharyngitis symptoms and identification |
whitish exudate covering tonsils, inflammation of pharynx, fever
|
|
|
complications of S. pyogenes |
-scarlet fever: toxin kills cells -septicimia: spread in bloodstream -rhuematic fever: inflammed organs/joints, eart valve damage -acute post streptococcal glomerulonphritisid |
|
|
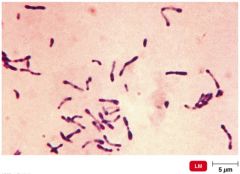
diptheria |
bacterial infection that occurs quickly and oreads easily, children under 5 and those over 60 at greater risk -caused by C. diphtheriae |
|
|
Corynebacterium diphtheriae |
|
|
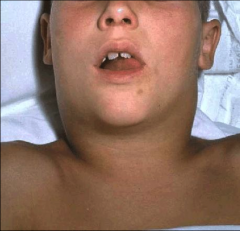
Diptheria symptoms |
-localized inflammatory response -barking cough(bc of fibrous membrane blocking airways) -difficulty swallowing -swelling of lymph glands -membranous pharyngitis |
|
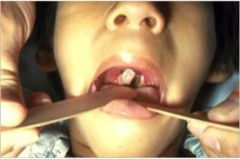
|
diptheria |
|
|
diptheria |
|
|
anthrax |
microbe: Bacillus anthracis or B. anthracis |
|
|
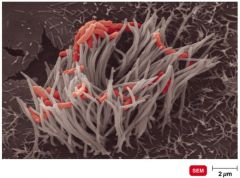
common cold |
-rhinoviruses cause 30-50% of colds -transmission by respiratory droplets -other common virus: coronavirus (SARS) |
|
|
common cold pathogenesis |
-replication in epithelial cells -stimulate kinins secretion -immune response clears virus -treatment: symptoms only |
|
|
common cold symptoms |
-runny, stuffy nose -cough -congestion -sneezing -watery eyes -fever -fatigue |
|
|
pertussis, whooping cough |
|
|
Pertussis |
microbe: Bordetella pertussis (B. pertussis) capsulated--> harder to destroy |
|
|
pertussis: pathogenesis, symptoms and prevention |
-path: replication of bacteria, release toxin -symptoms: cold like, vomiting (bc of cough), characteristic cough (whooping), turn blue bc of lack of air from cough -prevention: acellular vaccine (DTaP) |
|
|
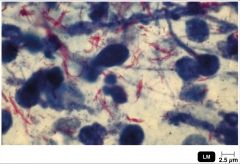
Tuberculosis |
microbe: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), acid fast rod |
|
|
tuberculosis, corded growth, used to identify |
|
|
Tuberculin skin test |
used to identify TB -positive=current or previous infection, may mean person was vaccinated or exposed to toxin -followed by x-ray, CT exam, acid fast staining of sputum, culturing of bacteria |
|
|
TB pathogenesis, symptoms, treatment, and prevention |
-path: inflammation and lesions of lung tissue, cellular immune (CT) response, slow growth -sympt: varies-->primary lesions, may spread to various tissues -treat: multiple antibiotics for up to 6 mo. -prevent: BCG vaccine-->live culture of M. bovid |
|
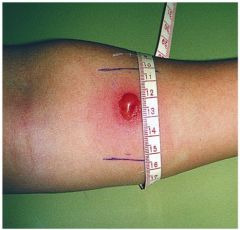
|
positive TB skin test (only look at raised red 15 mm or more is considered positive in anyone) |
|
|
S. pneumoniae (causes pneumococcal pneumonia) |
|
|
pneumcoccal pneumonia |
microbe: Streptococcal pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) encapsulated diplococci |
|
|
pneumococcal pneumonia sympt, diag, treat, prevent |
-sympt: infected alveoli of lungs fill with fluid, interferes with O2 uptake -diag: optochin-inhibition test or bile solubility test -treat: macrolides, fluoroquinolones prevent: pneumovax (pneumococcal vaccine) |
|
|
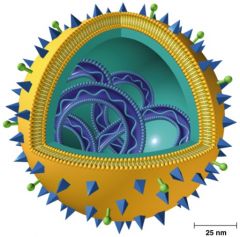
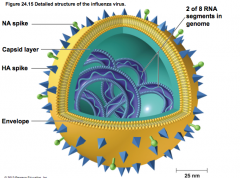
viral pneumonia |
complication of influenza, chicken pox, or measles |
|
|
|
|
|
influenza sympt, treat, prevent |
flu, typically RNA virus, types A,B,C -sympt: chills, fever, headache, muscle ache -treat: zanamivir and oseltomevivir, prevent secondary infections like pneumonia prevent: vaccine |
|
|
blastomycosis |
fungus: Blastomyces dermatitidis -sympt: abcesses, extensive tissue damage diag: isolate pathogen treat: amphotericin B, anitfungals |
|
|
dental diseases |
-caries: S. mutans, produce glucan, lactic acid (damage enamel) -periodontal disease: gingivitis-->inflammed gums; periodontidis: damage to tissue, B. intermedious |
|
|
staphylococcal food poisoning |
microbe: S. aureus (enterotoxin) -absorbed in blood stream -1-6hr after ingestion -nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain -from skin of food handler -incubate and grow: potato salad, processed meats, canned goods, dairy |
|
|
shigellosis (bacillary dysentery) |
microbe: shigella spp. -sympt: tissue damage and dysentery -infection: infection endotoxin and shiga exotoxin treat: fluoroquinolones |
|
|
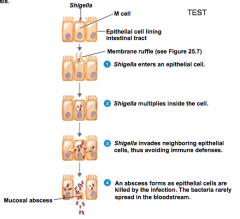
shigellosis (bacillary dysentery) |
|
|
typhoid fever |
microbe: Salmonella typhi -spread through body by phagocytosis -very virulent-->few bacteria make sick -sympt: severe fever/headache, weakness, rash, abdominal pain, last abt a month treat: cephalosporins, quinolones |
|
|
salmonellosis |
Salmonella species: pili adhere to GI tract, invasive growth -contaminated food, improper thawing, undercooked -sympt: abd pain, fever, diarrhea, last abt 3-5 days -treat: oral rehydration |
|
|
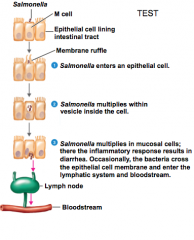
salmonellosis |
|
|
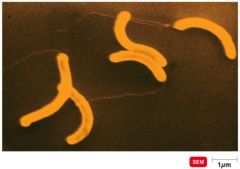
Vibrio cholerae (comma shape) |
|
|
cholera |
V. cholera sympt: diarrhea w/ large HOH loss cholera toxin (exotoxin) treat: rehydrate, doxycycline |
|
|
noncholera vibrios (long) |
V. parahaemolyticus cholera like diarrhea but milder infection, enterotoxin rehydrate, antibiotic |
|
|
noncholera vibrios (short) |
V. vulnificus rapidly spreading tissue distruction infection, siderophores antibiotics |
|
|
Escherichia coli |
many strains non pathogenic: -enteroinvasive: diarrhea in all -enteropathic: diarrhea in infants -enteroaggregative: severe dia. infants -enterotoxigenic: traveler's dia -enterohemorrhagic: E. coli O157:H7, hemolytic uremic syndrome, bloody dia, severe anemia, kidney failure; shigalike toxin |

