![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
292 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ATII causes constriction of afferent renal arterioles
T/F |
False
Efferent arterioles |
|
|
Where is renin released from?
|
Juxtaglomerular apparatus from the kidney
|
|
|
Causes of pre-renal azotemia?
|
Hypovolemia
|
|
|
What is the earliest sign of diabetic nephropathy?
|
Elevated albumin to creatinine ratio
>30mg/mmol |
|
|
What are some clinical settings in which urea would be elevated independent of renal function?
|
Volume depletion
GI hemorrhage High protein diet Sepsis Catabolic state with tissue breakdown Corticosteroid or cytotoxic agents |
|
|
What is normal urine pH?
|
pH 4.5 -7.0
|
|
|
What are some causes of persistently alkaline urine?
|
renal tubular acidosis
UTI w/ urease producing bacteria (proteus) |
|
|
RBC casts in the urine?
|
Glomerulonephritis
Vasculitis |
|
|
WBC casts in the urine?
|
Pyelonephritis
Interstitial nephritis |
|
|
Muddy brown (pigmented granular casts) in the urine?
|
ATN
Glomerulonephritis Interstitial nephritis |
|
|
Fractional excretion of Na+ <1% suggests what?
|
pre-renal causes
|
|
|
What are some signs and symptoms of hyponatremia?
|
Headache, nausea, malaise, lethargy, weakness, muscle cramps, anorexia, somnolence, disorientation, depressed reflexes, decreased LOC
|
|
|
Where is K+ reabsorbed in the kidney?
|
Mainly in the DCT and collecting tubule via the intercalated cell
|
|
|
What is a common cause of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus?
|
Lithium
|
|
|
How do you distinguish between central and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
|
Central DI
- ADH is low - on admin of DDAVP: a rise in urine osmolality and fall in urine volume Nephrogenic DI - ADH usually elevated - DDAVP fails to increase urine osmolality |
|
|
Name some factors which increase renal K+ loss
|
1. Hyperkalemia
2. increased distal tubular urine flow rate and Na delivery 3. Increased aldosterone 4. Metabolic alkalosis 5. Hypomagnesemia 6. Increased non-resorbable anions in tubule lumen like HCO3, penicillin, salicylate |
|
|
What is the approach of HYPOkalemia?
|
1. ABC's
2. ECG 3. Rule out transcelluar shifts of K (from insulin, Beta2 agonists, Metabolic alkalosis) 4. Assess dietary K intake 5. 24hr K excretion or spot urine K 6. If renal K loss, check BP and acid base status 7. Assess plasma renin, aldosterone, serum Mg levels |
|
|
What are some S&S of HYPOkalemia?
|
Usually asymptomatic
N/V Fatigue, generalized weakness, myalgia Muscle cramps Constipation IF Severe: - arrhythmias (more likely if on digoxin) - muscle necrosis |
|
|
What ECG changes are present in HYPOkalemia?
|
**U waves** (small wave following T wave)
Flattened or inverted T waves ST segment depression Prolongation of QT interval Widened QRS (severe hypokalemia) |
|
|
What is the treatment for HYPOkalemia?
|
Address underlying causes
Extreme caution in renally impaired pts If true K deficit: - Encourage oral intake K+ foods - IV (KCl) avoid dextrose (insulin release) - K sparing diuretics - Restore Mg if necessary (Co-transporter for K) |
|
|
Approach to HYPERkalemia?
|
1. ABC's
2. ECG 3. Rule out factitious, repeat blood 4. Hold exogenous K and any K retaining meds 5. Assess potential causes of transcellular shift 6. Estimate GFR |
|
|
Causes of HYPERkalemia?
|
Rhabdo
Insulin deficiency Metabolic acidosis Tumor lysis syndrome Drugs (beta blockers, digitalis overdose, succinylcholine) Renal failure Decreased execretion/function of aldosterone - Addisons, ACEi, CAH (21 hydroxlase), |
|
|
What are the S&S of HYPERkalemia?
|
Palpitations
Muscle weakness/stiffness Paresthesias Areflexia Hypoventilation ECG changes |
|
|
What ECG changes do you find in HYPERkalemia?
|
Peaked and narrow T waves
Decreased amplitude (eventual loss) of P waves Prolonged PR interval Widening of QRS AV block Vfib, asystole |
|
|
What is the treatment for HYPERkalemia?
|
1. Protect the Heart
- Ca gluconate 2. Shift K into cells - Regular insulin (10-20 U) w/ 1-2 amps of D5W - NaHCO3 1-3 amps (drives K into cells in exchange for H+) - Ventolin (Nebulized) 3. Enhance K removal - Via urine: furosemide - Via gut: Kayexalate (resonium), - Via dialysis: renal failure, life threatening hyperkalemia. |
|
|
What are some causes of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis?
|
MUDPILES
M-methanol U- uremia D- diabetic ketoacidosis P-paraldehyde I- isopropyl alcohol AND iron L- lactic acidosis E- ethylene glycol S - salicylates |
|
|
What are some risks to NaHCO3 therapy in someone with metabolic acidosis?
|
1. Hypokalemia
- causes K to shift into cells (correct K deficits first 2. ECF volume overload: Na load given with NaHCO3, can exacerbate pulmonary edema |
|
|
What are 6 actions of AT II ?
|
1. Constricts vascular smooth muscle
2. Constricts efferent arteriole (which acts to preserve renal function in low volume states) 3. Stimulates aldosterone secretion (Na/K pump - creates Na gradient) 4. Stimulates ADH secretion (water channel insertion in principle cells) 5. Increased PT Na/H activity (water reabsorption) 6. Stimulates hypothalamus - thirst |
|
|
Where is angiotensinogen secreted from ?
|
Liver
|
|
|
Where is Renin secreted from ?
|
Juxtaglomerular cells of kidney
|
|
|
What % of cardiac output goes to the kidneys?
|
20%
|
|
|
How is renal plasma flow calculated?
What substance is used as a marker? |
PAH
RPF= urine (PAH) x urine vol/ plasma (PAH) |
|
|
What are 3 ways to measure GFR?
|
1. Creatinine clearance
2. Cockcroft-Gault formula 3. Urea concentration |
|
|
What are the limitations of using Creatinine clearance to determine GFR?
|
- Can overestimate GFR particularly in azotemic pts
- Incomplete urine collection can alter the calculated GFR. - Rate of Cr production is determined by muscle mass |
|
|
On clinical examination what methods allow differentiation of the kidney from the spleen?
|
The spleen:
1. Has no palpable upper border 2. Has a notch that may be palpable 3. Spleen moves inferiomedially inspiration whereas the kidney moves inferiorally 4. Spleen is not ballottable |
|
|
What are the features of Nephritic syndrome?
|
PHAROH
P - Proteinuria H - Hematuria A - Azotemia R - RBC casts O - Oliguria H - Hypertension |
|
|
What are some causes of Nephritic syndrome in a patient with LOW complement level?
|
Post-infectious GN
Membranoprolif GN SLE Endocarditis Cryoglobulinemia |
|
|
What are some causes of Nephritic syndrome in a patient with NORMAL complement level?
|
IgA nephropathy
anti-GBM disease Polyarteritis nodosa Wegeners granulomatosis Henoch-schonlein purpura Goodpasteurs |
|
|
What are the features of Nephrotic syndrome?
|
Heavy proteinuria
Hypoalbuminemia Edema Hyperlipidemia (fatty casts) Hypercoagulable state |
|
|
A pt with rheumatoid arthritis presents with hematuria and worsening renal function. A biopsy demonstrates nodular deposits in the mesangium which when stained with congo red turn green under polarized light. What is the diagnosis?
|
Amyloidosis (Glomerular disease)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Goodpastures?
|
Plasma exchange
Cyclophosphamide Prednisone |
|
|
What is the antibody target in Goodpastures?
|
Type IV collagen
Present in Lungs and GBM |
|
|
What is the treatment for Wegeners Granulomatosis?
|
Cyclophosphamide
Prednisone ?sulfa |
|
|
A pt presents with purpuric rash, fever and arthralgia. He has noticed that on exposure to cold his fingers turn white, then blue, and then red.
On routine investigation his Creatinine is markedly elevated. What is the diagnosis? |
Cryoglobulinemia
(white/blue/red = Raynaud Phenom) |
|
|
There is a strong association between Hep C and which types of glomerular disease?
|
Cryoglobulinemia (50%)
Membranoproliferative GN |
|
|
There is a strong association between Hep B and which types of glomerular disease?
|
Membranous GN
Polyarteritis nodosa |
|
|
What are some causes of acute tubulointersitial nephritis?
|
1. Antibiotics: beta-lactams, sulfonamides, rifampin, quinolones, cephalosporins
2. Other drugs: NSAIDS, allopurinol, furosemide 3. Infections: strep, brucellosis, legionella, CMV, EBV 4. Immune: SLE, Sjogrens, sarcoidosis, cyroglobulinemia |
|
|
What are the Ix and treatment of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis?
|
1.Urinalysis and culture
- eosinophils if allergic 2.Blood -Cr, Ur, eosinophils, PO4, K, Na 3. Gallium scan - intense signal uptake d/t inflammatory infiltrate 4. Renal biopsy (definitive) 5. Treat underlying cause (stop drug etc) 6. Corticosteroids may be indicated for allergic or immune disease |
|
|
What is Fanconi's syndrome?
|
Decreased reabsorption in the proximal tubule causing glycosuria, aminoaciduria, phosphaturia
|
|
|
What are the 2 main causes of acute tubular necrosis?
|
1. Toxin
2. Ischemia |
|
|
Nephrotic sydrome leads to a hypercoagulable state.
True/False? |
True
|
|
|
In scleroderma what is the treatment for concurrent renal disease?
|
BP control with ACEI slows the progression of renal disease
|
|
|
What type of peripheral nervous system signs are seen in Renal failure?
|
"glove and stocking" sensory neuropathy
Wrist or food drop |
|
|
What are the 2 most common causes of acute renal failure in hospitalized patients?
|
1. ATN
2. Pre-renal azotemia |
|
|
How can you differentiate between pre-renal causes of acute renal failure from ATN?
|
Pre-renal ATN
Urinalysis normal Muddy brown casts Urine Na <20 >40 Urine Cr/Na >40 <20 Urine osmol >500 <350 Frac exc Na <1 >1 |
|
|
What are the initial investigations in Acute renal failure?
|
1. FBC, electrolytes, Cr, Ur, Ca, Phosphate
2. Urine volume, C&S, microscopy 3. Foley catheter 4. Fluid challenge (to rule out prerenal causes) 5. Abdo U/S KUB 6. ?biopsy |
|
|
What are the top 3 causes of chronic kidney disease in Canada?
|
1. Diabetes
2. HTN 3. Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
What medication can be used for hyperparathyroidism in CKD?
|
Cinacalcet (sensitizing parathyroid to Ca)
|
|
|
What are the 4 main diabetes renal complications?
|
1. Progressive Glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules)
2. Accelerated atherosclerosis (decr GFR, increase ATII) 3. Autonomic neuropathy (affects bladder, obstruction) 4. Papillary Necrosis |
|
|
What are the renal priorities in the management of pts with DM?
|
1. ACEI + antiplatelet therapy
2. BP control, glycemic control, lifestyle mods, lipid control 3. Renal protection in nephropathy - T1DM - ACEI - T2DM - CrCl >60: ACEI or ARB -T2DM - CrCl <60: ARB - 2nd line Diltiazem, verapamil |
|
|
What are some S&S of fluid overload?
|
1. Raised JVP (i.e. above 3 cm
2. Peripheral edema 3. Sacral edema 4. Dyspnea 5. Rales at lung bases 6. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea |
|
|
What are the indications for dialysis in acute renal failure (acute kidney injury)?
|
1. Hyperkalemia (refractory)
2. Acidosis (refractory) 3. Volume overload (refractory) 4. Elevated BUN 5. Pericarditis 6. Encephalopathy 7. Pulmonary edema |
|
|
What is the managment of the long term complications of chronic kidney disease?
|
NEPHRON
N - low nitrogen diet E - electrolytes: monitor K P - pH: metabolic acidosis H - Hypertension R - RBCs manage anemia w/ EPO O - Osteodystrophy: Give Ca b/w meals and Ca w/ meals (to bind PO4) N - Nephrotoxins: avoid NSAIDS, gentamicin, other renally excreted drugs |
|
|
What are the 5 stages of chronic kidney disease?
|
1. Normal >90
2. Mild 60-89 3. Moderate 30-59 4. Severe 15-29 5. End stage <15 |
|
|
Child with recent URI presents with brown urine. Kidney biopsy demonstrates bumpy depostis of IgG on the renal basement membrane.
The serum C3 is low. Dx? |
Post-streptococcal GN
or Post-infectious GN |
|
|
Young male presents with fever, brown urine and flank pain. Labs show elevated IgA. Renal biopsy shows mesangial cell proliferation.
What is the treatment? |
IgA nephropathy (Bergers)
Occasionally self limited ACE-I and statins for persistent proteinuria Give corticosteroids if nephrotic syndrome develops |
|
|
25 year old man presents with hemoptysis, dyspnea, myalgia, and hematuria. Renal biopsy shows IgG staining in a linear pattern along the basement membrane.
What is the treatment? |
Goodpasteurs
1. Plasmaphoresis 2. Pulsed corticosteroids 3. Immunosuppression |
|
|
10 year boy presents with asymptomatic hematuria. His mother mentions that he has a hearing abnormality present since birth.
What is the hereditary defect? |
Alport's syndrome
Hereditary defect in collagen IV in basement membrane |
|
|
8 year presents with increased frequency of infections. O/E BP is elevated and there is 3+ proteinuria.
What finding would be seen on electron microscopy of the kidney? |
Minimal change disease
Flattening of foot processes on basement membrane (fusion of epithelial foot processes) |
|
|
A recently migrated African male presents uncontrolled hypertension. Urinalysis reveals microscopic hematuria. He is HIV +ve
What is the diagnosis? |
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
A spike and dome pattern of basement membrane thickening is seen on EM of a renal biopsy.
What is the treatment? |
Membranous GN
Corticosteriods Cytotoxic agents ACE-i Statins ?anticoagulation in thrombosis |
|
|
On EM microscopy of a renal biopsy, basement membrane thickening with a tram track appearance is noted.
What is the treatment? |
Membranoproliferative GN
Corticosteroids combined w/ aspirin or dipyridamole may delay progression to renal failure |
|
|
Pt presents with progressive renal failure. There is a long Hx of DM. On biopsy their is basement membrane thickening and round nodules.
What are these nodule called and what type of disease do they indicate? |
Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules
Indicate the nodular (as opposed to diffuse) type of diabetic nephropathy. |
|
|
65 year black male presents with swelling of his legs, and frothy urine. Labs reveal hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia. He is otherwise well except for some lower back pain that has been getting progressively worse over the last year that keeps him up at night. His clothes appear loose fitting. On kidney biopsy nodules can be seen which exhibit apple-green birefringence when stained with congo red. What is the Dx?
|
Renal amyloidosis secondary to multiple myeloma.
|
|
|
Name some drugs which cause acute kidney injury?
|
NSAIDs
Aminoglycosides ACEi ARB |
|
|
Which of the following drugs is primarily excreted by the kidney?
Digoxin Gentamicin Vancomycin Enoxaparin |
All of them are renally excreted (NB adjust dosing in renal failure)
Digoxin Gentamicin Vancomycin Enoxaparin |
|
|
What structure is injured in 90% of cases of epistaxis
|
Keisselbach's plexus (aka Little's area)
|
|
|
What are the functions of the facial nerve?
|
"Ears, tears, face and taste
Stapedius muscle Lacrimation and salivation Muscles of facial expression Sensory ant. 2/3 of tongue |
|
|
Borders of the anterior triangle of the neck?
|
Lower border Mandible
Midline of neck Anterior border of SCM |
|
|
What structures are contained in the anterior triangle of the neck?
|
Tail of parotid
Submandibular gland Hypoglossal nerve Carotid bifurcation Lymph Nodes |
|
|
Borders of the posterior triangle of the neck?
|
Post. border of SCM
Ant. border of trapezius Middle third of clavicle |
|
|
What structures are contained in the posterior triangle of the neck?
|
Spinal accessory nerve
Lymph nodes |
|
|
What are some causes of vertigo due to peripheral (non-central) abnormalities?
|
Benign positional vertigo
Meniere disease Vestibular neuronitis Labyrinthitis Acoustic neuroma |
|
|
Which nerves can be implicated in referred pain causing otalgia?
|
CN V
CN IX CN X |
|
|
What are some of causes of referred pain causing otalgia?
|
10 T's +2
Eustachian Tube TMJ syndrome Trismus Teeth Tongue Tonsil Tic (glossopharyngeal neuralgia) Throat Trachea (foreign body, tracheitis) Thyroiditis Geniculate herpes and Ramsay hunt syndrome CN VII palsy (Bell's palsy) |
|
|
What medications can cause tinnitus as a side effect?
|
Aminoglycosides
Salicylates NSAIDs Antimalarials Antidepressants Heavy metals |
|
|
Pt with a Weber test lateralizing to the right ear and a Rinne BC > AC of the right ear has which type of hearing loss?
|
Right sided conductive hearing loss
|
|
|
Pt with a Weber test lateralizing to the left ear and a Rinne AC > BC bilaterally has which type of hearing loss?
|
Right-sided sensorineural hearing loss.
|
|
|
50 year pt presents with periods vertigo, tinnitus and fluctuated hearing loss of the L. ear lasting about an hour. She describes a feeling of fullness in the ear. Apart from a stressful work environment she is otherwise healthy.
What is short and long term managment? |
Meniere's Disease
Acute management: - Bed rest - Anti-emetics - Betahistine (anti-vertiginous) Long term: - Low salt diet - Diuretics esp: thiazides, amiloride and triamterene) - ? surgical |
|
|
A 12 year old swimmer presents with complaints of R. ear pain and hearing loss. When the auricle is moved intense pain is triggered. The mother notes that when she usually swabs his ears she sees only cerumen but in the last few days she has noticed that the colour and consistency of his ear swabs (Q-tips) has changed.
What are the likely implicated organisms? |
Otitis externa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas vulgaris E. coli S. aureus Candida Aspergillus |
|
|
A 35 year old pregnant women presents with hearing loss. She says that she first noticed the loss in hearing when she was 20 but the loss in hearing has recently progressed quickly. She mentions that her mother also had similar problems. On auroscopy the tympanic membrane is normal with a specific area which is more pink than the rest of the TM.
What is the diagnosis? |
Otosclerosis (2nd most common cause of conductive hearing loss from 15 -50)
Autosomal dominant Neovascularization of otosclerotic bone = pink blush (Schwartz's sign) Responds to hormone and hence worsens during pregnancy. |
|
|
A 15 year old male presents with recurrent unilateral epistaxis. He denies digital trauma. What is the diagnosis?
|
Juvenille nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA)
Most common benign tumor of the nasopharynx |
|
|
T/F
The most common type of thyroid carcinoma is a follicular thyroid carcinoma |
FALSE
Papillary is the most common then follicular |
|
|
What are the 3 most common causes of acute otitis media in children?
|
1. Strep pneumoniae
2. H. influenzae 3. M. catarrhalis S. aureus and pyogenes also causes |
|
|
What is first line treatment for acute otitis media?
|
Amoxycillin 40mg/kg/day bd x 10 days
|
|
|
What is the treatment for acute epiglottitis?
|
IV access + rehydration
antibiotics IV: cefuroxime, cefotaxime or ceftriaxone Humidified air Monitor for menigitis Monitor for airway compromise Minimal airway agitation |
|
|
What is Samters triad?
|
1. Nasal polyps
2. Asthma 3. ASA sensitivity AKA aspirin induced asthma |
|
|
Why must nasal septal hematomas be drained?
|
Cause of septal necrosis with perforation (saddle nose deformity)
|
|
|
What is the window period for closed reduction of a nasal fracture?
|
Best reduction is immediately <6hrs or when swelling subsides (5-7 days)
|
|
|
A pt presents with sore throat, dysphagia, and odynophagia. There is extensive peritonsilar swelling but the tonsil appears normal. O/E the palate fails to elevate.
Dx? |
Peritonsillar abscess (Quinsy)
|
|
|
What are the signs of Vit A deficiency?
|
Dermatitis
Night blindness Keratomalacia Xeropthalmia |
|
|
What are the signs of Vit E deficiency?
|
Rare hemolysis
Anemia Neuronal axonopathy Myopathy |
|
|
What are the most common causes of acute bronchitis?
|
80% Viral
- Rhinovirus - Coronavirus - Adenovirus - Influenza 20% Bacterial - M. pneumonaie - C. pneumonaie - S. pneumonaie |
|
|
What is the managment of stable ischemic heart disease?
|
1. Lifestyle mods (diet, exercise, etoh, smoking)
2. Anti-platelet therapy 3. Beta-blocker (all pts post-MI or with CHF) 4. ACEi (pts >55) 5. Statin therapy (pts with coronary disease) |
|
|
What are most common causes of acute rhinitis (common cold)?
|
PRIMA
P - paramyxovirus R- Rhinovirus I - Influenza virus M - Myxoviruses A - Adenoviruses **Most common Rhinoviruses |
|
|
Criteria for depression?
|
MSIGECAPS
M - Mood depression S - Sleep disturbance I - Interest Loss G - Guilt E - Energy decreased C - Concentration decreased A - Appetite changes P - Psychomotor agitation/retardation S - Suicidal ideation Need 5 of 9 for Dx; must have interest loss/ahedonia and depressed mood |
|
|
Spousal abuse is a criminal act and requires mandatory reporting.
True/False? |
FALSE
While it is a criminal act, it is not mandatory to report. Permission from the pt must be obtained before reporting. |
|
|
What are some red flags in a person presenting with fatigue?
|
Fever
Weight loss Night sweats Neuro deficits Ill-appearing |
|
|
What is the term for age related hearing loss?
|
Presbycussis
|
|
|
What is the recommended therapy for the treatment of HTN in a pt with ischemic heart disease?
|
Beta blockers
ACEi |
|
|
What is the recommended therapy for the treatment of HTN in a pt with diabetes mellitus?
|
ACEi
ARB |
|
|
What is the recommended therapy for the treatment of HTN in a pt with renal disease?
|
ACEi
|
|
|
What is the recommended therapy for the treatment of HTN in a pt with asthma?
|
K-sparing + thiazide
|
|
|
What is the recommended therapy for the treatment of HTN in a pt who smokes?
|
Low dose thiazides
ACEi |
|
|
What is the recommended therapy for the treatment of HTN emergency?
|
Labetolol
Nifedipine |
|
|
What are the red flags for back pain?
|
BACKPAIN
B - bowel or bladder dysfunction A - anesthesia (saddle) C - Consitutional symptoms (malignancy wt loss etc) K - Kronic disease P - Paraesthesias A - Age >50 I - IV drug use N - Neuromotor deficits |
|
|
Pt dx with gonococcal urethritis/cervicitis. What is the treatment?
|
Cefixime 400mg PO single dose
|
|
|
Pt dx with Chlamydial urethritis/cervicitis infection. What is the treatment?
|
Azithromycin 1g PO single dose or
Doxycycline for 7 days bd |
|
|
What is the treatment for syphillis?
|
Penicillin G (IM)
|
|
|
What are some signs of sinusitis?
|
Maxillary toothache
Hx of purulent nasal discharge Poor response to decongestants Abnormal transillumination Purulent secretions O/E |
|
|
What is the managment of acute sinusitis?
|
Amoxicillin x 10days (TMP-SMX if penicillin allergy)
|
|
|
What are some common causes of clubbing?
|
CF
Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchiectasis Lung Ca Mesothelioma AV fistula Cyanotic cogenital heart conditions IBD Cirrhosis |
|
|
True/False
Clubbing is commonly seen in COPD. |
FALSE
If clubbing is seen in COPD think malignancy. |
|
|
Causes of obstructive lung disease?
|
1. Asthma
2. COPD 3. Bronchiectasis 4. Cystic fibrosis |
|
|
Causes of restrictive lung disease?
|
1. intersitial lung disease
2. Neuromuscular disease 3. Chest wall disease 4. Pleural disease 5. Parenchymal disease (pneumonia) |
|
|
What are some important red flags in Asthma?
|
Fatigue
Diminished resp effort Cyanosis Silent chest Decreased LOC Signs of respiratory distress |
|
|
What is the max LPM of oxygen and the % these delivery devices can offer?
1. Nasal Prong 2. Simple face mask 3. Partial rebreather 4. Non-rebreather |
1. Nasal prong: ~5L = 35%
2. Face mask: ~10L = 50% 3. Partial rebreather: ~15L = 70% 4. Non-rebreather: ~15L = 90% |
|
|
What are the key factors in determining prognosis in COPD?
|
1. Chronic hypoxemia
2. Pulmonary hypertension 3. Cor pulmonale |
|
|
What conditions might be associated with Kerley B lines?
|
1. CHF causing pulmonary edema
2. Interstitial lung disease |
|
|
V/Q scans have a high sensitivity and low specificity.
True/False |
True
|
|
|
What are potential masses of the anterior mediastinum?
|
5T's
T - Thymoma T - Thyroid enlargement T - Teratoma T - Thoracic aortic aneurysm T - Tumors (lymphomas, pararthyroids, esophageal) |
|
|
What are some causes of transudative pleural effusions?
|
CHF
Cirrhosis Nephrotic syndrome PE (can be either trans or exudative) Peritoneal dialysis Hypothyroidism CF |
|
|
What are some causes of exudative pleural effusions?
|
Infection
Malignancy Vascular/Cardiac (RA, SLE, PE) Trauma |
|
|
What are some clinical signs suggesting life threatening pneumothorax requiring immediate treatment.
|
Severe respiratory distress
Tracheal deviation to contralateral side Distended neck veins Hypotension |
|
|
PaO2 is decreased, PaCO2 is normal, FiO2 is normal. There is diffusion impairment (dLCO). What is the suggested pathology?
|
Interstitial lung disease
|
|
|
In a pt with COPD dubbed a "CO2 retainer" what should be the target O2 saturation?
|
88-92%
|
|
|
What are some causes of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
|
Aspiration (gastric or drowning)
Pneumonia Gas inhalation (oxygen toxicity, smoke) Pancreatitis Blood transfusion Drug overdose Head trauma |
|
|
What characteristics on CXR of a pulmonary nodule would suggest the lesion is malignant?
|
>3cm
Irregular, spiculated margin No calcification |
|
|
55 year old male pt presents with muscle weakness in his legs. An edrophonium test is negative. On exercise testing the pt demonstrates an incremental response to repetitive stimulation (post-exercise facilitation). What is the diagnosis?
|
Lambert-Eaton Myathenic Syndrome from a Small cell carcinoma of the lung
|
|
|
SIADH is paraneoplastic syndrome associated with which malignancy?
|
Small cell lung carcinoma
|
|
|
Hypercalcemia from PTHrP is paraneoplastic syndrome associated with which malignancy?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
HR: Increased
BP: Decreased JVP: Decreased Extremities cold What type of Shock? |
Hypovolemic
|
|
|
HR: Increased, N or decreased
BP: Decreased JVP: Increased Extremities cold Bilateral crackles on auscultation What type of Shock? |
Cardiogenic
|
|
|
HR: Increased
BP: Decreased JVP: Increased Extremities: Normal or cold What type of Shock? |
Obstructive (ie Massive PE, tension pneumo)
|
|
|
HR: Increased
BP: Decreased JVP: Decreased Extremities Warm What type of Shock? |
Septic (also anaphylaxis)
|
|
|
What are some distinguishing factors of stridor and wheeze?
|
Stridor
- Usually inspiratory - |
|
|
What are the 5 most common causes of community acquried pneumonia in healthy adults?
|
1. S. pneumoniae
2. Mycoplasma 3. Chlamydia 4. H. influenzae 5. Viral |
|
|
What are the 5 most common causes of community acquried pneumonia in the elderly/nursing home?
|
1. S. pneumonaie
2. H. influenzae 3. Gram neg bacilli 4. S. aureus 5. Legionella |
|
|
What are the 5 most common causes of nosocomial acquried pneumonia?
|
1. Enteric gram-neg rods
2. Pseudomonas 3. S. aureus |
|
|
What are some of the pulmonary complications of HIV infection?
|
1. TB
2. Pneumocystis jiroveci 3. Fungal pneumonias 4. HIV related pulmonary hypertension |
|
|
What is the managment for bronchiolitis?
|
Mild
- Supportive therapy - humidified oxygen - inhaled bronchodilator Moderate to severe - as above - intubation if necessary |
|
|
What does a stage IIIA NSCLC lung cancer indicate?
|
direct extension to chest wall pleura, pericardium, or ipsilateral mediastinal nodes
|
|
|
What does a stage IIIB NSCLC lung cancer indicate?
|
advanced local involvement (malignant effusion, major structures) or contralateral nodes positive
|
|
|
In which age groups is L. monocytogenes an important consideration in the etiology of menigitis?
|
Very young and very old
Neonates Elderly |
|
|
What medications are commonly used for prophylaxis for household and close contacts of pts with Hib or N. meningitidis meningitis?
|
Rifampin
Ciprofloxacin |
|
|
At what adult age is a pneumococcal vaccination recccomended?
What type of vaccination? |
-65 and older
- Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (Pneumovax) |
|
|
What are some of the clinical features which differentiate typical pneumonia from atypical pneumonia?
|
Typical
- SOB, pleuritic chest pain, productive cough, tachypnea - Dullness to percussion, bronchial breathing - CXR: dense lobar consolidation Atypical - Insidious onset of fever, non-productive cough, headache, myalgias, malaise - rales, ronchi, rarely consolidation CXR: interstitial patchy bronchopneumonic infiltrates |
|
|
What does the term rhonchi mean?
|
Wheeze or snoring sound
|
|
|
Zanamivir and oseltamivir are effective against both Type A and B influenza.
True/False? |
False
Effective only against Type A |
|
|
Which virus was implicated in the SARS pandemic of 2002?
What is the structure of this virus? |
Coronavirus
ssRNA Enveloped |
|
|
What is the risk of contracting the following following needle stick injury?
1. HIV 2. HCV 3. HBV |
1. 0.3%
2. 3% 3. 30% |
|
|
What % of acutely infected Hep C pts will go onto to being chronically infected?
|
80%
|
|
|
What % of acutely infected Hep B pts will go onto to being chronically infected?
|
5%
|
|
|
What fungus is commonly associated with exposure to chicken coops, bird roots and bat caves?
|
Histoplasmosis capsulatum
|
|
|
A Philipino, diabetic with HIV and in the 3rd trimester of her first pregancy presents with flu like symptoms after a recent trip to Arizona.
What infectious agent should be suspected? |
Coccidioides immitis
|
|
|
What muscle opens the eye?
What nerve innervates that muscle? |
Levator palpebrae superioris
(CN III oculomotor n.) |
|
|
What is trichiasis?
|
eyelashes turned inwards
|
|
|
What is an Entropion?
|
lid margin turns in towards globe causing tearing, foreign body sensation and red eye. Commonly affects lower lid
|
|
|
What is an Ectropion?
|
Lid margin turns outward from globe causing tearing and possibly exoposure keratitis
|
|
|
What is the test for an entropion?
|
Forced lid closure: lid rolls inwards
|
|
|
What is the test for an Ectropion?
|
Snapback test: pull eyelid inferiorly. If positive lid remains away from globe.
|
|
|
What is a hordeolum?
|
AKA stye. acute inflamm. of eyelid gland (meibomian or other)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a stye?
|
- Warm compress, lid care gentle massage
- Topical erythromycin ointment BID) |
|
|
What is a chalazion?
|
Chronic granulomatous inflamm. of Meibomian gland
|
|
|
What are the important DD of a suspected chalazion?
|
BCC
Sebaceous cell adenoma Meibomian gland carcinoma |
|
|
What is the treatment for a chalazion after 1 month with no improvement?
|
Consider incision and curettage.
|
|
|
What is Blepharitis?
|
inflamm. of lid margins
commonly caused by S. aureus |
|
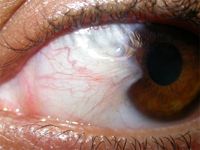
Diagnosis?
|
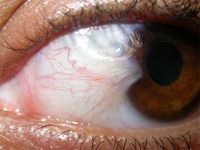
Pterygium
|
|
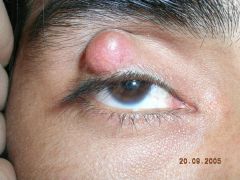
Diagnosis and important DD
|
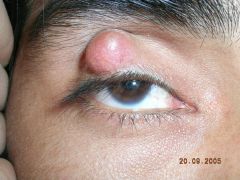
Chalazion
DD: BCC, Sebaceous cell adenoma, Meibomain gland carcinoma |
|
|
A long term user of contact lens presents with red eyes with mucoid discharge from the eyes. What is the likely diagnosis?
|
Giant paillary conjunctivitis
(immune rxn to mucus debris on lenses, a subtype of allergic conjunctivitis) |
|
|
What are the features of viral conjunctivitis which would help differentiate it from bacterial cause?
|
Viral
- Serous discharge - pre-auricular node often palpable Bacterial - purulent discharge - chemosis - lid swelling |
|
|
Neonate presents on day 10 of life with conjunctivitis. What is the most likely cause?
|
Chlamydial infection
|
|
|
Neonate presents on day 2 of life with conjunctivitis. What is the most likely cause?
|
Gonorrhea
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Chlamydial conjunctivitis?
|
topical and systemic tetracyclines
|
|
|
What are some connective tissue diseases associated with Scleritis?
|
SLE
RA Ank spondylitis (AS) |
|
|
What structure provides 2/3 of the refractive power of the eye?
|
Cornea
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the cornea?
|
V1
|
|
|
What is the treatment for HSV keratitis?
|
topical antiviral (trifluridine)
consider systemic antiviral acyclovir MUST AVOID STEROIDS (initially)! |
|
|
What 3 structures comprise the uveal tract?
|
Iris
Ciliary body Choroid It is the vascularized middle layer of the eye |
|
|
What must be ruled out in a pt with a suspected vitreous hemorrhage? What test is used?
|
Retinal detachment
Can use ultrasound (B-scan) |
|
|
What question must be asked in a pt with post-traumatic endophthalmitis?
|
Vaccination status for tetanus
|
|
|
A cherry red spot at the centre of the macula and retinal pallor. What is the diagnosis?
|
Central retinal artery occulsion (emboli or thrombus)
|
|
|
What are the 5 classes of medications which can be used to treat glaucoma?
|
Increase aqueous outflow:
- Cholinergics - Prostaglandin analogues - Alpha adrenergics Decrease aqueous production: - beta blockers - carbonic anhydrase inhib - alpha adrenergics |
|
|
Long term use (>4 weeks) of optical topical steroids decreases intraocular pressure.
T/F ? |
FALSE
INCREASES IOP |
|
|
What is the treatment for acute closed angle glaucoma?
|
Immediate treatment
- Refer to ophthalmologist - laser iridotomy BACH B - beta-blockers A - Adrenergics C - Cholinergics H - Hyperosmolar agents (acetazolamide, mannitol) |
|
|
What are the 5 targets of retinal signals and what is their role?
|
1. Pre-tectal nucleus (pupillary reflex/eye movements
2. Lateral geniculate nucleus 3. Superior colliculus (eye movements) 4. Suprachiasmatic nucleus (optokinetic) 5. Accessory optic system (circadian rhythm) |
|
|
What are the screening guidelines for diabetic retinopathy in T1DM?
|
Beginning annually 5 years after disease onset
- not indicated before onset of puberty |
|
|
What are the screening guidelines for diabetic retinopathy in T2DM?
|
At diagnosis then annually
|
|
|
What are the key ocular features under ophthaloscopy which suggest chronic HTN retinopathy?
|
AV nicking
Blot retinal hemorrhages Microaneurysms Cotton wool spots |
|
|
Management of suspected globe rupture?
|
CAN'T forget
C - CT orbits A - Ancef (cefazolin) IV N - NPO T - Tetanus status |
|
|
What are the 6 A's of Anesthesia?
|
A - amnesia
A - autonomic stability A - anesthsia A - anxiolysis A - areflexia A - analgesia |
|
|
What is the recommended amount of fasting time prior to anesthesia after ingestion of human breast milk?
|
4 hours
|
|
|
What is the recommended amount of fasting time prior to anesthesia after ingestion of non-human milk?
|
6 hours
|
|
|
What equipment is needed to put a pt under general anesthesia?
|
MD SOLES and MABLE
M - Monitoring equipment D - Drugs S - Suction O - Oxygen L - laryngoscopes (+ alternates, and light sources) E - ETT S - Stylet, Syringe MABEL M - Masks (sizes, alternates) A - Airway devices/assists (Geudel, NPA, Suction, ) B - Bag (+ auto external refilling bag) E - ETT (sizes) L - Laryngoscopes (light sources, different blades) |
|
|
In determining the speed of induction of anesthesia using volatiles, an increase in the cardiac input decreases the length of time for the induction of anesthesia.
T/F? |
FALSE
Increased CO, greater gas uptake to the blood which decreases alveolar gas concentration thus increasing the length of time for induction. |
|
|
Where is plasma cholinesterase, which breaks down succinylcholine, mivacurium and ester local anesthetics, produced?
|
Liver
|
|
|
What two anti-muscarinic drugs are commonly used to prevent the muscarinic side effects when reversing neuromuscular blockade?
|
Atropine
Glycopyrrolate |
|
|
What side effects are prevented with atropine is given when reversing neuromuscular blockade?
|
Salivation
Bradycardia Increased gut peristalsis |
|
|
At what spinal level does the trachea bifircate?
|
T5
|
|
|
What are the 5 advantages to ETT over other forms of airway managment?
|
5 P's
P - protect airway P - positive pressure ventilation P - patency ensured P - allows suctioning (Pulmonary toilet) P - pharmacological medication can be administered |
|
|
What the approx size ranges for ETT in :
1. Males 2. Females 3. Pediatric |
1. 8 - 9mm
2. 7 - 8 mm 3. Age/4 + 4 mm |
|
|
What are the length ranges on endotracheal tubes which indicate that the ETT is placed in the proper position?
1. Men 2. Women |
Men - 19.0cm - 21.0cm
Women - 20.0cm - 23.0cm |
|
|
How can you estimate the FiO2 in someone receiving nasal prong O2?
What is the Fi02 in someone receiving 3L of NP O2? |
1L = 4%
3L = 12% 12% + 21% = 33% |
|
|
Whats the max FiO2 which can be achieved w/ a Hudson mask?
At what flow rate? |
At 10L /min
FiO2 = 55% |
|
|
Whats the max FiO2 which can be achieved w/ a non-rebreather mask?
At what flow rate? |
At 10-15 L /min
>80% |
|
|
What are 2 options in oxygen therapy for the delivery of high flow oxygen at specified and consistent levels
|
Venturi mask
Puritan mask |
|
|
What effect does hyperthermia have on CO2 in a pt under anesthesia?
|
Can cause hypercapnia
HypOthermia can cause hypOcapnia |
|
|
What effect does hypothermia have on:
1. Wound infections 2. Hospitalization 3. Platlet function 4. V-tach and other morbid CV events 5. Metabolism of anesthetic agents |
1. increases risk of infection thru inhibition of immune system
2. Increases hospital stay (infection) 3. Decreases platelet function 4. Triples the incidence of V-tach and other morbid CV events 5. Decreases the metabolism of anesthetic agents |
|
|
From an anesthetic POV, what must be ruled out in intraoperative bradycardia?
|
Hypoxia
|
|
|
What are the 6 types of shock?
|
1. Cardiogenic
2. Hypovolemic/Hemorrhagic 3. Neurogenic (decreased sympathetic tone) 4. Anaphylatic 5. Obstructive (PE, tension pneumo, tamponade) 6. Septic |
|
|
What is the treatment for severe anaphylatic shock
|
1. ABC's
2. IV or nebulized epinephrine (1:1000, 0.1 - 0.3 mg) repeat as necessary 3. Anti-histamines (Benadryl 50mg IV (~1mg/kg) 4. Steroids - hydrocortisone (100mg IV )or methylprednisolone (1mg/kg IV q6h x 24 hrs) 5. Consider crystalloids |
|
|
What are the approx daily water requirements in a healthy adult?
What are areas of fluid loss and how much? |
~2500ml / day
1. Fecal loss = 200ml/day 2. Insensible losses = 800ml/day 3. Urine losses = 1500ml/day |
|
|
What is the rule for calculating maintenance fluids?
|
4ml/kg/hour for the 1st 10kg
2ml/kg/hour for the 2nd 10 kg 1ml/kg/hour after >20kg eg. 70kg maintenance fluid 4ml/kg/hour x 10kg = 40ml 2ml/kg/hour x 10 kg = 20ml 1ml/kg/hour x 50kg = 50ml TOTAL is 110ml/kg/hour Applies to cystalliods only |
|
|
What are the daily requirements for:
1. Sodium each day 2. Potassium each day |
1. Na = 150mEq/day
2. K = 100 mEq/day |
|
|
What % of body wt is total body water?
1. Males 2. Females |
1. Males = 60%
2. Females = 50% |
|
|
Of total body water:
1. How much is ICF and ECF? 2. Of ECF how much is interstitial and intravascular? |
1. ICF = 2/3
ECF = 1/3 2. ECF = 3/4 intersitial + 1/4 intravascular |
|
|
Oliguria, orthostatiic hypotension, tachycardia, low volume pulse, cool
extremities, reduced filing of peripheral veins and CVP. are signs of what level of dehydration? |
Moderate = 6%
|
|
|
What is the general rule in crystalloid volume replacement in a pt under going surgery with blood loss.
|
3:1 rule
3ml of crystalloid per 1ml of blood loss |
|
|
What is the consequence of giving too much Normal saline?
|
Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
Crystalloids distribute within the _______ volume, whereas colloids distribute within the ________volume
|
Crystalloids = ECF
Colloids = intravascular |
|
|
Give examples of crystalloids?
|
NS
Ringers Hartmans |
|
|
Give examples of colloids?
|
RBCs
FFP albumin Voluven Pentaspan |
|
|
NS contains how much of the following components?
Na K Ca Mg Cl HC03 m0sm/L |
Normal saline
Na = 154mmol/L K = 0 Ca = 0 Mg = 0 Cl = 154mmol/L HC03 = 0 m0sm/L = 308 |
|
|
Ringers lactate contains how much of the following components?
Na K Ca Mg Cl HC03 m0sm/L |
RL
Na = 130mmol/L K = 4mmol/L Ca = 3mmol/L Mg = 0 Cl = 109mmol/L HC03 = 28 (converted from lactate) m0sm/L = 273 |
|
|
How much does 1U of PRBCs increase the Hb in a 70kg patient?
|
10g/L
|
|
|
What is the blood volume in a:
1. Term infant 2. Adult male 3. Adult female |
1. Term infant = 80ml/kg
2. Adult male = 70ml/kg 3. Adult female = 60ml/kg |
|
|
List the 6 immune transfusion reactions in blood transfusion?
|
1. Non-hemolytic: Febrile
2. Non-hemolytic: Allergic 3. Non-hemolytic: Anaphylatoid 4. Transfusion related lung injury: TRALI 5. Hemolytic: Acute 6. Hemolytic: Delayed |
|
|
What are the criteria for extubation?
|
1. patient must no longer have intubation requirements
2. patency: airway must be patent 3. protection: patient must have intact airway reflexes 4. patient must be oxygenating and ventilating spontaneously 5. adequate level of consiousness |
|
|
List 4 therapeutic options for post-op nausea?
|
1. dimenhydrinate (gravol)
2. prochlorperazine (stemitil) 3. metoclopromide (maxeran, maxalon) 4. ondansetron (zofaran) |
|
|
What 5 groups of pts must caution be used if giving NSAIDs
|
1. Renal insufficiency
2. Asthma 3. Coagulopathy 4. GI ulcers 5. Pregnant 3rd trimester |
|
|
What are some signs of malignant hyperthermia?
|
1. Unexplained rise in end-tidal C02
2. Increase in minute ventilation 3. Tachycardia 4. Rigidity 5. Hyperthermia (late sign) |
|
|
A pt with decreased renal function and liver failure is to undergo surgery. Which muscle relaxant should be used when intubating the patient?
|
Cisatracurium (Hoffman elimination)
- is not metabolized by the kidney or liver unlike Rocuronium, Vecuronium and others |
|
|
What is the max dose of:
1. Lidocaine (w/epinephrine 2. Bupivicaine (w/ epinephrine) |
1. Lidocaine (+epi) = 7mg/kg
2. Bupivicaine (+epi) = 3mg/kg |
|
|
What is glycopyrrolate?
|
An anti-cholinergic (muscarinic)
Commonly given while administering neostigmine or pyridostigmine (for NM blockage reversal) to prevent bradycardia, salivation, bowel persitalsis |
|
|
What are the so called "B symptoms" of lymphoma?
|
1. wt loss >10% in the last 6months
2. Night sweats 3. Fever >38 |
|
|
What is the ocular manifestation of neurofibromatosis type 1
|
Lisch nodules
- pigmented hamartomas of the iris |
|
|
What is the ocular manifestation of Marfans syndrome?
|
Lens dislocation
|
|
|
What are some extradisease manifestations of Rheumatoid arthritis?
|
1. Neuro
- Peripheral neuropathies 2. Skin - Rheumatoid nodules 3. Respiratory - lung fibrosis, 4. Cardiac - myocarditis, vavular disease 5. Ocular - scleritis, episcleritis 6. Head and neck - Xerostomia - Hashimoto's thyroiditis |
|
|
What is the treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
|
1. Reduction of inflammation and pain
- NSAIDS - Acetominophen a. Steroids - local or systemic Low dose prednisone (5-10mg) for refractory disease - mod to high dose >20mg for cardiopulmonary disease and vasculitis 2. Disease modifying agents - nonbiologics eg methotrexate, leflunomide, sulfasalazine, hydroxycloroquine - biologics eg inflixamab, entanercept |
|
|
What malignancies are associated with dermatomyositis?
|
1. Breast
2. Lung 3. Colon 4. Ovarian |
|
|
What is the classic triad in Sjogrens syndrome which identifies 93% of patients with the disease?
|
1. Dry eye (keratoconjunctivitis sicca)
2. Dry mouth (xerostomia) 3. Arthralgia (sml joint, asymmetrical, non-erosive) |
|
|
What autoantibodies can be found in a pt with Sjogrens syndrome?
|
Anti-Ro
Anti-La |
|
|
What autoantibodies can be found in a pt with dermatomyositis?
|
Anti-Jo
Also: ANA, anti-Mi-2, anti-SRP |
|
|
What type of cancer are pts with Sjogrens syndrome at higher risk for ?
|
non-Hodgkins lymphoma
|
|
|
What triad is commonly found in pts with Churg-Strauss syndrome?
|
1. Allergic rhinitis/and or asthma
2. Eosinophilia (infiltrative disease resembling pneumonia) 3. Vasculitis (systemic) |
|
|
Polyarteritis nodosa is associated with what type of infection?
|
Hep B
specifically Hep B surface Ag+ pts |
|
|
What are extra-articular manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis?
|
6 A's
A - Atlanto-axial subluxation A - Anterior uveitis A - Apical lung fibrosis A - Aortic incompetence A - Amyloidosis (kidney) A - Autoimmune bowel disease (UC) |
|
|
1. What nerve roots contribute to the femoral nerve and the obturator nerve?
2. How can you differentiate between a radiculopathy or a peripheral nerve lesion in the above nerves? |
1. L2, 3 and 4 for both the femoral and obturator nerve
2. Femoral nerve = hip flexion Obturator nerve = hip adduction therefore if both hip flexion and adduction are reduced it suggests a radiculopathy. |
|
|
What muscle does the superficial peroneal nerve innervate? What is its action?
|
Peroneal muscles
Ankle EVersion |
|
|
What muscle does the tibial nerve innervate? What is its action?
|
Tibialis posterior
Ankle INversion |
|
|
What is the most common cause of late onset seizures (>50 years old)?
|
Stroke
|
|
|
What are some common causes of delirium?
|
I WATCH DEATH !!
I - Infection W - Withdrawal A - Acute metabolic disorder T - Toxins C - CNS pathology H - Heavy metals D - Deficiency in vitamins E - endocrine disorders A - acute vascular insults T - Trauma H - Hypoxia |
|
|
What is the definition of the terms:
1. Aphasia 2. Agnosia 3. Apraxia |
1. Aphasia - language disturbance
2. Agnosia - failure to recognize or name objects despite intact sensory function 3. Apraxia - Inability to carry out motor tasks despite intact motor function |
|
|
Lesions involving the cavernous sinus can affect which cranial nerves?
|
CN III, IV, V1, V2, VI
|
|
|
What is Cushing's triad of raised intracranial pressure?
|
Hypertension
Bradycardia (late sign) Abnormal resp. pattern |
|
|
What are some key features of myopathies?
Proximal/distal? Pain? Flaccid paralysis or myotonia? |
Proximal muscles affected
Myalgias common but not sensory Myotonia common |
|
|
What are some common medications that cause myopathies?
|
Statins
Steroids anti-retrovirals |
|
|
Patient presents after a stroke with hemianesthesia which then progresses to persistent spontaneous burning contralateral to lesion and altered response to light cutaneous and deep painful stimuli.
Where is the lesion? What is the syndrome called? |
Dejerina Roussy Syndrome
- injury to ventral posterolateral (VPL) and ventral posteromedial (VPM) nuclei of the thalamus |
|
|
What structures are involved in the nociception of headache?
|
Dura
Large intracranial vessels CN V |
|
|
Patients with narcolepsy have decreased levels of what in the CSF?
|
Hypocretin
|
|
|
Common causes of bacterial meningitis in Neonates?
|
GBS
E. coli L. monocytogenes |
|
|
Common causes of bacterial meningitis in elderly and immunocompromised?
|
S. pneumoniae
N. meningitidis L. monocytogenes |
|
|
Common causes of bacterial meningitis in adolescents and adults?
|
S. pneumoniae
N. meningitidis H. influenzae |
|
|
Common causes of viral meningitis?
|
Enteroviruses
HIV HSV-2 West Nile |
|
|
Common causes of encephalitis?
|
HSV
MMR West Nile HIV Polio CMV |
|
|
How does a lacunar stroke typically present?
|
Pure motor hemiparesis that typically affects the face, arm or leg of one side.
|
|
|
What is Todd's paresis?
|
Post-ictal paresis which typically affects one side of the body after seizure, usually self-limited
|
|
|
What gene has been associated with increased risk of multiple sclerosis?
|
HLA-DR2
|
|
|
What is the associated risk of developing MS if:
1. Monozygotic twin with MS? 2. Parent or sibling with MS? |
1. 30%
2. 2-4% |
|
|
What is the Female:Male ratio of MS in the 17-35 age group?
|
3:1
|
|
|
What are the common signs of a tumor in the cerebellopontine angle?
|
Commonly acoustic neuromas
- affects CN V, VII, VIII |
|
|
What are the branches of the Left coronary artery?
|
LAD
L. circumflex |
|
|
What are the branches of the Right coronary artery?
|
Acute marginal
AV nodal artery Posterior interventricular artery |
|
|
What are some of the side effect of Digitalis?
|
Palpitations
fatigue visual changes (yellow vision) decreased appetite hallucinations confusion and depression |
|
|
What % stenosis is considered hemodynamically significant in CAD?
|
70%
|
|
|
What are some absolute contraindications for thrombolysis in STEMI?
|
-prior intracranial hemorrhage
-known structural cerebral vascular lesion - known malignant IC neoplasm - significant closed head or facial trauma within 3months - Ischemic stroke within 3 months - active bleeding - suspected aortic dissection |
|
|
Person presents with chest pain suggestive of cardiac ischemia. What is your initial management and investigation?
|
ABC's
1. Morphine prn 2. O2 3. ASA 162 mg chewed 4. Nitroglycerin SL 5. ECG 6. Cardiac enzymes |
|
|
What is the initial treatment for an NSTEMI?
|
BEMOAN
B - beta blocker E - enoxaparin M - morphine O - oxygen A - ASA N - nitroglycerin IV |
|
|
In ejection fraction of the Left ventricle the following grades correspond to:
Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 |
Grade 1: >60% (normal)
Grade 2: 40-59% Grade 3: 20-39% Grade 4: <20% |
|
|
What are the 5 most common causes of CHF?
|
1. CAD (60-70%)
2. HTN 3. Idiopathic (often dilated cardiomyopathy) 4. Valvular (AS, AR, MR) 5. Alcohol |
|
|
What abnormal laboratory finding would you find in dilated cardiomyopathy?
|
High BNP
High Cr High LFTs Low bicarb Low Na |
|
|
What is Becks triad in cardiac tamponade?
|
Hypotension
Elevated JVP Muffled heart sounds |

