![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pharmacokinetics effects |
Those that explain what the body does to the drug Effects include: Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) of a drug molecule |
|
|
Pharmacodynamics effects |
Those that explain what the drug does to the body Effects include: Intensity, duration, and mechanism action of the same drug molecule Intrinsic within is the ability of tge drug molecule to interact with its biological target |
|
|
Biological targets |
Cab be organized into 4 catagories: Receptor Enzymes Nucleic acids Excitable memebranes/other biopolymers Typically composed of proteins or nucleic acids |
|
|
Specific properties of functional groups that allow drug molecules to exert the desired effect |
•Overall water/lipid solubility •Route of administration •Ability to interact with specific biological targets •Mechanism of action •Route of metabolism and elimination •Duration of action •Suitability for a specific therapeutic situation •Tendency to cause adverse effects or drug interactions |
|
|
Three overriding concepts that should consider when examining drug molecules |
1: every atom within the structure of a drug molecule is part of a specific functional group 2: within any given drug molecule or class of drug molecule, some functional groups will be more important than others 3- it is possible to alter functional groups to enhance activity, increase absorption, decrease adverse effects, or provide other therapeutic benefits |
|
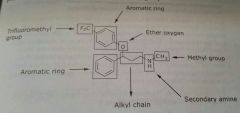
|
Fluoxetine Antidepressant Selectively blocks reuptake of serotonin |
|
|
Indomethacin NSAID Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
|
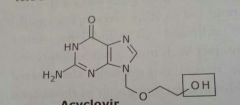
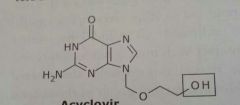
|
Acyclovir Zovirax Antiviral |
|
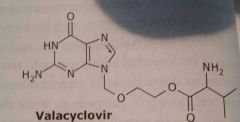
|
Valacyclovir Valtrex Antiviral |
|
|
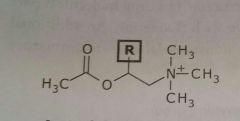
Acetylcholine Bethanecol Neurotransmitter |
|
|
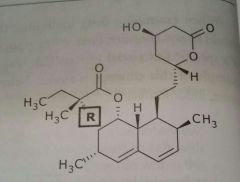
Lovastatin (mevacor) Simvastatin (zocor) Antihyperlipodemic Antihyperlipodemic |
|
|
3 major chemical properties of functional groups |
1- electronic effect 2- solubility effect 3- steric effect |
|
|
The addition of a functional group to a molecule will the ______ electronics, solubility, and steric dimensions of the molecule |
Overall Will effect all the effects. Not just one |
|
|
The overall effect of a given functional group depends upon ____ of the other functional groups surrounding or attached to it |
All |
|
|
Electronic effects |
Is measured by its ability to either donate it's electrons to adjacent atoms or functional group |
|
|
2 main components that comprise tge overall electronic effect of functional group |
1 - its ability to participate in resonance 2- its intrinsic inductive effects |
|
|
Reasonace |
Occurs when electrons are shared among a group of atoms that have adjacent double bonds and lone pairs of electrons. Since electrons are being shared, the overall structure is actually a hybrid of all the possible resonance structures |
|
|
The ability to allow a postive or negative charge to be _____ among multiple atoms is exyre important since it enhances the acidity or basic it of a specific functional group |
Shared |
|

|
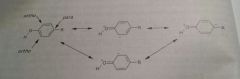
Reasonace structures of carboxylic acid |
|
|
Reasonace structures of an aromatic hydroxyl group |
|
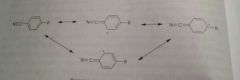
|
Reasonace structures of an aromatic nitrile group |
|
|
Intrinsic inductive character |
Of an atom or functional group depends on its overall electronegativity |
|
|
Electronegativity |
A chemical property that defines the ability of an atom or functional group to attract electrons towards itself and away from other atoms or functional groups |
|
|
The ______ the electronegativity the greater the ability of an atom or functional group to attract electrons |
Larger |
|
|
F, O, Cl, N have the _____ electronegativies, respectively, among the atoms in the peroid table |
Highest All above 3 |
|
|
With the sole exception of ___, O will inductive attract electrons from all other atoms |
F |
|
|
O, N, and the 4 halogens (F, Cl, Br, and I) will inductively attract electrons from _____. |
C |
|
|
Carbon will inductively attract electrons from ____ |
H |
|
|
Dipole |
Inductive effects (due to differences in electronegativity) will create a partial charge separation which results in a dipole |
|
|
Dipoles are very important in enhancing _____ _______ and allow a drug molecule to interact with its biological target |
Water solubility |
|
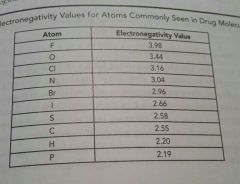
|
Electronegativity chart |
|

|
Example of a dipole |
|
|
Electron donating functional groups |
•negatively charged functional groups, such as carboxylic acid, can donate electrons through induction Also true for acidic fun groups •functional groups that contain a lone pair of electrons, such as a hydroxyl group, an aromatic amine, an aromatic thiol, or methyl group, can donate electrons into phenyl or aromatic ring system •alkyl groups, such as methyl group or ethyl group can serve as electrons donating groups through induction |
|
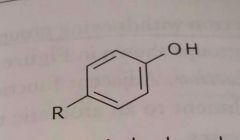
|
Aromatic hydroxyl Phenol Electron donating group |
|
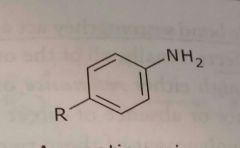
|
Aromatic amine Can be primary, secondary, or tertiary Electron donating functional group |
|
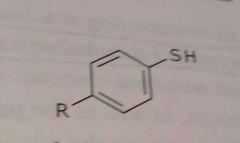
|
Aromatic thiol Electron donating functional group |
|
|
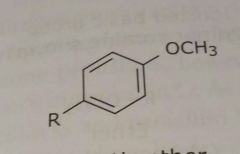
Aromatic ether (Methoxy group shown) Electron donating functional group |
|
|
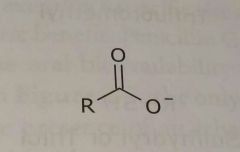
Ionized acidic group Carboxylic acid Electron donating functional group |
|
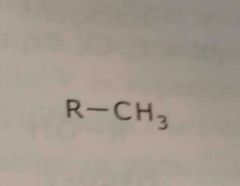
|
Alkyl group Methyl Electron donating functional group |
|
|
Nucleoplilic group |
"Nucleus loving" Attracted to the postive charge present in the necessary of an atom Involved in the formation of hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Nucleoplilic groups contain either a ______ charge or a _____ _____ of electrons that can be used to form covalent bond with a biological target, drug molecule, or endogenous compound |
Negative, lone pair |
|

|
Glutathione Has nucleophile |
|
|
Electron withdrawing functional groups |
• halogens, trifluoromethyl groups, as well as positively charged functional groups, such as ionized amine, will pull or withdraw electrons through induction • when hydroxyl groups, sulfa y dry groups, and ether groups are not adjacent to either an aromatic ring or a double bond system, they act as electron withdrawing groups as a result of thier inductive effects |
|
|
All electron withdrawing functional groups can withdrawal electrons through either ______ or _______ |
Resonance or induction Adjacent functional groups will determine the relative involvement of these 2 processes |
|
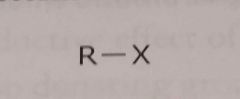
|
Halogen X= F, Cl, Br, or O Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
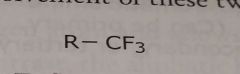
|
Trifluoromethyl Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
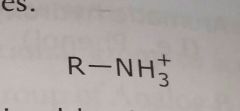
|
Ionized basic group (Primary amine shown) Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
|
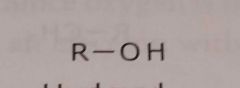
Hydroxyl Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
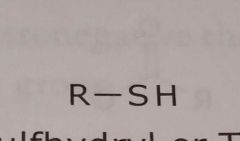
|
Sulfhydryl or thiol Electron withdrawing functional group |
|

|
Ether (Methoxy shown) Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
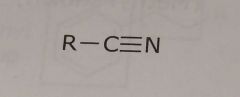
|
Nitrile group Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
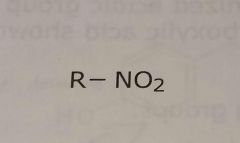
|
Nitro group Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
|
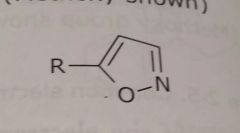
Aromatic hetrocycle Isoxazole ring shown Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
|
Aldehyde Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
|
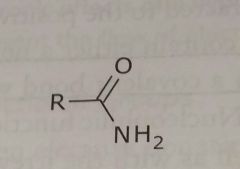
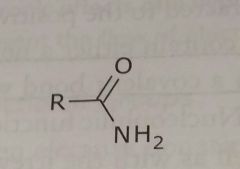
Amide Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
|
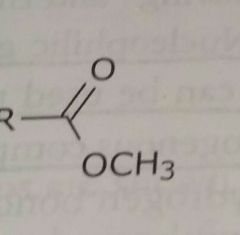
Ester Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
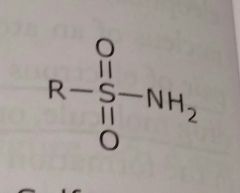
|
Sulfonamide Electron withdrawing functional group |
|
|
Electrophilic group (electrophile) |
"Electron loving" Contain postive charges or a good leaving group, such as a halogen or an ester |
|
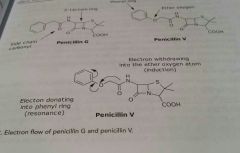
|
Example of electron flow, electron withdrawing effect |
|
|
The overall water and/or lipid ______ of a drug molecule affects it's route of administration, distribution within the body, metabolism, duration of action, and route of elimination |
Solubility |
|
|
The ______solubility is a composite sumer of the contribution of each functional group present in the drug structure |
Overall |
|
|
Hydrophilic functional groups |
Enhances the water solubility of a drug molecule |
|
|
2 major properties that contribute to the water solubility of a functional group |
• Ability to ionized •Ability to form H bonds |
|
|
Functional group ionization imparts an increase in water solubility of a drug molecule |
Acidic and basic functional groups are capable of ionization and can become negatively or positively charged |
|
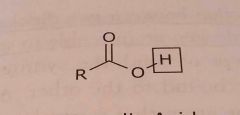
|
Carboxylic acid Acidic functional group |
|
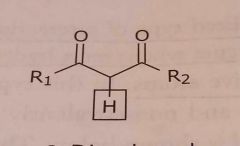
|
B-Dicarbonyl Acidic functional group |
|
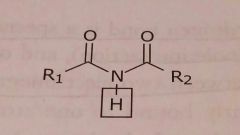
|
Imide Acidic functional group |
|
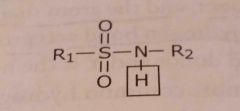
|
Sulfonamide Acidic functional group |
|
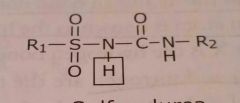
|
Sulfonylurea Acidic functional group |
|
|
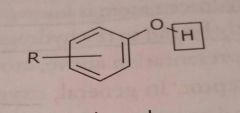
Phenol Acidic functional group |
|
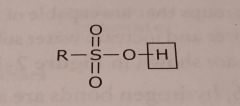
|
Sulfonic acid Acidic functional group |
|
|
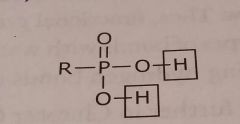
Phosphoric acid Acidic functional group |
|
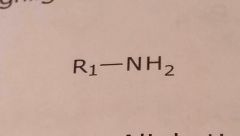
|
Primary aliphatic amine
Basic functional group |
|
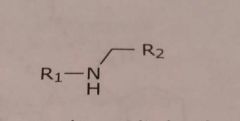
|
Secondary aliphatic amine Basic functional group |
|
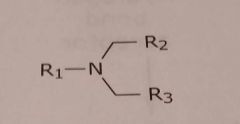
|
Tertiary aliphatic amine Basic functional group |
|
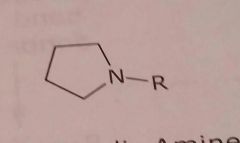
|
Alicyclic amine Basic functional group |
|
|
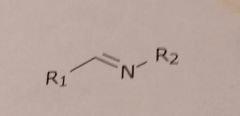
Imine Basic functional group |
|
|
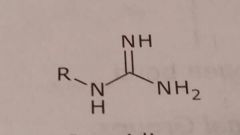
Guanidine Basic functional group |
|
|
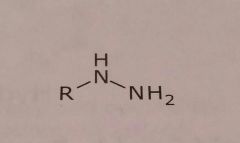
Hydrazine Basic functional group |
|
|
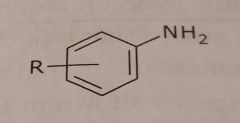
Primary aromatic amine Basic functional group |
|
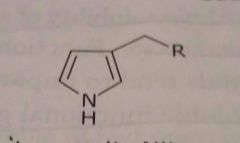
|
Pyrrole ring Hetrocyclic ring Basic functional group |
|
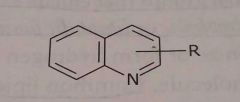
|
Quinoline ring Hetrocyclic nitrogen Basic functional group |
|
|
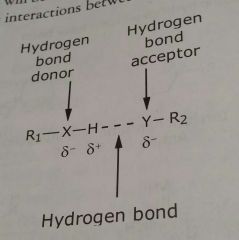
Hydrogen bonds |
Specialized type of interaction between two dipoles (a dipole - dipole interaction) |
|
|
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is able to serve as a _____ between two _________ atoms |
Bridge, electronegativity H is covalently bonded to one atom and non-covalently bonding to the other atom |
|
|
Hydrogen bond donor |
Atom covalently bound to the hydrogen atom |
|
|
Hydrogen bond acceptor |
Atom that is non-covalently bonded to H |
|
|
Example of hydrogen bond |
|
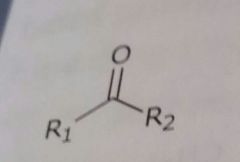
|
Ketone Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
|
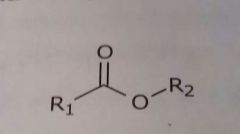
Ester Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
|
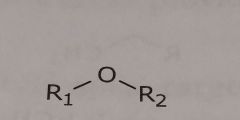
Ether Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
|
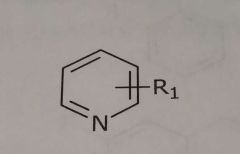
Pyridine Hetrocyclic nitrogen Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
|
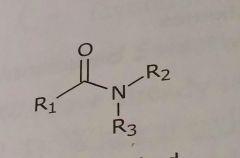
Disubstituted amides Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
|
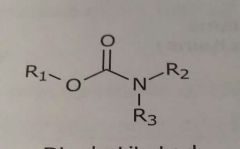
Disubstituted carbamates Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
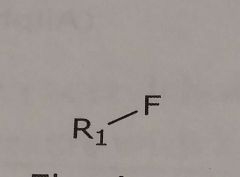
|
Fluorine Hydrogen bond acceptor |
|
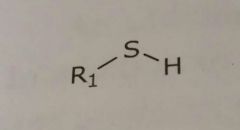
|
Thiol Hydrogen bond donor |
|
|
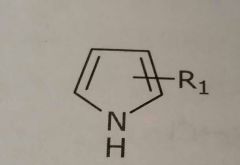
Pyrrole ring Hetrocyclic nitrogen Hydrogen bond donar |
|
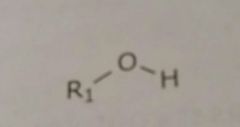
|
Hydroxyl Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
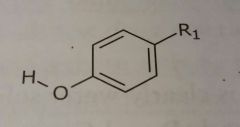
|
Phenol Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
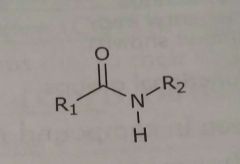
|
Amide Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
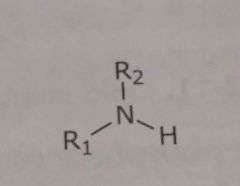
|
Primary and secondary unionized amines Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
|
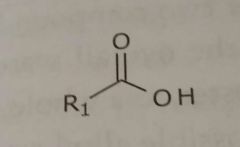
Unionized carboxylic acid Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
|
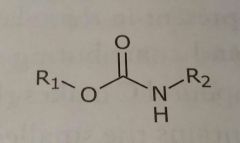
Carbamates Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
|
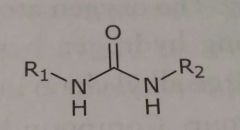
Urea Hydrogen bond acceptors and donors |
|
|
Lipid soluble functional groups |
Hydrophobic or lipophilic Functional groups that enhance the lipid solubility of a drug molecule |
|
|
Functional groups that _____ the ability to either ionized or form H bonds tend to lend a drug molecule some lipid solubility |
Lack |
|
|
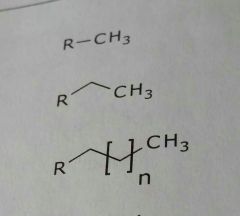
Common lipid soluble functional groups |
•Unsubstituted aromatic rings •Alkyl groups (aliphatic side chains) •Unsubstituted carbon rings (alicyclic rings) •Halogens |
|
|
Alkyl chains (aliphatic chains) Lipid soluble functional group |
|
|
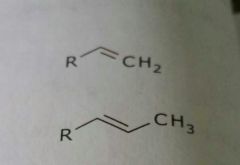
Alkenes Lipid soluble functional group |
|
|
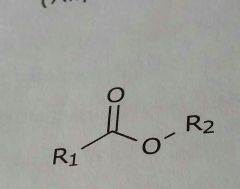
Ester Lipid soluble functional group |
|
|
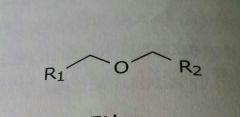
Ether Lipid soluble functional group |
|
|
Every atom within the structure of a drug molecule is part of a specific _______ ______ |
Functional group |
|
|
The importance of a given functional group will vary among drug molecules and drug classes |
• a specific functional group can produce different effects on different drug molecules
• it is possible for a single functional group ti serve more than one distinct purpose on a single drug molecule |
|
|
Each functional group has an electronic effect, solubility effect, and ______ effect |
Steric |
|
|
It is possible for a functional group to alter only one of _______, _________, _______ properties without effecting the others |
Electronic, solubility, and steric |
|
|
The relative importance of electronic, solubility, and steric properties will vary depending upon the _______ ____ |
Functional group |
|
|
The overall electronic effect of a given functional group depends on both its ability to participate in _______ delocalization and it's intrinsic _____ effect |
Reasonace, inductive |
|
|
Some electron donating groups can also act as _______, where's electron withdrawing groups acts can also act as ________. |
Nucleophile, electrophile |
|
|
The two key properties that contribute to water solubility of a functional group are it's ability to ____ and it's ability to participate in ________ _____ interactions |
Ionize, hydrogen bonding |
|
|
Each functional group has a finite size or ______ dimension that contributes to the overall conformation of a given drug molecule |
Steric |
|
|
The _____ effect of a given functional group is dependent upon other adjacent or surrounding functional groups |
Overall |
|
|
Functional groups can be altered ti provide specific _____ benefits |
Therapeutic |

