![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
alleles |
different forms of the same gene |
|
|
gametes |
haploid |
|
|
germ cells |
divide to create gametes |
|
|
fertilization |
diploid number restored; when two haploid gametes (one egg and one sperm, for example) fuse to form a zygote |
|
|
meiosis 1 |
1 diploid nucleus to 2 haploid nuclei |
|
|
prophase 1 |
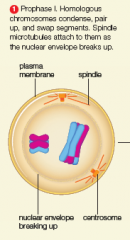
|
|
|
metaphase 1 |
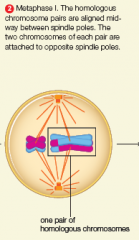
|
|
|
anaphase 1 |
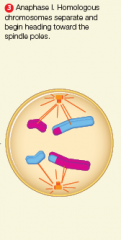
|
|
|
telophase 1 |
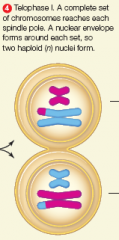
|
|
|
meiosis 2 |
2 haploid nuclei to 4 haploid nuclei |
|
|
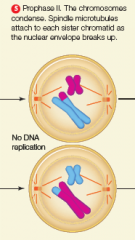
prophase 2 |
|
|
|
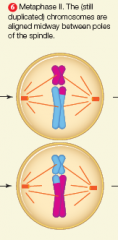
metaphase 2 |
|
|
|
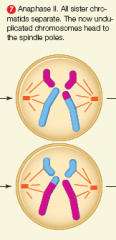
anaphase 2 |
|
|
|
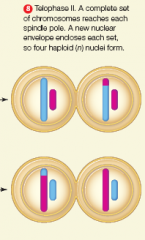
telophase 2 |
|
|
|
crossing over |
a chromosome and its homologous partner exchange corresponding pieces of DNA |
|
|
chromosome segregation |
Each nucleus contains one of eight (2^3) possible combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes; human gametes have 23 pairs of chromosomes, not 3, so in reality its 2^23 possible combinations |
|
|
sporophyte |
typically diploid, and spores form by meiosis; Spores consist of one or a few haploid cells, which undergo mitosis and give rise to gametophytes |
|
|
gametophytes |
multicelled haploid bodies inside which one or more gametes form |

