![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fisher effect
|
i = r + l
|
|
|
Investor Psychology
|
is the theory that people don't always behave rationally; they don't always use logical approaches when making decisions
|
|
|
Bandwagon effect
|
refers to the fact that people often do things only because many other people are doing the same thing
|
|
|
predicting Investor psychology and bandwagon effects
|
is almost impossible to do
|
|
|
Firm-level risks (Exchange rate risk)
|
risks to an individual firm include transaction risk, translation risk, and economic risk
|
|
|
Transaction risk (firm-level risks)
|
the extent to which the income from individual transactions is affected by fluctuations in foreign exchange values
can impact PAYABLES and RECEIVABLES |
|
|
Translation risk (firm-level risks)
|
impact of exchange rate changes on a firm's consolidated financial statements
Fluctuations in exchange rates may impact investor's perceptions of the firm's financial performance Ex: if peso goes down, they wont be able to buy as many dollars as before |
|
|
Economic risk (firm-level risks)
|
the extent to which a firm's future international earning power is affected by changes in exchange rates
impacts SALES and OPERATING expenses a firm may need to reconfigure its operating structure to reduce economic risk |
|
|
Risks to National Economies (Exchange Rate Risk)
|
Impacts the overall ATTRACTIVENESS OF ITS EXPORTS
nations may LOSE MANUFACTURING OPERATIONS (due to high currency values) variability in exchange rates makes a nation LESS ATTRACTIVE TO GLOBAL INVESTORS |
|
|
Exchange Rate Risk Management tools
|
Forecasting
Payment Strategies Financial Hedging Operational Hedging |
|
|
Forecasting (Exchange Rate Risk Management tools)
|
only works if you are ACCURATE IN YOUR PREDICTIONS of the exchange rate
Efficient Market School - predictions taken from WSJ, newspapers, etc; best prediction Inefficient Market School - belief that using one's own hypothesis is best |
|
|
Fundamental Analysis (Forecasting)
|
uses economic theory to form sophisticated econometric models for predicting exchange rate fluctuations
|
|
|
Technical Analysis (Forecasting)
|
Doesn't focus on inflation and interest rates
more focused on things like investor psychology and bandwagon effects looks at trends and patterns of PRICE AND VOLUME DATA over time |
|
|
Head and Shoulder Approach (Technical Analysis) (Forecasting)
|
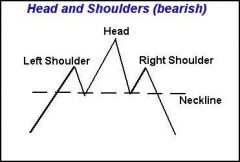
FIRST SHOULDER is a spike in an asset, then it goes back down
the second SUPER SPIKE is the HEAD and then the asset goes back down then there is a 3rd spike (2nd SHOULDER) but doesn't go as high as the head |
|
|
Lead Strategies (Payment Strategy) (Exchange Rate Risk Management)
|
when a firm swiftly attempts to collect foreign currency receivables when the foreign currency is expected to DEPRECIATE
paying foreign accounts payable BEFORE they're due when a foreign currency is expected to APPRECIATE |
|
|
Lag Strategy (Payment Strategy) (Exchange Rate Risk Management)
|
when a firm delays on collecting foreign currency receivables if that currency is expected to APPRECIATE
when a firm delays paying foreign account payables if the foreign currency is expected to DEPRECIATE |
|
|
Financial Hedging (Exchange Rate Risk Management)
|
Forward Contracts
Options Currency Swaps |
|
|
Forward Contracts (Financial Hedging)
|
WHAT IT IS: a contract between 2 parties to exchange currencies on a future date at an agreed upon exchange rate. Usually for 30, 90, or 180 days
REASON: eliminates risk because you nailed down the future exchange rate today, BUT you can miss out on an upward gain if exchange rates fluctuate in your favor |
|
|
Options (Financial Hedging)
|
gives the right, NOT obligation, to buy or sell a certain amount of foreign currency at a SET EXCHANGE RATE at a specified time
gives more FLEXIBILITY Options result in asymmetric risk: ONLY THE HOLDER OF THE OPTION WILL GAIN IF THERE IS A CHANGE IN THE VALUE OF THE CURRENCIES Premiums are usually higher for options than for forward contracts (8% instead of 2-3%) |
|
|
Currency Swaps (Financial Hedging)
|
foreign exchange transaction between 2 firms in which one currency is converted into another at Time 1, with an agreement to revert back to the original currency at a specific Time 2 in the future
BENEFIT of currency swap - not necessarily a profit-generating transaction, because it's usually between a parent company and subsidiary, or banks taking advantage of 2 customers with different currencies Swaps bring together 2 counter-parties with opposite hedging needs |
|
|
Operational Hedging (Exchange Rate Risk Management)
|
seeks to distribute the firm's productive assets to various locations and to create slack in the firm's supply chain
|
|
|
Types of Securities (Structure of the Global Capital Market)
|
Equity vs Debt Loans
|
|
|
Participants in the Global Capital Market (Structure of the Global Capital Market)
|
Corporations
Governments Investors Financial Institutions |
|
|
Growth of the Global Capital Market
|
Advantages in information technology
Deregulation by governments |
|
|
The Borrower's Perspective (Benefits of Financial Globalization)
|
Lower cost of capital
Increase investor pool --> more potential investors to loan money at lower interest rates; the lower the cost for capital, the better it is for business because there are more possibilities for more projects to invest in |
|
|
The Investor's Perspective (Benefits of Financial Globalization)
|
Portfolio Diversification
Higher Returns |
|
|
Excessive Capital flows (Dangers of Financial Globalization)
|
too much investors and capital may result in inflation
|
|
|
Contagion (Dangers of Financial Globalization)
|
"Hot Money"
"Patient Money" |
|
|
"Hot Money" (Contagion) (Dangers of Financial Globalization)
|
one is seeking out a very quick return; NOT necessarily a long-term commitment; as soon as things start to cool off, the investor will pull out and go to the next hot opportunity
CONSTANTLY MOVING AROUND. ANY HINT OF TROUBLE AND YOU'RE OUT AND ONTO THE NEXT OPPORTUNITY Makes capital flows more challenging if there is no restrictions on people pulling out money whenever they want |
|
|
"Patient Money" (Contagion) (Dangers of Financial Globalization)
|
Money invested over a long period of time that is left there even if there is minor downturn
STAYS IN ONE PLACE. STAYS EVEN WITH LITTLE HINTS OF TROUBLE |
|
|
The Eurocurrency Market
|
A eurocurrency is any currency banked outside of its country of origin to be beyond the reach of the national government who issued it
DOES NOT NECESSARILY HAVE TO DO WITH THE EURO not going to put restrictions on the foreign currency because they are less worried about the movement of the foreign currency than their own Saves them money because they don't have to have the reserve requirements Eurocurrency market is made up of financial institutions that accept deposits and makes loans in foreign currencies Eurocurrency accounts are outside the regulation of the country issuing the currency |
|
|
Foreign Bonds (The Global Bond Market)
|
are sold outside the BORROWER's country and are denominated in the currency of the country in which they are issued
Example: if the cost of capital were CHEAPER in Mexico, the US might sell bonds in Mexico instead of the US because it lowers the cost of capital if issued in other markets |
|
|
Eurobonds (The Global Bond Market)
|
are underwritten by a syndicate of banks and placed in countries other than the one in whose currency the bond is denominated
Example: US sold eurobonds to Japanese firms that are denominated in euros. A bond sold in Japan in someone else's currency is not under Japan's government's control. GIVES BUSINESSES MORE FLEXIBILITY because they're NOT CONSTRAINED by governmental regulation |
|
|
The Global Equity Market
|
More firms are listing their stock in the equity markets of other nations and issuing stock in foreign markets to RAISE NEW CAPITAL and INCREASE THE POOL OF POTENTIAL INVESTORS
Corporate nationality is becoming less relevant because investors in the nation where a firm is headquarted may not be the dominant source of the company's investor pool The country is no longer restricted to their domestic market |
|
|
Advantages of the Eurocurrency Market
|
Less regulations/restrictions
Reserve requirements for eurocurency accts aren't regulated; all the money can be lent out Eurocurrency accts have a smaller interest rate spread than domestic accts Investors gain more money and borrowers spend less money SAVERS earn a HIGHER INTEREST RATE and BORROWERS pay a LOWER INTEREST RATE with eurocurrency accts |
|
|
Disadvantages of the Eurocurrency Market
|
Higher risk of bank failure since it's unregulated
Individuals and companies borrowing eurocurrencies can be exposed to foreign exchange risk (can be counted with forward contracts, currency swaps, etc) |
|
|
Foreign Exchange Risk and the Cost of Capital
|
Unfavorable changes in exchange rates can increase the cost of foreign-currency loans
Borrowers can use financial hedging to reduce their exchange rate risk, BUT this will RAISE COSTS Borrowers must weigh the benefits of a lower interest rate against the risk of an increase in the cost of capital due to unfavorable exchange rate movements |
|
|
Ethnocentrism
|
characterized by or based on the attitude that one's own group is superior
|
|
|
Cultural Determinism
|
Nurture beats nature
is the idea that the culture we are raised in determines the emotional and behavioral aspects of our personalities. It argues that environment determines who we are, rather than biology. |
|
|
Foreign Exchange Risk
|
The risk of an investment's value changing due to changes in currency exchange rates
|
|
|
Foreign Exchange Market
|
The market in which participants are able to buy, sell, exchange and speculate on currencies.
|
|
|
Communication Context
|
The extent to which a message must be inferred from contextual or situational aspects
|
|
|
Low-Context Communication
|
information expressed is contained in words
|
|
|
High-Context Communication
|
the message is contained in SITUATIONAL or CONTEXTUAL factors
Ex: In Japan, "i'll have to check with my boss and get back to you" is a polite way of turning down a business transaction |
|
|
Cross-Cultural Literacy
|
understanding how cultural differences can affect the way business is practiced
|
|
|
Cultural Awareness
|
provides insights into the way cultures vary
|
|
|
Cultural Distance
|
is a measure of the degree of difference between 2 cultures
|
|
|
Cultural Frameworks
|
tools for measuring cultural distance
can provide a good first guess for how to interact with people from other cultures should be used as a "compass" rather than a map; don't use as a recipe but more as guidelines; use your judgement |
|
|
Power Distance (Hofstede)
|
society's tolerance for inequality
|
|
|
Uncertainty Avoidance (Hofstede)
|
extent to which a culture accepts ambiguous situations and tolerates uncertainty
|
|
|
High Uncertainty Avoidance
|
clear, structured rules and policies; avoids uncertainty at all costs
|
|
|
Low Uncertainty Avoidance
|
more relaxed laissez-faire, spontaneous
not intimidated by an environment where everything needs to get done "go with the flow" |
|
|
Masculinity vs Femininity (Hofstede)
|
the degree to which people in a culture accept traditional Western gender roles
|
|
|
Masculinity (Hofstede)
|
"American Dream" - having a big house, nice car, etc
VERY MATERIALISTIC $ = happiness |
|
|
Femininity (Hofstede)
|
money doesn't necessarily bring happiness
NOT MATERIALISTIC family oriented |
|
|
Time Orientation/Confucian Dynamism (Hofstede)
|
attitudes towards time, persistence, and respect for tradition
attention to which a culture focuses on long-term goals and planning |
|
|
Time Orientation (Hofstede)
|
US has very low time orientation; we focus on the short term; not much planning for future
|
|
|
Confucian Dynamism (Hofstede)
|
very long term views of planning; plan years/decades out
Ex: Asian companies with business plans 500 years out |
|
|
Strengths of Hofstede's Research
|
over 100,000 responses from 53 different nations
impressive because: the number of countries involved huge sample size results replicated in later research |
|
|
Weaknesses of Hofstede's Research
|
-used average responses for each country rather than individual responses
NOTE: the 2 scores were different between patterns of individual responses and the averages of the countries -survey wasn't designated to test culture -assumed a one-to-one correspondence between culture and nation state -potential cultural biases of researchers -data was based on a single industry and single firm -data is becoming dated |
|
|
Phases of Cultural Adjustment
|
lengthy process through the stages; takes 3-5 years to get to the mastery stage
-usually US business endeavors last 2-3 years -average for Japan is 7 years but they will have mastered the culture Phases: honeymoon culture shock adjustment mastery |
|
|
Honeymoon (Phases of Cultural Adjustment)
|
sense of excitement/adventure; exciting challenges of exploring new city
|
|
|
Culture Shock (Phases of Cultural Adjustment)
|
after initial excitement wears off, the differences between cultures are no longer exciting, but become frustrating.
- Characterized by feelings of annoyance, frustration, and loss of self esteem -Everyone goes through culture shock. If not, you're not interacting with the culture |
|
|
Adjustment (Phases of Cultural Adjustment)
|
Understanding the culture and becoming more comfortable in daily life and understanding how to communicate
|
|
|
Mastery (Phases of Cultural Adjustment)
|
-Fluid in the culture
-Able to interact and communicate with coworkers and people in community -Have a greater awareness in cultural differences -May not change your world view, but you will have a greater appreciation for what other cultures believe |
|
|
Preparing for Culture Shock
|
-have realistic expectations
-cultural training -language training -practical training - everyday things like currency, how they drive, etc |
|
|
Arbitrage
|
The simultaneous purchase and sale of an asset in order to profit from a difference in the price.
|
|
|
Cost-Leadership Strategy
|
Ex: Southwest Airlines: no assigned seating, lower costs due to operational efficiency, etc.
-Controls their cost structure in order to beat all other industries and then gives you the option to be the price leader. -If you LOWER YOUR PRICE you'll end up with the MOST CUSTOMERS |
|
|
Uniqueness
|
giving your customers something that your competitors don't.
-with this uniqueness, you can charge a premium price Ex: Nordstrom. High-end retailer that creates a pleasant shopping experience, visually-appealing displays of merchandise, great customer service, handwritten thank you notes for purchasing a pair of shoes. -its all about creating a wonderful shopping experience so you stay in there longer -Nordstrom gets fewer customers compared to Walmart, but it does make up for the profit margin on the amount of shoes sold. Create value that consumers are willing to pay for |
|
|
Strategic Reasons for Global Expansion
|
-Leveraging Products and Competencies
-Location Economies -Experience Effects -Leveraging Subsidiary Skills |
|
|
Floating Exchange Rate
|
exchange rates fluctuate according to market forces. Governments DO NOT INTERVENE to change the value of the currency
Benefits: - maintain monetary policy autonomy - allow currency devaluations to adjust trade imbalances (not everyone says this is true -- just because your goods are cheaper doesn't mean people want to buy them if they're manufactured poorly) Drawbacks: - volatility of exchange rates (makes it harder for businesses and investors to plan and predict what the currency is going to work, since the exchange rate fluctuates all the time) - currency speculation and contagion - lack of accountability |
|
|
Fixed Exchange Rate
|
Nation sets and maintains a target value for its currency
Benefits: - provides predictability - encourage monetary discipline - forces the country to be responsible in their monetary and fiscal policies Drawbacks: - limits flexibility to deal with economic problems - requires substantial foreign exchange reserves |
|
|
Big Mac PPP
|
survey done by The Economist that determines what a country's exchange rate would have to be for a Big Mac in that country to cost the same as it does in the US
-the measure gives an impression of how overvalued or undervalued a currency is |
|
|
PPP
|
Purchase power parity
P1 S= ------ P2 S = exchange rate of currency 1 to currency 2 P1= cost of good "x" in currency 1 P2= cost of good "x" in currency 2 theory that currencies adjust according to changes in their purchasing power |
|
|
Currency Speculation
|
Currency speculation involves buying, selling and holding currencies in order to make a profit from favorable fluctuations in exchange rates
|
|
|
The Impossible Trinity
|
1 Exchange Rate Stability
2 Independent Monetary Policy 3 Capital Mobility can only have 2 of the 3 |
|
|
Vertical Differentiation
|
refers to the location of decision-making responsibilities within a firm
-with centralized decision making, strategiv and operating decisions are made at the upper levels of the organization -decision-making responsibilities are pushed lower in the organizational hierarchy with decentralized decisions making |
|
|
Horizontal Differentiation
|
the formal division of the organization into subunits
- responsibilities are often allocated based on function, product, area, or customer - a matrix organizational structure combines 2 classifications of organizational structures on the same hierarchical level |
|
|
Incentives
|
used to reward and encourage appropriate employee behavior
|
|
|
Control Systems
|
establish the performance measures used to evaluate the performance of subunits
- may be based on personal, bureaucratic, output, or cultural controls |
|
|
Personal (Types of Control Systems)
|
personal contact with subordinates
|
|
|
Bureaucratic (Types of Control Systems)
|
budgets, capital spending rules and procedures to direct the actions of subunits
|
|
|
Output (Types of Control Systems)
|
objective performance metrics such as profitability, productivity, growth, market share, and quality
|
|
|
Cultural (Types of Control Systems)
|
norms and value systems of the firm control employee behavior
|
|
|
Organizational Culture
|
refers to the norms and value systems that are shared among the employees of an organization
- employees learn the organizational culture through formal and informal socialization - strong organizational cultures have a consistent set of values and norms that more reliably determine employee behavior |
|
|
Parent-Country Nationals
|
Advantages:
- familiar with corporate culture - loyal to the firm - effective communication with headquarters Disadvantages: - expensive - face cultural learning curve - unfamiliar with foreign environment |
|
|
Host-Country Nationals
|
Advantages:
- familiar with local culture and competitive environment - good for public relations and morale Disadvantages: - not familiar with corporate culture - may face communication challenges - may lack certain technical skills - loyalty may be to country not to company |
|
|
Third-Country Nationals
|
Advantages:
- have broad international experience - have greater cultural empathy - cultural distance may be less Disadvantages: - host government perception - can be expensive - may face communication challenges - may not be familiar with corporate culture |
|
|
Staffing Policy
|
Ethnocentric, polycentric, geocentric
|
|
|
Ethnocentric
|
all key management positions are filled by PARENT-COUNTRY NATIONALS
- Strategic appropriateness: international Advantages: - overcomes lack of qualified managers in host nation - unified culture - helps transfer core competencies Disadvantages: - produces resentment in host country - can lead to cultural myopia |
|
|
Polycentric
|
requires HOST-COUNTRY NATIONALS to be recruited to manage subsidiaries, while parent-country nationals occupy key positions at corporate headquarters
- Strategic Appropriateness: localization Advantages: - alleviates cultural myopia - inexpensive to implement Disadvantages: - limits career mobility - isolates headquarters from foreign subsidiaries |
|
|
Geocentric
|
seeks the best people for key jobs throughout the organization, regardless of nationality
Strategic Appropriateness: global standardization and transnational Advantages: - uses human resources efficiently - helps build strong culture and informal management networks Disadvantages: - national immigration policies may limit implementation - expensive |

