![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How do microbes affect our lives |
In our stomach, water treatment, weapons, vaccine, agriculture, bioremediation (removes pollutants) |
|
|
|
3 domains of life |
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya |
|
|
|
Pasteur contribution |
Pasteurization/ fermentation |
|
|
|
Virchow contribution |
All cells arise from pre-existing cells |
|
|
|
Hooke contribution |
All living things are composed of cells |
|
|
|
Leeuwenhoek contribution |
Used 1st microscope/ described live microorganisms as Animalcules |
|
|
|
Koch contribution |
Used his postulates to prove a specific microbe causes a specific disease |
|
|
|
Jenner contribution |
Created the 1st vaccine |
|
|
|
Ehrlich contribution |
Made drug to treat syphilis |
|
|
|
Fleming contribution |
Discovered 1st antibiotic |
|
|
|
Define spontaneous generation |
Living organisms arise from nonliving matter |
|
|
|
Biogenesis |
Organisms arise from pre-existing life |
|
|
|
Structure of an Atom |
Electron, Neutron, Proton |
|
|
|
Electron charge |
Negative |
|
|
|
Proton charge |
Positive charge |
|
|
|
Neutron charge |
No charge |
|
|
|
Ionic bond |
Transfer 1 or more electrons |
|
|
|
Covalent bond |
Share electrons |
|
|
|
Non polar |
Equal sharing |
Covalent |
|
|
Polar bond |
Unequal sharing |
Covalent |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
Between a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to another atom |
|
|
|
What is an Increased amount of OH- atoms |
Base |
High PH |
|
|
An increased amount of H+ atoms |
Acid |
Low PH |
|
|
The concentration of Hydrogen atoms in a solution |
PH |
|
|
|
Define metabolism |
The chemical process within a living cell or organism necessary for life |
|
|
|
Define Anabolism |
Synthesis of molecules in a cell |
A+B=AB |
|
|
Condensation |
Making large molecules |
A+B=AB |
|
|
Catabolism |
Decompensation reactions in a cell |
AB= A+B |
|
|
Define Hydrolysis |
Breaking down of large molecules |
AB= A+B |
|
|
Define Organic compounds |
Contain Carbon |
|
|
|
Define Inorganic Compounds |
Lack of Carbon |
|
|
|
Name the 4 Organic molecules |
Carbohydrates, Lipids, proteins, nucleic acids |
|
|
|
Structure of carbohydrates |
Mono, Di, or polysaccharide |
Sugars |
|
|
Building blocks of carbohydrates |
Sugars |
|
|
|
Structure of proteins |
Amine group, carboxyl group, variable group |
Groups |
|
|
Building blocks of proteins |
Amino acids |
|
|
|
Structure of Nucleic acids |
Phosphate, sugars, base |
|
|
|
Building blocks of Nucleic acids |
Nucleotides |
Similar name |
|
|
Structure of Lipids |
Triglycerides |
3 |
|
|
Building blocks of Lipids |
Glycerol & 3 fatty acids |
|
|
|
Prokaryotic cell structures |
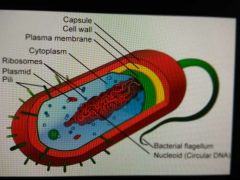
|
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cell structure |
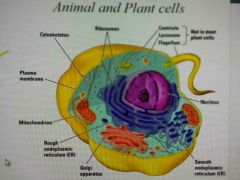
|
|
|
|
Cell structure of a prokaryote cell |
No nucleus, 1 circular chromosome, no histones, no organelles, peptidoglycan cell wall |
|
|
|
How do prokaryote cells reproduce |
Binary fission |
|
|
|
How do Eucaryote cells reproduce |
Mitosis & Meiosis |
|
|
|
Cell structure of Eukaryote cells |
Nucleus, paired chromosomes, histones, organelles, polysaccharide walls |
|
|
|
3 shapes of bacteria |
Cocci, bacilli, spiral |
|
|
|
Eukaryote cell |
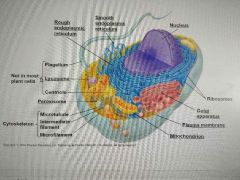
|
|
|
|
What shape is cocci |
Spherical |
|
|
|
What shape is bacilli |
Rod-shaped |
|
|
|
Arrangements of Diplo |
Pairs |
|
|
|
Arrangements of staphylo |
Clusters |
|
|
|
Arrangements of strepto |
Chains |
|
|
|
Structure of glycoclyx (prokaryote) |
Outside cell wall usually sticky |
|
|
|
Glycocalyx capsule |
Neat organized |
|
|
|
Glycocalyx slime layer |
Loose, organized |
|
|
|
Function of capsule |
Prevents phagocytosis |
|
|
|
Function of slime layer |
Attachment. Helps cells eat |
|
|
|
Where are flagella located |
Outside of cell |
|
|
|
What are flagella attached to |
Protein hook |
|
|
|
Fimbriae allow what |
Attachment |
|
|
|
What is the function of pili |
Join cells together for DNA transfer |
|
|
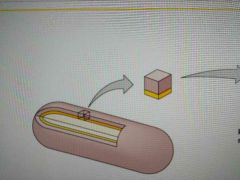
What kind of cell is this |
Gram positive cell |
|
|
What kind of cell is this |
Gram negative cell |
|
|
|
Archaea cells have what type of walls |
Wall-less or walls of pseudomurein |
|
|
|
What do mycoplasmas walls lack |
Cell walls |
|
|
|
What is the structure of a plasma membrane |
Phospholipid bilayer |
|
|
|
Function of plasma membrane |
Protection and regulates movement of substances in and out of cell |
|
|
|
Define simple Diffusion |
Movement of a solute from high concentration area to a low concentration area |
|
|
|
Define Facilitative diffusion |
Solute combines with a transporter protein in membrane from higher concentration to lower concentration |
|
|
|
Define osmosis |
Movement of water from an area of high water concentration to area with low water concentration |
|
|
|
Define active transport |
Substance require a transporter protein and ATP. From lower solute concentration to a higher solute concentration |
|
|
|
Define Endocytosis |
Used to move Large molecules into the cell |
|
|
|
Define Exocytosis |
Move Large molecules out of cells |
|
|
|
Function of Nucleus |
Genetic control center. Stores DNA |
|
|
|
Function of Smooth ER |
Detoxification |
|
|
|
Function of Rough ER |
Production of New membrane from phospholipids & proteins |
|
|
|
Function of Ribosomes |
Protein synthesis |
|
|
|
Function of Golgi Apparatus |
Receives, modify, stores, packages and secretes proteins |
Cell post office |
|
|
Function of Mitochondria |
Cellular Respiration ( makes ATP) |
|
|
|
Function of Chloroplasts |
Preforms Photosynthesis |
Only in plants |
|
|
Function of Lysomes |
Digest waste and dead cell debris |
|
|
|
Function of Peroxisomes |
Break down toxins |
Found in liver |
|
|
Function of Vesicles |
Move material around |
|
|
|
Function of Vacuoles |
Engulfs things |
|
|
|
Function of Cytoskeleton |
Support and cell movement |
|
|
|
Function of cilia & Flagella |
Cell movement |
|
|
|
Flagella & Cilia are made of |
Microtubules |
|
|
|
Define Endosymbiosis theory |
Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells |
|

