![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
gn
|
|
|
|
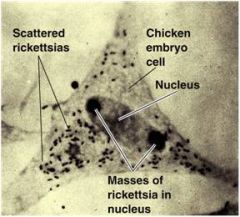
Parts of a Microscope (Labeled)
|
|
|
|
|
magnification
|
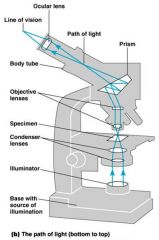
In a compound microscope the image from the objective lens is magnified again by the ocular lens.
Total magnification = objective lens ocular lens (10X) objective lens 4X, 10X, 40X, 100X |
|
|
|
Resolution (resolving power)
|
the ability of the lenses to distinguish between two points.
|
|
|
|
wavelength
|
part of resolution; (visible light)
|
|
|
|
numerical aperature
|
part of resolution; size of cone of light entering objective.
|
|
|
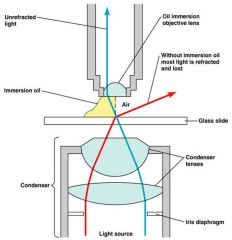
Refractive index
|
the light-bending ability of a medium; Immersion oil is used to keep light from bending.
|
|
|
|
Bright field Illumination
|
dark objects are visible against a bright background; light reflected off the specimen does not enter the objective lens.
|
|
|
|
Almost all cocci are: + or -
|
Gram Positive (blue)
exception: Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
|
|
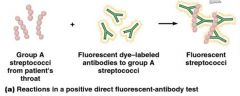
Fluorescence Microscopy
|
Uses Ultraviolet light
Cells may be stained with fluorescent dyes (fluorochromes) Identify unknown organisms in clinical specimens Fluorescent dye linked to specific antibody |
|
|
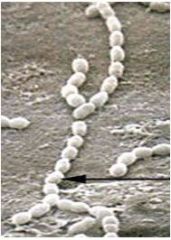
Electron Microscopy (EM)
|
Uses electrons instead of visible light
The shorter wavelength of electrons gives greater resolution; either scanning or transmission |
|
|
|
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
|
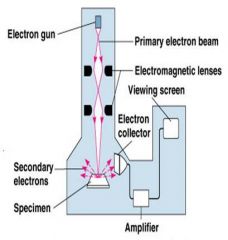
|
An electron gun produces a beam of electrons that scans the surface of a whole specimen.
Secondary electrons emitted from the specimen produce the image. |
|
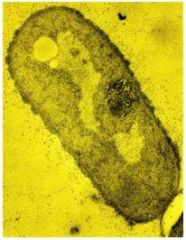
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
|
whole bacteria and viruses or ultra thin sections of bacteria and viruses
Light passes through specimen, then an electromagnetic lens, to a screen or film. Specimens may be stained with heavy metal salts. |
|
|
|
Basic Dye (+)
|
the chromophore is a cation (+)
Bacteria have a net (-) charge on their surface and are stained by basic dyes. |
|
|
|
acidic dye (-)
|
the chromophore is an anion (-)
Bacteria repel acidic dyes.Only the background is colored Staining the background instead of the cell is called negative staining. |
|
|
|
Differential staining
|
distinguishes between two types of bacteria – uses two different colored basic stains
EX: gram stain |
|
|
|
Gram stain
|
The Gram stain classifies bacteria into gram-positive (blue) and gram-negative (red).
Important because: Gram-positive bacteria tend to be killed by penicillin and detergents. Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics. |
|
|
|
acid-fast
|
Cells that retain a basic stain in the presence of acid-alcohol
|
|
|
|
Non–acid-fast cells
|
cells that lose the basic stain when rinsed with acid-alcohol, and are usually counterstained (with a different color basic stain) to see them.
|
|

