![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what causes gout?
|
Gout results from an imbalance between uric acid production and renal excretion, producing hyperuricemia
|
|
|
where does uric acid come from
|
purine metabolism
|
|
|
can you have hyperuricemia without gout?
|
yes
|
|
|
Onset of gout marked by acute inflammatory arthritis (acute gouty arthritis) caused by ...?
|
deposition of crystals of monosodium urate in and around joints and tendons
|
|
|
how do the uric crystals lead to pain in the join?
|
it leads to activation of inflammatory response such as prostaglandins, IL-1, etc
|
|
|
Fever often accompanies attacks
Enlarging tophi develop Hyperuricemia may also result in nephrolithiasis (stone formation in kidneys) these are symptoms associated with...? |
gout
|
|
|
what 3 things can hyperuricemia lead to?
|
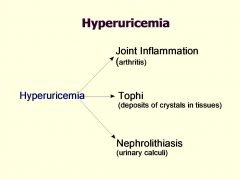
|
|
|
this drug inhibits uric acid synthesis and is used for prevention of gout...
|
allopurinol
|
|
|
these 2 drugs Increase uric acid elimination and are used for prevention of gout..
|
probenicid and sulfinpyrazone
|
|
|
these drugs (one general and one specific) Inhibit immune responses to uric acid and can be used for an acute attack of gout
|
NSAIDs and colchicine
|
|
|
how do NSAIDs work in acute gout attacks?
|
decreasing inflammatory process
|
|
|
what is the main effect of NSAIDs?
|
Main effect is to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis
|
|
|
what is a side effect of chronic NSAID use?
|
GI bleeding
|
|
|
what are the 3 As of NSAIDs?
|
analgesic and antipyretic properties as well as anti-inflammatory
|
|
|
what is the traditional treatment for relief of acute gout? what type of drug is this?
MUST KNOW |
Indomethacin
NSAIDs |
|
|
how does chronic use of NSAIDs lead to GI bleeding?
|
prostaglandin make mucin and bicarb in the stomach which protect it
NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin formation, thus leading to loss of the protection and bleeding it also inhibits cycloxygenase, which will inhibit platelet release |
|
|
Ibuprofen. Group and used for
|
NSAID
Gout |
|
|
what does colchicine do?
|
inhibits PMNs (leukocytes) from being able to aggregate to a joint
thus reducing the inflammation seen in gout |
|
|
is colchine an analgesic? how bout uricosuric? what is it used for?
|
Niether
it binds to intracellular protein tubulin preventing polymerization into microtubules; this prevents leukocyte migration and phagocytosis. Also inhibits LTB4 formation for the treatment of gout |
|
|
describe the pharmacokinetics of colchicine (time to work, how it is taken, where it is metabolized)
|
Takes about ½ day for some relief
Used orally except in special cases Metabolized in liver |
|
|
what are the side-effects of colchicine?
|
Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea (NVD)
colic |
|
|
is the TI wide or narrow for colchicine?
|
NARROW
|
|
|
A risk of hair loss, bone marrow depression, peripheral neuropathy but risk is low unless given by IV can be seen in this gout treatment
**** |
Colchicine
|
|
|
Side effects of colchicine are most often seen where?
|
GI
|
|
|
what do you use to treat 2nd line for acute gouty arthritis? What would be first line?
|
Colchicine
first line is NSAIDs |
|
|
Adrenal Corticosteroids can be used to treat what? Why?
|
Used for acute attacks of gout
They have Antiinflammatory properties |
|
|
so what are the 2 drugs used for an acute attack of gout?
|
NSAIDs and Colchicine
|
|
|
what does allopurinol do?
|
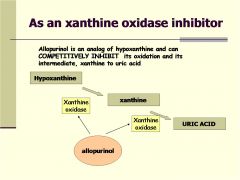
inhibits the synthesis of uric acid
|
|
|
comic of the lecture
|

|
|
|
how is allopurinol cleared?
|
kidneys
|
|
|
does allopurinol cause a ton of side effects? what is it used for again?
|
not really
inhibits Uric Acid Synthesis |
|
|
what may happen during the early therapy of treatment with allopurinol? what do you want to give to prevent this?
**** |
May produce acute gouty attacks (systemically) during initial treatment, so give colchicine or NSAID before starting!
|
|
|
what does febuxostat do? so it is similar to? what type of patient is it better for?
|
A xanthine oxidase inhibitor similar to allopurinol
May be better for pts with renal insufficiency |
|
|
what drug acts at anionic transport sites in renal tubules to cause a net decrease in uric acid reabsorption? what are the 2 examples
|
Uricosuric drugs (probenecid and sulfinpyrazone)
|
|
|
what blocks the reabsorption of uric acid?
|
Uricosuric drugs
|
|
|
what do low does of Uricosuric agents do?
|
inhibit renal active secretion of UA (increasing blood levels of UA – BAD!)
|
|
|
what do high does of Uricosuric agents do?
|
inhibit renal reabsorption of UA (to decrease blood levels)
|
|
|
what kind of drug is Probenecid? what does it do?
|
Uricosuric agents
inhibit renal reabsorption of UA |
|
|
what is a side effect of Probenecid?
|
increased risk of kidney stones
|
|
|
when do you use Probenecid (3)
|
Use after acute gouty attacks
Use when allopurinol is not tolerated Use when evidence of tophi appears |
|
|
What type of drug is Sulfinpyrazone? what is it similar to? What type of agent is it? What is the major difference btw it and the one it is similar too
|
prevents uric acid reabsorption
Probenecid Uricosuric Agents Causes more GI problems |
|
|
45 yo male with uric acid levels of 8mg/dL. Has recently recovered from acute attack of gout. What are you going to use to treat further attacks?
**** |
allopurinol
|
|
|
pt doesnt tolerate allopurinol, what would you use?
*** |
Probenecid
|

