![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
145 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
OPT template : phase 1 stabilization endurance : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
A properly designed court training program helps an individual gain |
Neuromuscular control, stability, muscular endurance, strength, & power of the core. |
|
|
|
Core |
The structures that make up the LPHC, including the lumbar spine, the pelvic girdle, abdomen, & hip joint. |
|
|
|
Center of gravity (COG)What three things in the muscles of the LPHC establish neuromuscular efficiency throughout the entire H is |
Located where all the movements originate in the core. |
|
|
|
What 3 things in the muscles of the LPHC establish neuromuscular efficiency throughout the entire HMS?Optimal |
Optimal length (length tension relationships) Recruitment patterns (force couple relationships) Joint motions (arthrokinematics) |
|
|
|
Optimal length (length tension relationships), recruitment patterns (force couple relationships), and joy emotions (Arthrokinematics) allow for efficient |
Acceleration, deceleration, and stabilization during dynamic movements. |
Prevention of possible injuries. |
|
|
The core musculature has been divided into what 3 systems? |
Global stabilization system Local stabilization system The movement system |
|
|
|
The Local core stabilizers are muscles that |
Attached directly to the vertebrae, primarily type 1 (slow twitch) muscle fibers with a high density of muscle spindles. |
|
|
|
Course stabilizing muscles are primarily responsible for |
Intervertebral & intersegmental stability, working to limit excessive compressive, sheer, and rotational forces between. |
|
|
|
A High density of muscle spindles help to aid in |
proprioception & postural control. |
|
|
|
The primary muscles that make up the local stabilization systems include the |
Multifidus Pelvic floor muscles Diaphragm Transverse abdominis Internal obliques |
There are 5 |
|
|
The primary muscles that make up the local stabilization system contribute to what kind of stability & how? |
Segmental spinal Increasing intra-abdominal pressure (pressure within the abdominal cavity) Generating tension in the thoracolumbar fascia (connective tissue of the low back) Increasing spinal stiffness for improved intersegmental neuromuscular control |
|
|
|
Human movement efficiency |
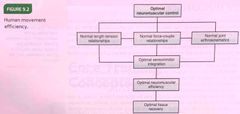
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Muscles of the core : local stabilization, global stabilization, & movement systems |
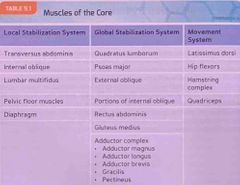
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core musculature pictured : |
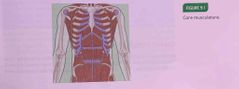
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
The muscles of the global stabilization attach from |
The pelvis to the spine |
|
|
|
The muscles of the global stabilization system act to |
Transfer loads between upper & lower extremity Provide stability between the pelvis & spine Provide stabilization & eccentric control of the core during functional movements |
There are 3 |
|
|
The primary muscles that make up the global stabilization system include the |
Quadratus lumborum Psoas major External obliques Portions of the internal obliques Gluteus medius Adductor complex Rectus abdominis
|
There are 7 |
|
|
The movement system includes muscles that |
Attach the spine &/or pelvis to the extremities. |
|
|
|
The movement system muscles are primarily responsible for |
Concentric force production Eccentric deceleration during dynamic activities. |
|
|
|
The primary muscles that make up the movement system are |
Latissimus dorsi Hamstring complex Hip flexors Quadriceps |
There are 4 |
|
|
Muscles of the core : local stabilization, global stabilization, & movement systems : |
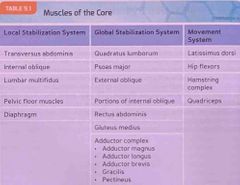
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Collectively all of the muscles within each system (local, global, movement) provide |
Provide dynamic Stabilization & neuromuscular control of the entire core LPHC. |
|
|
|
The muscles of the local, global, & movement systems do what? |
Produce force (concentric contractions) Reduce force (eccentric contractions) Provide dynamic stabilization in all planes of movement during functional activities |
There are 3 Produce, reduce, provide |
|
|
The muscles of the local, global, &The bodies course stabilization system Hass to be operating with maximal efficiency to movement systems enhanced ability in your muscular control through their |
Synergistic interdependent functioning. |
|
|
|
The bodies core stabilization system Hass to be operating with maximal efficiency to effectively use the |
Strength, power, & endurance that has been developed in the prime movers. |
|
|
|
Performing a lunch, squat, or OH press with excess a spinal extension is an example of |
Compensation, synergistic dominance, & inefficient movements. |
|
|
|
80% |
80% |
|
|
|
Those with chronic LBP have decreased activation ofThose with chronic LBP since I have |
Certain muscles or muscle groups Including the transverse of dominoes, internal obliques, pelvic floor muscles, multi fighters, diaphragm, erector spinae. |
|
|
|
Those with chronic LBP tend to have weaker |
Back extensor muscles & decreased muscular endurance. |
|
|
|
What is an independent risk factor for developing LBP?Course |
Trunk muscle weakness. |
|
|
|
Core stabilization exercises restore what in individuals with LBP? |
Size, activation, and endurance of the multifidus (deep spine muscle) |
|
|
|
Clients & athletes with lower extremity pain, long-standing adductor (inner thigh) pain, hamstring strain, IT-band syndrome (runners knee), and LBP have a decreased chance of |
Injury, less recurrence of injury, & improved performance measures after active rehabilitation program aimed at improving strength in neuromuscular control of the core (LPHC) muscles. |
|
|
|
Drawing-in maneuver |
Used to recruit the local core stabilizers by drawing the naval in toward the spine. |
|
|
|
Bracing |
Contracting both of the abdominal, lower back, and buttock muscles simultaneously. |
|
|
|
Low back hyper extension exercises without proper LPH stabilization have been shown to increase |
Pressure on the disks to dangerous levels, causing damage to the ligaments supporting the vertebrae. |
|
|
|
Muscular endurance of the global & local musculature when contracted together, create the most benefit for |
Those with LBP compared with traditional LBP training methods. |
|
|
|
Bracing focuses on global trunk stability, not on segmental vertebral stability, meaning that |
The global muscles, given the proper endurance training, will work to stabilize the spine. |
|
|
|
The drawing in maneuver focuses on the |
Local stabilization system. |
|
|
|
Bracing focuses on the |
Global stabilization system. |
|
|
|
A comprehensive core training program should be |
Systematic Progressive Produce force concentric Reduce force eccentric Dynamic stabilization isometric And emphasize the entire muscle action spectrum. |
There are 6 |
|
|
Core training parameters |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
A core training program should regularly manipulate |
Playing of motion ROM Modalities (tubing, stability ball, medicine bar, both super, airex pad) Body position Amount of control Speed of execution Amount of feedback Specific acute training variables (sets, reps, intensity, tempo, frequency)
|
There are 8 |
|
|
When designing a core training program first create a |
Proprioceptively enriched (controlled yet unstable training environment), selecting the appropriate exercises to elicit a maximal training response. |
|
|
|
Core exercises performed in an unstable environment such as with the stability ball have been demonstrated to increase |
Activation of the local and global stabilization systems. |
|
|
|
The bola for training is to develop optimal levels of |
Neuromuscular efficiency Stability (intervertebral Lumbopelvic stability — local & global stabilization systems) Functional strength (movement system) |
There are 3 The systems |
|
|
Damage to the ligaments supporting the vertebrae may lead to |
A narrowing of openings in the vertebrae that spinal nerves pass through. |
|
|
|
Increasing proprioceptive demand by using a multisensory environment & multiple modalities is |
More important than increasing external resistance. |
|
|
|
The focus of the program should be ___ & quality of ___ should be stressed over ___. |
Focus should be on function Quality of movement Over quantity |
|
|
|
1. Intervertebral stability 2. Lumbopelvic stability 3. Movement efficiency |
1. Intervertebral stability 2. Lumbopelvic stability 3. Movement efficiency |
|
|
|
Core training parameters |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
The client made progress through the program once they |
Mastered the exercises that were performed in the previous level, while demonstrating intervertebral stability & Lumbopelvic stability. |
|
|
|
A client has appropriate intervertebral stability when able to maintain the |
Drawing-in position while performing various exercises. |
|
|
|
The client has appropriate lumbopelvic stability when able to performWhat |
Functional movement patterns (squats, lunges, step ups, single leg movements, pressing, pushing) without excessive spinal motion (flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation, singly or in combination) |
|
|
|
What are the 3 levels of the OPT model? |
Stabilization Strength Power |
|
|
|
During core-stabilization training (phase 1), exercise involves |
Little to no movement in the spine & pelvis. |
|
|
|
Core stabilization training Is designed to improve |
Neuromuscular efficiency & intervertebral stability. |
|
|
|
Electromyogram EMG activity is increased during |
Pelvic stabilization & transverse abdominis activation when the drawing-in maneuver is initiated before activity. |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization training focuses on |
Drawing-in & then bracing during the exercises. |
|
|
|
How long will the client typically spend in core-stabilization training? |
4 weeks |
|
|
|
Sample exercises for core stabilization training are : |
Marching Floor bridge Floor prone cobra Prone iso ab |
There are 4 They are all done on the back or stomach |
|
|
Core-stabilization : exercises marching : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : 2 leg floor bridge |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : floor prone cobra : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : prone iso abs (plank) : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In the core-strength training (phases 2, 3 & 4) exercises involve more |
Dynamic, eccentric, & concentric movements of the spine throughout a full ROM |
Clients perform the activation techniques learned in corestabilization training (drawing-in & bracing). |
|
|
What is progressed during core-strength training? |
Specificity, speed, & neural demands. |
|
|
|
How long do clients typically spend in the course strength training? |
4 weeks |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization : exercises marching : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : 2 leg floor bridge |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : floor prone cobra : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : prone iso abs (plank) : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core training exercises : back extension : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core strength exercises : reverse crunch : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-strength exercises : cable rotation : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In core-power training (phase 5), exercises are designed to improve |
Rate of force production of the core musculature. |
|
|
|
Core strength training exercises prepare an individual to |
Dynamically stabilize & generate force at more functionally applicable speeds. |
|
|
|
Core-strength exercises : ball crunch : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core training exercises : back extension : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core strength exercises : reverse crunch : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-strength exercises : cable rotation : |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core power exercises : front MB oblique throw : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core power exercises : soccer throw : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core training program design : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-power exercises : rotation chest pass : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
If a forward protruding head is noticed during the drawing in maneuver what muscle is preferentially recruited? |
The sternocleidomastoid (large muscle) |
|
|
|
When the sternocleidomastoid is preferentially recruited during the draw-in maneuver what happens? |
Compressive forces in the cervical spine are increased, leading to pelvic instability & muscle imbalances as a result of the pelvo-ocular reflex. |
|
|
|
Because of the pelvo-ocular reflex it is important to |
Maintain level eyes during movement. |
|
|
|
If the sternocleidomastoid muscle is hyperactive & extends the upper cervical spine, the pelvis |
Anteriorly rotates to realign the eyes. |
|
|
|
Bracing is also commonly referred to as |
Bearing down or tightening. |
|
|
|
Low back hyper extension exercises without proper LPH stabilization have been shown to increase |
Pressure on the disks to dangerous levels, causing damage to the ligaments supporting the vertebrae. |
|
|
|
Muscular endurance of the global & local musculature when contracted together, create the most benefit for |
Those with LBP compared with traditional LBP training methods. |
|
|
|
Bracing focuses on global trunk stability, not on segmental vertebral stability, meaning that |
The global muscles, given the proper endurance training, will work to stabilize the spine. |
|
|
|
The drawing in maneuver focuses on the |
Local stabilization system. |
|
|
|
Bracing focuses on the |
Global stabilization system. |
|
|
|
A comprehensive core training program should be |
Systematic Progressive Produce force concentric Reduce force eccentric Dynamic stabilization isometric And emphasize the entire muscle action spectrum. |
There are 6 |
|
|
Core training parameters |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
A core training program should regularly manipulate |
Playing of motion ROM Modalities (tubing, stability ball, medicine bar, both super, airex pad) Body position Amount of control Speed of execution Amount of feedback Specific acute training variables (sets, reps, intensity, tempo, frequency)
|
There are 8 |
|
|
When designing a core training program first create a |
Proprioceptively enriched (controlled yet unstable training environment), selecting the appropriate exercises to elicit a maximal training response. |
|
|
|
Core exercises performed in an unstable environment such as with the stability ball have been demonstrated to increase |
Activation of the local and global stabilization systems. |
|
|
|
The bola for training is to develop optimal levels of |
Neuromuscular efficiency Stability (intervertebral Lumbopelvic stability — local & global stabilization systems) Functional strength (movement system) |
There are 3 The systems |
|
|
Damage to the ligaments supporting the vertebrae may lead to |
A narrowing of openings in the vertebrae that spinal nerves pass through. |
|
|
|
Increasing proprioceptive demand by using a multisensory environment & multiple modalities is |
More important than increasing external resistance. |
|
|
|
The focus of the program should be ___ & quality of ___ should be stressed over ___. |
Focus should be on function Quality of movement Over quantity |
|
|
|
1. Intervertebral stability 2. Lumbopelvic stability 3. Movement efficiency |
1. Intervertebral stability 2. Lumbopelvic stability 3. Movement efficiency |
|
|
|
During an integrated core training program the client begins at what level? |
The highest level at which they can maintain stability & optimal neuromuscular control (coordinated movement). |
|
|
|
The client made progress through the program once they |
Mastered the exercises that were performed in the previous level, while demonstrating intervertebral stability & Lumbopelvic stability. |
|
|
|
A client has appropriate intervertebral stability when able to maintain the |
Drawing-in position while performing various exercises. |
|
|
|
The client has appropriate lumbopelvic stability when able to performWhat |
Functional movement patterns (squats, lunges, step ups, single leg movements, pressing, pushing) without excessive spinal motion (flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation, singly or in combination) |
|
|
|
What are the 3 levels of the OPT model? |
Stabilization Strength Power |
|
|
|
During core-stabilization training (phase 1), exercise involves |
Little to no movement in the spine & pelvis. |
|
|
|
Core stabilization training Is designed to improve |
Neuromuscular efficiency & intervertebral stability. |
|
|
|
Electromyogram EMG activity is increased during |
Pelvic stabilization & transverse abdominis activation when the drawing-in maneuver is initiated before activity. |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization training focuses on |
Drawing-in & then bracing during the exercises. |
|
|
|
How long will the client typically spend in core-stabilization training? |
4 weeks |
|
|
|
Sample exercises for core stabilization training are : |
Marching Floor bridge Floor prone cobra Prone iso ab |
There are 4 They are all done on the back or stomach |
|
|
Core-stabilization : exercises marching : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : 2 leg floor bridge |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : floor prone cobra : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-stabilization exercises : prone iso abs (plank) : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In the core-strength training (phases 2, 3 & 4) exercises involve more |
Dynamic, eccentric, & concentric movements of the spine throughout a full ROM |
Clients perform the activation techniques learned in corestabilization training (drawing-in & bracing). |
|
|
What is progressed during core-strength training? |
Specificity, speed, & neural demands. |
|
|
|
How long do clients typically spend in the course strength training? |
4 weeks |
|
|
|
The transverse abdominis Creates tension in the ___, contributing to ___, & compresses the ___ increasing ___. |
Creates tension in the thoracolumbar fascia Contributing to spinal stiffness Compressing the sacroiliac joint Increasing stability |
|
|
|
The exercises involved in core-strength training are designed to improve |
Concentric strength (force production), eccentric strength (force reduction), & neuromuscular efficiency of the entire kinetic chain. |
|
|
|
Exercises in the core strength training level include : |
Ball crunch Back extensions Reverse crunch Cable rotations |
|
|
|
Core-strength exercises : ball crunch : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core training exercises : back extension : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core strength exercises : reverse crunch : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core-strength exercises : cable rotation : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In core-power training (phase 5), exercises are designed to improve |
Rate of force production of the core musculature. |
|
|
|
Core strength training exercises prepare an individual to |
Dynamically stabilize & generate force at more functionally applicable speeds. |
|
|
|
Exercises in the core-power training level include : |
Rotation chest pass Ball medicine ball (MB) pull over throw Front MB oblique throw Soccer throw |
All of the exercises use a medicine ball or stability ball. |
|
|
Core-power exercises : rotation chest pass : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Maintaining a neutral spine during core training helps to improve |
Posture, stabilization, & muscle balance. |
|
|
|
Core power exercises : ball MB Pullover throw : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core power exercises : front MB oblique throw : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core power exercises : soccer throw : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Core training program design : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
OPT template : phase 1 stabilization endurance : |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
If a forward protruding head is noticed during the drawing in maneuver what muscle is preferentially recruited? |
The sternocleidomastoid (large muscle) |
|
|
|
When the sternocleidomastoid is preferentially recruited during the draw-in maneuver what happens? |
Compressive forces in the cervical spine are increased, leading to pelvic instability & muscle imbalances as a result of the pelvo-ocular reflex. |
|
|
|
Because of the pelvo-ocular reflex it is important to |
Maintain level eyes during movement. |
|
|
|
If the sternocleidomastoid muscle is hyperactive & extends the upper cervical spine, the pelvis |
Anteriorly rotates to realign the eyes. |
|
|
|
Bracing is also commonly referred to as |
Bearing down or tightening. |
|

