![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
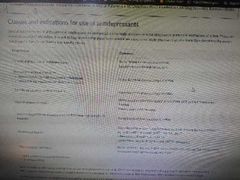
Classes of Antidepressants |
|
|
|
|
TCA name |
Name based on chemical structure Includes mirtazapine and mianserin |
Mirtazapine |
|
|
Mirtazapine |
TCA |
|
|
|
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors - reversible |
Reversible include moclobemide (MAO-A selective) |
|
|
|
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors - nonreversible |
Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine |
|
|
|
SSRI |
Name based on action |
Sertraline, citalopram (Celexa), Escitalopram (Lexapro), Fluoxetine (Prozac), Paroxetine (Paxil) |
|
|
Zoloft |
Sertraline an SSRI |
|
|
|
Dual reuptake inhibitors |
Name based on action (both 5HT3 and NA blocked; dose dependent) |
|
|
|
Multimodal agents |
What it sounds like Agomelatine - melatonin and 5HT2C Vortioxetine - SERT, 5HT1A, 5HT7 |
Eg Agomelatine - melatonin and 5HT2C antagonist |
|

Amygdala processes rewards and threats |
Neuroimaging shows amygdala overactive in depression, and responds excessively to negative events |
|
|
|
Amygdala connects to: |
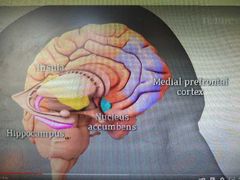
Hippocampus involved in memory formation Hippocampus and medial PFC both vulnerable to stress effects Depressed people are more susceptible to stress, which can cause atrophy of hippocampus which may cause inappropriate responses to emotional events Medial PFC regulates how strongly we react to emotional stimuli |
|
|
|
Depression Triggers |
Chronic stress leading to atrophy of hippocampus and PFC? Altered neuroplasticity? |
|
|
|
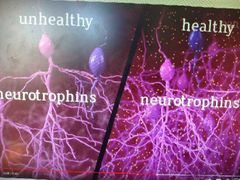
Hippocampus healthy vs depression |
In a healthy hippocampus, experience can lead to changes in the connections between neurons, resulting in learning (plasticity) Stress REDUCES plasticity Healthy also makes new neurons; numbers reduced in stress, possibly due to reduced neurotrophins |
|
|
|
Healthy vs unhealthy less neurotrophins in unhealthy Neurotrophins are proteins which increase neuronal growth and plasticity |
|
|
|
How do most antidepressants work? |

Increase serotonin and or norepinephrine available in synapse! Takes weeks Prolonged treatment can increase neurotrophin expression and rebuild hippocampal plasticity! |
|
|
|
Can ECT help? |
Can help plasticity in mice |
|
|
|
What does a k hole have to do with this? |
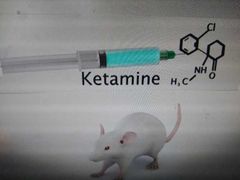
Ketamine has rapid antidepressant effects lasting for days!! |
|
|
|
How does ketamine work? |
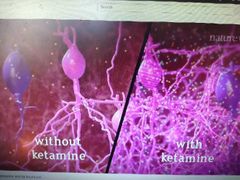
Ketamine blocks a type of synaptic transmission, leading to activation if a number of signalling pathways and increased neurotrophin production |
|
|
|
Animal models may confine discoveries of more molecules which act on monoamines |
They also might confine discoveries of novel compounds based on NMDA receptor antagonist in the wake of recent effectiveness of ketamines interaction with glutamate (NMDA) receptor!! |
|
|
|
NMDA receptor aka Glutamate receptor antagonist |
Ketamine! |
|
|
|
Biogenic amine hypothesis of antidepressant action |
Tricyclics block reuptake of monoamines (NA) Depression due to deficit in synaptic cleft of biogenic amine transmitters which antidepressants reverse (Schildkraut) HOWEVER Reuptake blocked in 24 hr, but therapeutic effect only after 1-4 weeks |
|
|

Receptor adaptation hypothesis |
alpha 2 are inhibitory; sensitivity deceased by chronic antidepressant treatment |
|
|
|
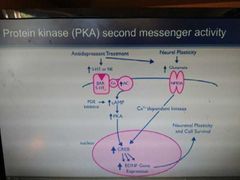
Chronic AD drugs need to stimulate making of Brain derived neurotrophic factor |
BDNF |
|
|
|
BDNF production |

G protein - AC - Cyclic AMP - protein kinase A - CREB phosphorylation |

|
|
|
PKA second messenger activity |
|
|
|
|
BDNF |

|
|
|
|
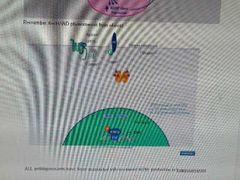
Signalling Pathway for CREB |
|
|
|
|
Monoamine theory and issues |

|
|
|
|
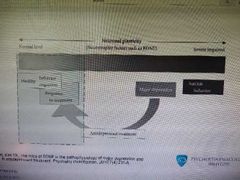
Neurotrophic hypothesis of depression |

|
|
|
|
MAOI that can kill with tyramine |
Phenelzine Tranlycpromine |
|
|
|
Reversible MAOI that doesn't interact with tyramine |
Moclobemide (MAOA) |
|
|
|
Bupropion |
NDRI = noradrenaline dopamine RI |
|
|
|
SNRI |
Venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, duloxetine, milnacipran |
|
|
|
Mirtazapine |
Noradrenergic and specific serotonin antidepressant (Nassa) |
|
|
|
Nefazodone |
Serotonin agonist/reuptake inhibitor (SARI) |
|
|
|
TCA side effects |
Side effects of tricyclics areAnticholinergic (for example, dry mouth,blurred vision, constipation, urinaryretention)Noradrenergic (for example, posturalhypotension)Cardiac arrhythmias (particularly inoverdose, lofepramine less so thanamitriptyline)Reduction of seizure thresholdWeight gain andSexual dysfunction |
|
|
|
TCA vs SSRIs |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors(SSRIs), for example, fluoxetine, are of equal efficacy to tricyclics, but are less sedative and have fewer cardiovascular effects.As a class of antidepressants, SSRIs cause few anticholinergic side effects. Paroxetine is the SSRI most likely to cause anticholinergic effects.More commonly reported SSRI side effects are:Gastrointestinal problemsAgitationInsomnia andHeadache. |
|
|
|
TCA Nortriptyline |
Nortriptyline is a strong norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and a moderate serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Nortriptyline is an active metabolite of amitriptyline by demethylation in the liver. Chemically, it is a secondary amine dibenzocycloheptene and pharmacologically it is classed as a first-generation antidepressant.[33]Nortriptyline may also have a sleep-improving effect due to antagonism of the H1 and 5-HT2A receptors.[34] In the short term, however, nortriptyline may disturb sleep due to its activating effect.In one study, nortriptyline had the highest affinity for the dopamine transporter among the TCAs (KD = 1,140 nM) besides amineptine (a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor), although its affinity for this transporter was still 261- and 63-fold lower than for the norepinephrine and serotonin transporters (KD = 4.37 and 18 nM, respectively).[22] |
|
|
|
SNRIs |
SNRIs (and their brand names) that healthcare providers currently prescribe in the United States include:Desvenlafaxine (Khedezla®, Pristiq®).Duloxetine (Cymbalta®, Drizalma®, Irenka®).Levomilnacipran (Fetzima®).Milnacipran (Savella®).Venlafaxine (Effexor®). |
|
|
|
TCA cardiac side effects |
The side effects of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are related to their anticholinergic, antihistaminergic and antiadrenergic properties. It is known that even at therapeutic doses TCAs can cause:Prolonged QTFlattened T waveDepressed ST segment, andTachycardia.They can be lethal in overdose and cause cardiac arrhythmias. This could occur after about 72-96 hours after an overdose |
|
|
|
Mirtazapine induced weight gain and sedation |
H1 receptor antagonsim |
|
|
|
SSRI induced GI disturbances |
5HT3 receptor agonism |
|
|
|
Priapism |
Alpha 1 blockade |
|
|
|
Priapism |
Alpha 1 blockade |
|
|
|
Priapism |
Alpha 1 blockade |
|
|
|
Presynaptic 5HT1D stimulation |
Antipsychotics reduce 5HT function by acting as agonsits to the terminal autireceptor. Thus has been shown to aggravate OCD symptoms |
|
|
|
Weight gain receptors |
5HT2C, H1, H3 |
|
|
|
Bupropion |
NDRI Increases dopamine at nerve terminal in limbic area so helpful in smoking cessation |
|

