![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
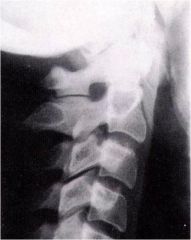
whats the anomaly?
|
accessory articulation of the SP's at C1 and C2
|
|
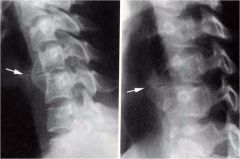
whats the anomaly?
|
accessory articulation of the TVPs
|
|
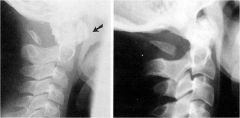
whats the anomaly?
|
agenesis of the posterior arch
|
|
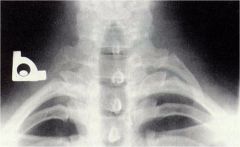
whats the anomaly?
|
cervical rib
|
|
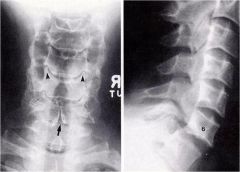
whats the anomaly?
|
cervical spondylolisthesis
|
|
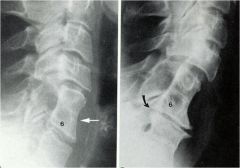
whats the anomaly?
|
congenital block vertebra
|
|
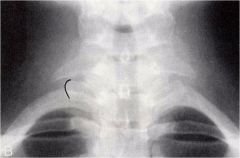
whats the anomaly?
|
elongated TVP
|
|
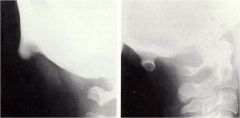
whats the anomaly?
|
enlarged EOP occipital spur
|
|
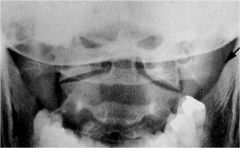
whats the anomaly?
|
epitransverse process
|
|
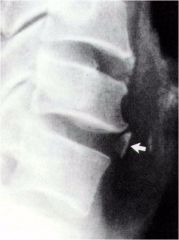
whats the anomaly?
|
intercalary bone
|
|
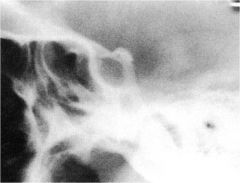
whats the anomaly?
|
interclinoid ligament calcification
|
|
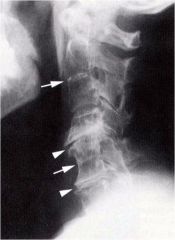
whats the anomaly?
|
kippel feil syndrome
|
|
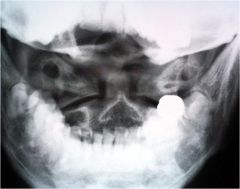
whats the anomaly?
|
Lateral ponticle
|
|
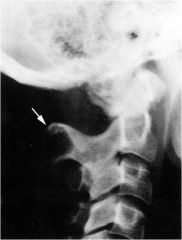
whats the anomaly?
|
megaspinous
|
|
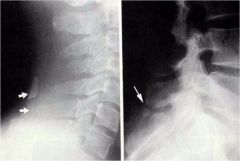
whats the anomaly?
|
nuchal bone
|
|
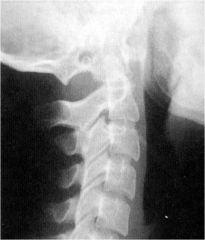
whats the anomaly?
|
Occipitalization of C1
|
|
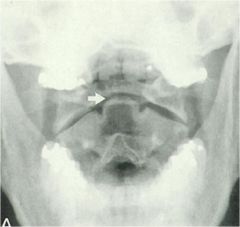
whats the anomaly?
|
os odontoideum
|
|
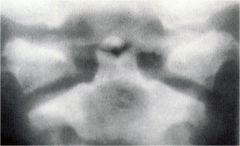
whats the anomaly?
|
os terminale of Bergman
|
|
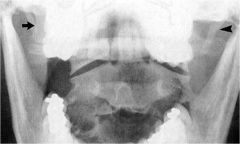
whats the anomaly?
|
paracondylar process
|
|
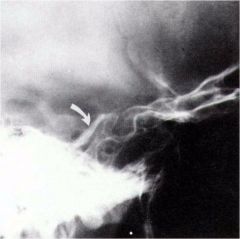
whats the anomaly?
|
petroclinoid ligament calcification
|
|
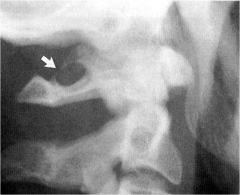
whats the anomaly?
|
posterior ponticle
|
|
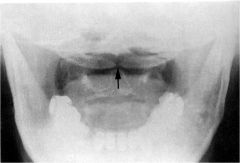
whats the anomaly?
|
spina bifida occulta SBO
|
|
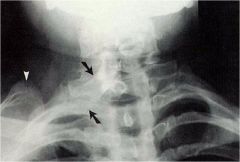
whats the anomaly?
|
Sprengels deformity with omovertebral bone
|
|
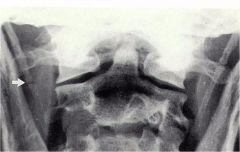
whats the anomaly?
|
stylohyoid ligament calcification
|
|
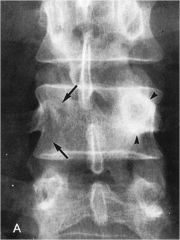
what anomaly?
|
Agenetic pedicle with contralateral sclerosis
|
|
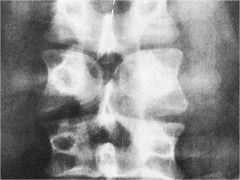
whats the anomaly?
|
Butterfly vertebrae
|
|
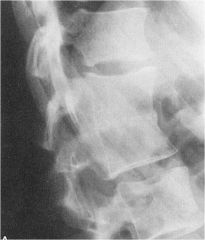
whats the anomaly?
|
congenital blocked vertebrae
|
|
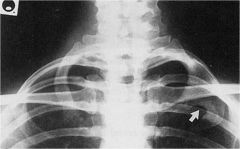
whats the anomaly?
|
congenital fusion of first and second ribs
|
|
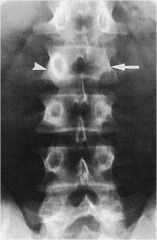
whats the anomaly?
|
congenital pedicle absence
|
|
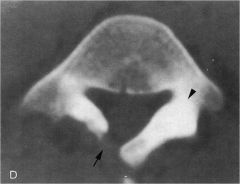
whats the anomaly?
|
CT scan unilateral pars defect with contralateral sclerosis of pedicle and pars
|
|
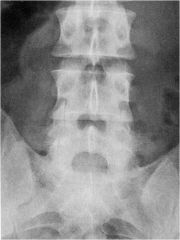
whats the anomaly?
|
facet tropism
|
|
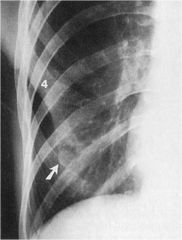
whats the anomaly?
|
Focal bifurcation of the 4th rib, note nipple shadow (arrow)
|
|
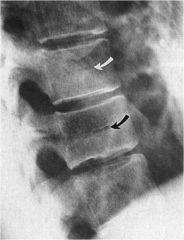
whats the anomaly?
|
Hahn's venous clefts
|
|
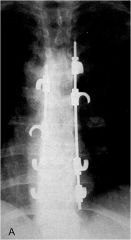
whats the anomaly?
|
Harrington Rod procedure, two rods placed on either side of the spine
|
|
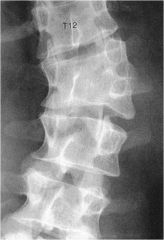
whats the anomaly?
|
Hemivertebrae
|
|
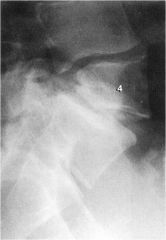
whats the anomaly?
|
Hemivertebrae
|
|
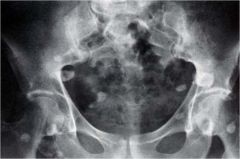
whats the anomaly?
|
injection granuloma
|
|
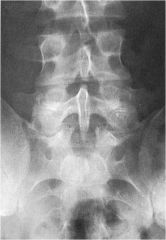
whats the anomaly?
|
Knife-clasp deformity
|
|
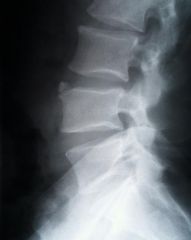
whats the anomaly?
|
Limbus bone
|
|
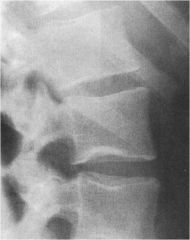
whats the anomaly?
|
Notochordal impression
|
|
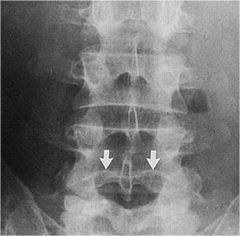
what the anomaly?
|
Notochordal impression
|
|
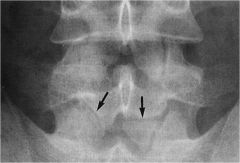
whats the anomaly?
|
Oppenheimers ossicle
|
|
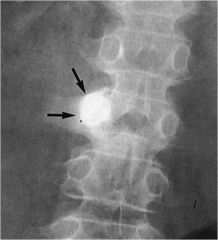
whats the anomaly?
|
Osteiod Osteoma
|
|
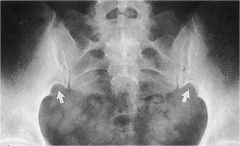
whats the anomaly?
|
paraglenoid sulci
|
|
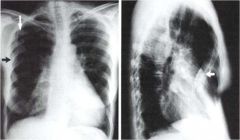
whats the anomaly?
|
pectus excavatum
if the sternum is anteriorly protruding it is called pectus carinotum |
|
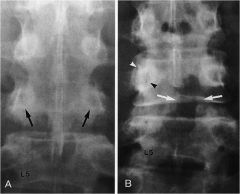
whats the anomaly?
|
Pedicle stress hypertrophy from contralateral laminectomy A- PreOp B- Post Op
|
|
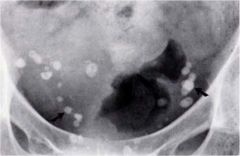
whats the anomaly?
|
phleboliths
|
|
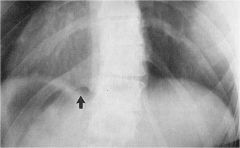
whats the anomaly?
|
rib anomaly- synostosis
|
|
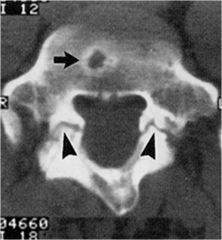
whats the anomaly?
|
Schmorl's Node
|
|
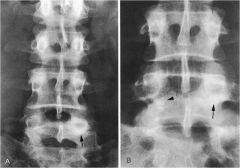
whats the anomaly?
|
Sclerotic pedicle with no apparent pars defect
|
|
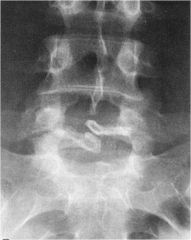
whats the anomaly?
|
spina bifida occulta
|
|
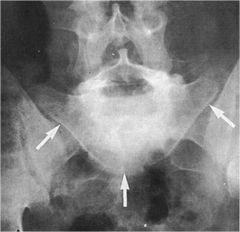
whats the anomaly?
|
Spondlyoptosis Bowline of Brailsford
|
|
whats the anomaly?
|
spondy- dysplastic Type 1
|
|
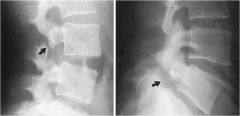
whats the anomaly?
|
spondy- dysplastic Type 2
isthmic |
|
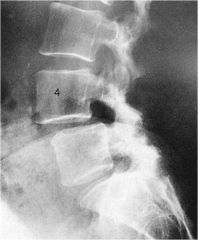
whats the anomaly?
|
Spondy- type 3- degenerative
|
|
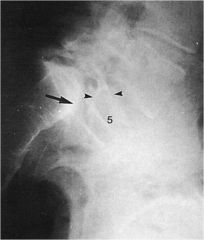
whats the anomaly?
|
spondylotosis
|
|
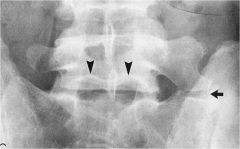
whats the anomaly?
|
transitional segment
|
|
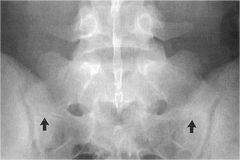
whats the anomaly?
|
transitional segment
|
|
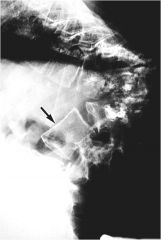
whats the anomaly?
|
Tuberculous sponylitis (Pott’s Disease)
|
|
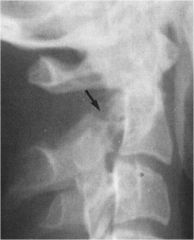
whats the anomaly?
|
type 4- Traumatic Spondylolisthesis or hangmans fracture
|
|
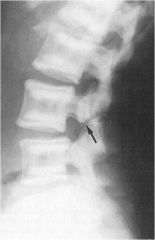
whats the anomaly?
|
type 5- Pathologic Spondylolisthesis- Osteopetrosis - Bone is brittle and prone to fracture
|
|
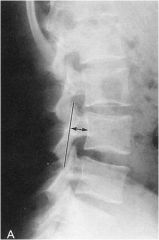
what the line of mensuration?
|
EISENSTEIN’S METHOD OF SAGITTAL CANAL MEASUREMENT
less than 15mm may be indicative of stenosis of the spinal canal |
|
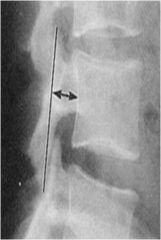
what the line of mensuration?
|
EISENSTEIN’S METHOD OF SAGITTAL CANAL MEASUREMENT
less than 15mm may be indicative of stenosis of the spinal canal |
|
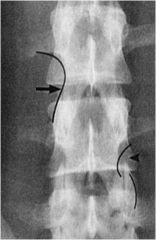
whats the line of mensuration?
|
HADLEY “S” CURVE
lines 1 and 2 should form a smooth "S" |
|
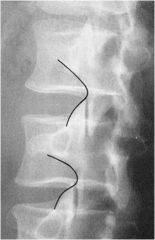
whats the line of mensuration?
|
HADLEY “S” CURVE
|
|
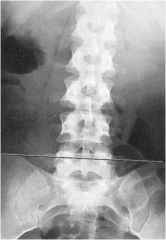
what is the line of mensuration?
|
INTERCRESTAL LINE
around L4 disc or inferior endplate of L4 if higher could show disposition to L4 to L5 degeneration if lower could show disposition to L5 S1 degeneratoin |
|
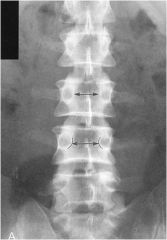
what is the line of mensuration?
|
INTERPEDICULATE DISTANCE
INTERPEDICULATE DISTANCE Cervical spine: average 28-29mm Thoracic spine: decreases gradually from T1-T7 then increases gradually caudally Lumbar spine: gradually increases caudally. |
|
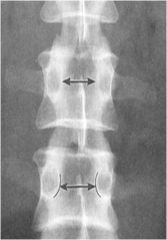
what is the line of mensuration?
|
INTERPEDICULATE DISTANCE
Cervical spine: average 28-29mm Thoracic spine: decreases gradually from T1-T7 then increases gradually caudally Lumbar spine: gradually increases caudally. |
|
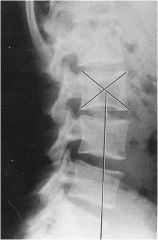
what is the line of mensuration?
|
LUMBAR GRAVITATIONAL LINE
normally: the vertical line should fall through the superior sacral surface (some sources say anterior 1/3 of the sacral base) anterior shift- line falls anterior to the sacral bast posterior shift- line falls posterior to sacral base |
|
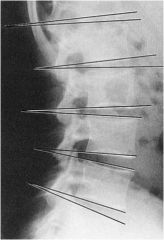
what is the line of mensuration?
|
Lumbar intervertebral disc angles
|
|
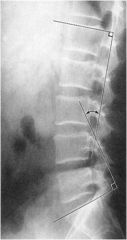
what is the line of mensuration?
|
lumbar lordosis
50-60 degrees average |
|
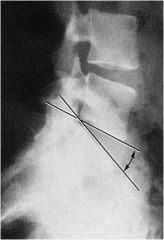
what is the line of mensuration?
|
Lumbosacral disc angle
normally between 10-15 degrees (some sources say 15-20) |
|
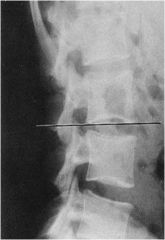
what is the line of mensuration?
|
McNABB’S LINE
|
|
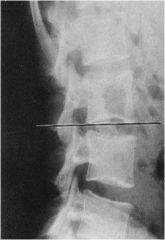
what is the line of mensuration?
|
McNABB’S LINE
normally should not intersect the tips of the superior articular facet of the level below |
|
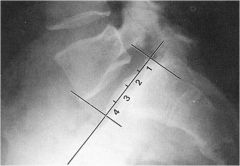
what is the line of mensuration?
|
MEYERDING’S CLASSIFICATION OF SPONDYLOLISTHESIS
|
|
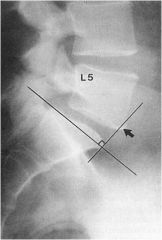
what is the line of mensuration?
|
ULLMAN’S LINE
aka: Garland-Thomas line the anterior inferior margin of L5 should not intersect the perpendicular line and should reside behind the line. Normally ~8mm posterior to ullman's line |
|
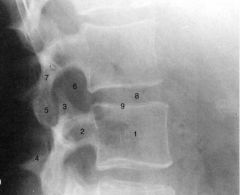
|
1. Vertebral body
2. pedicle 3. superior articular process 4. spinous process 5. inferior articular process 6. intervertebral foramen 7. pars interarticularis (isthmus) 8. intervertebral disc 9. vertebral endplate |
|
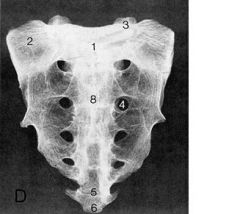
|
1. 1st sacral tubericle
2. sacral ala 3. superior articular process of the sacrum 4. 2nd sacral foramen 5. sacral coccygeal junction 6. coccyx 7. sacroiliac joint 8. third sacral tubercle |
|
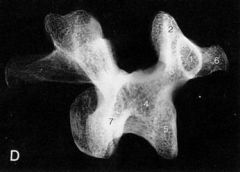
|
1. pedicle
2. superior articular process 3. pars interarticularis 4. lamina 5. inferior articular process 6. transverse process |
|
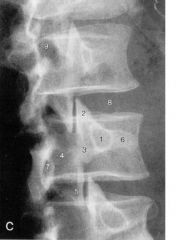
|
1. pedicle
2. superior articular process 3. pars interarticularis 4. lamina 5. inferior articular process 6. transverse process 7. spinous process 8. intervertebral disc 9. interlaminar space |
|
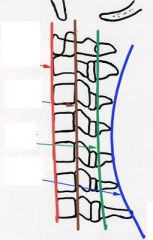
name the lines of mensuration
|
Red = anterior body line
Brown = posterior body line (George's line) green= spinolaminar (junction) line blue = posterior spinous line |
|
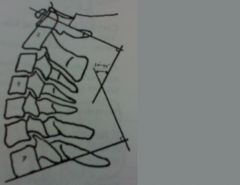
|
angle of cervical curvature cervical lordosis
the angle should be between 30-45 degrees hypolordosis <30 hyperlordosis >45 |
|
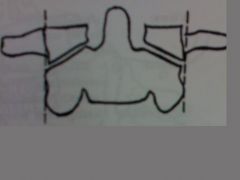
|
atlanto-axial alignment
these 2 landmarks should line up if not may be indicative of a burst fracture of C1 this may be normal in <4year old |
|
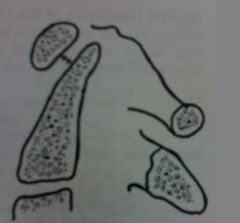
|
atlatodental interspace
child no greater than 5mm adult no greater than 3mm |
|
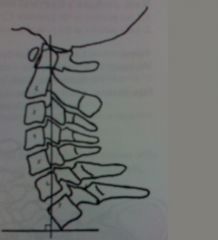
|
cervical gravitaional (wieght bearing) line- line
should pass through the superior anterior margin of C7 if the line is anterior to this may be indicative of forward head posturing, head forward carriage, anterior weight bearing |
|
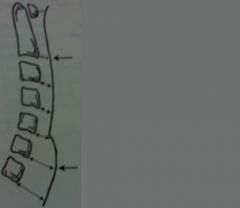
|
cervical prevertebral soft tissue space
At C2 its called Retropharyngeal soft tissue space and should be no more than 7mm At C7 its called Retrotracheal soft tissue space children no more than 14mm adults no more than 22mm |
|
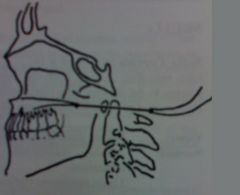
|
Chamberlain's line
odontoid tip should not extend more than 5mm above this line |
|
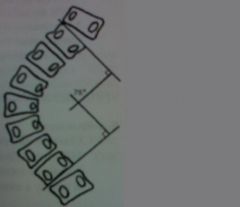
|
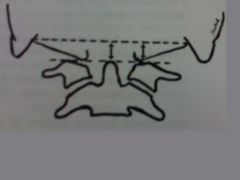
cobb's method
for scoliosis |
|
|
digastric line
the odontoid-digastric distance 1-21mm the atlanto occipital joint 4-20mm more than either of these measurements could be indicative of a basilar impression |
|
|
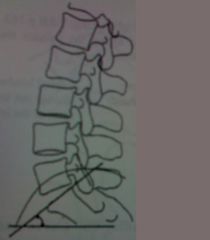
ferguson's lumbosacral angle
normal range between 26-57 degrees with a average of 41 degrees |
|

|
George's Line (posterior body line)
misalignment between vertebral levels may represent fracture, dislocation, degenerative changes, or ligamentous laxity |
|
|
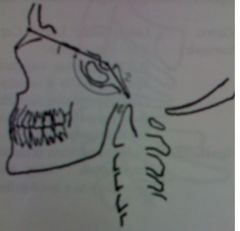
Martin's Basilar angle
no larger than 152 degrees no less than 123 degrees increased angle in platybasia, flatting of the skull base can be congenital or secondary due to bone softening |
|
|
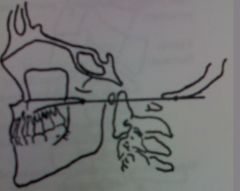
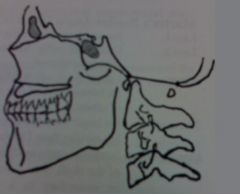
McGregor's Line
superior position is indicative of basilar impression. may be congenital or secondary to a bone softening disease |
|
|
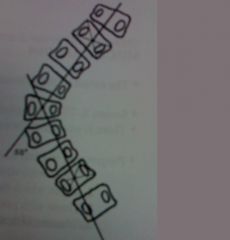
McRae's Line
superior position is indicative of basilar impression. may be congenital or secondary to a bone softening disease |
|
|
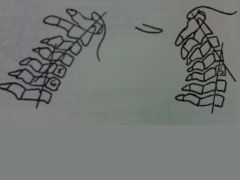
Risser-ferguson
measure the angle of intersection of the lines |
|
|
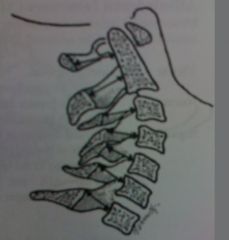
Ruth Jackson's cervical Stress line
flexion lines intersect between C5 and C6 extension lines intersect between C4 and C5 |
|
|
sagittal dimension of the cervical spinal canal
average is 22mm at C1 and 17mm and C7 At C1 less than 16mm and At mid to lower cervical less than 12mm is indicative of sagittal stenosis greater than C1 at C1 and greater than 22mm in mid to lower cervicalis indicative of spinal cord neoplasm |
|
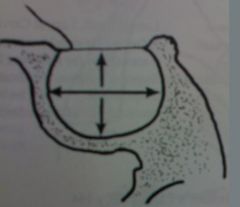
|
sella turcica size
16mm max horizontal 12mm max vertical enlargement may be caused by pituitary neoplasm |
|

|
spinolaminar line
misalignment or disruption of this line may be indicative of fracture, dislocation, degenerative changes, or ligamentous laxity more useful than george's line at the level of C1 |
|
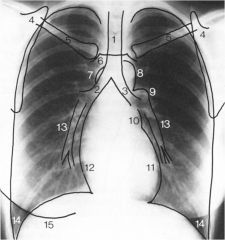
|
1. trachea
2. right main stem 3. left main stem 4. scapula 5. clavicle 6. manubrium 7. superior vena cava 8. aortic knob (transverse aorta) 9. left pulmonary hilus 10. left atrial border 11. left ventricle border 12. right atrial border 13. pulmonary artery 14. costophrenic angle 15. liver |
|
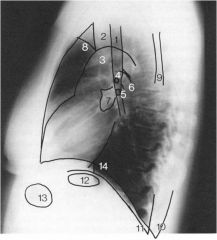
|
1. trachea
2. 3. aortic arch 4. right upper lobe bronchus 5. left upper lobe bronchus 6. 7. hilus 8. retrosternal space 9. scapula 10. left posterior costophrenic angle/ sulcus 11. right posterior costophrenic angle/ sulcus 12. magenblasse 13. gastric air bubble - (FIP's) 14. left hemidiaphragm |

