![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A bike travels 100m in 10 seconds. What is their speed? |
100 / 10 = 10m/s |
|
|
What's the difference between average speed and instantaneous speed? |
average speed of an object is the speed of an object over a period of time instantaneous speed of an object is the speed of an object at a particular instant. |
|
|
What is the displacement of an object at a given moment? |
its net distance from its starting point together with an indication of direction |
|
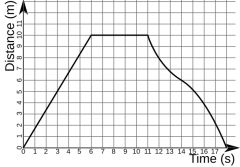
Describe this journey |
Constant speed Stationary Travelling back to the start quickly then more slowly then more quickly again |
|
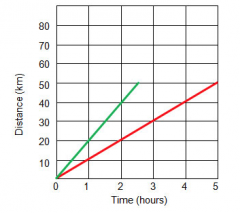
In which line is the speed faster? |
a steeper gradient is a higher speed so the one on the left |
|
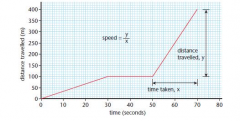
Calculate the speed from the gradient |
300 / 20 = 15 m/s |
|
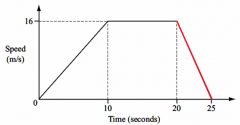
Describe this journey |
Constant acceleration Constant speed Constant deceleration |
|
|
What does acceleration mean? |
the change in speed of an object in a given time interval |
|
|
What is instantaneous velocity? |
its instantaneous speed together with an indication of the direction |
|
|
What is meant by a positive and negative velocity? |
the velocity of an object moving in a straight line is positive if it is moving in one direction and negative if it is moving in the opposite direction |
|
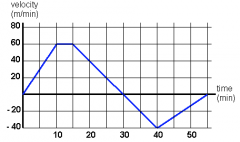
What happened in this graph when the line crossed the x axis |
It changed direction |
|
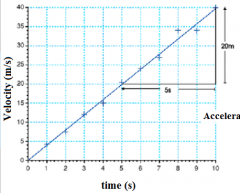
Calculate the acceleration from the gradient |
20 / 5 = 4m/s/s |
|
|
If a car accelerates from 0m/s to 20m/s in 10s what's it's acceleration? |
20 / 10 = 2 m/s/s |
|
|
What arises from an interaction between two objects? |
A force |
|
|
when two objects interact, both always experience a force called... |
an interaction pair |
|

What are the 2 interaction pair forces? |
The gases push the space shuttle forwards, with the same size force in the opposite direction. |
|
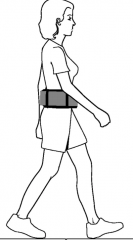
What are the 2 interaction pair forces? |
foot pushed back on the ground ground pushed forwards on her foot |
|
|
The two forces in an interaction pair are ...... in size and ............ in direction, and that they act on ................. objects |
equal opposite different |
|
|
What is friction? |
The interaction between two surfaces which slide (or tend to slide) relative to each other: each surface experiences a force in the direction that prevents (or tends to prevent) relative movement |
|
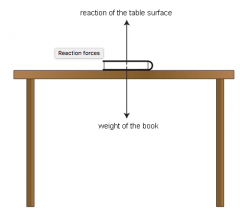
Describe what this shows |
the object pushes down on the surface, the surface pushes up on the object with an equal force, and this is called the reaction of the surface |
|
|
friction and the reaction of a surface arise in response to the action of an applied force, and their size matches the applied force. Will they match this force infinitely? |
No, only up to a limit then it will suddenly move |
|

describe the forces on the car |
driving force from engine counter force due to friction with the ground and air resistance wheels push back on the ground ground pushes forwards on the wheels |
|
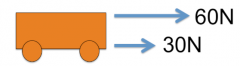
What is the resultant force? |
90N to the right |
|

What is the resultant force |
20N to the right |
|
|
if a resultant force acts on an object, it causes a change of ?????? in the direction of the force |
momentum |
|
|
A rocket with a mass of 1,000kg is launched with a velocity of 100m/s upwards. What's its momentum? |
1000 x 100 = 100,000kg m/s |
|
|
the size of the change of momentum of an object is proportional to the size of the ....... acting on the object and to the ....... for which it acts: |
resultant force time |
|
|
If an object has a a change of momentum of 300 kg m/s and a resultant force of 20N, how long did it act for? |
300 / 20 = 15s |
|
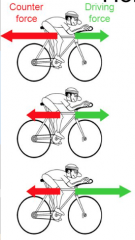
What will happen in each of these? |
slow down constant speed speed up |
|
|
In a collision there is a change in momentum. For a given change in momentum, the longer the duration of the impact, the smaller the ....... |
average force |
|
|
car seat- belts, crumple zones, air bags, and cycle and motorcycle helmets all work in the same way. They increase the time of the collision. why is this beneficial? |
It decreases the force so there is less injury |
|
|
If the resultant force on an object is zero, will the momentum change? |
No if it is stationary, it stays at rest; if it is already moving, it continues at a constant velocity [a steady speed in a straight line] |
|
|
What is kinetic energy? |
the energy of a moving object |
|
|
What is GPE? (Gravitational Potential Energy) |
The energy an object gains as it is raised and decreases as it falls It is the object's potential to fall due to gravity |
|
|
What is "doing work"? |
when a force moves an object, it does work when work is done on an object, energy is transferred to the object and when work is done by an object, energy is transferred from the object to something else |
|
|
If a ball is lifted 1m using a force of 20N, how much work is done? |
1 x 20 = 20Joules |
|
|
work done is equal to the amount of ........ transferred |
energy |
|
|
when an object is lifted to a higher position above the ground, work is done by the lifting force; this increases the ??????????? |
GPE |
|
|
If a roller coaster moves up a ramp to 100m above ground and gains 30,000J in GPE, what is the weight of the roller coaster cart? |
30,000 / 100 = 300N |
|
|
when a force acting on an object makes its velocity increase, the force does work on the object and this results in an increase in its ........ energy |
kinetic |
|
|
What 2 things will increase the kinetic energy? |
mass speed |
|
|
Does mass or speed have a bigger effect on the kinetic energy of a moving object? |
speed because it is squared in the equation |
|
|
an object’s kinetic energy changes by an amount equal to the work done on it by an applied force ... if we ignore what forces? |
friction & air resistance |
|
|
Why do air resistance or friction will cause the gain in an object’s kinetic energy to be less than the work done on it by an applied force in the direction of motion? |
because some energy is dissipated through heating |
|
|
Energy is always c.............. |
conserved (it cannot be created or destroyed, it is just transferred from one energy store to another e.g. GPE to kinetic + thermal) |

