![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the dose, route and frequency of Methergine administration? |
0.2mg every 2-4 hours, IM |
|
|
What is the dose, route and frequency of hemabate administration? |
0.25mg, IM or intramyometrial, every 15-90 minutes, 8 dose max |
|
|
Risk factors for vaginal hematoma: |
Operative delivery Nulliparity Coagulation disorders PEC Multiple gestation Compound presentation Rapid descent |
|
|
Hematoma vessel sources: |
Branches of: Internal pudendal artery (anterior) Inferior rectal artery (posterior) Uterine artery (paravaginal)
Perineal venous plexus |
|
|
Symptom concerning for retroperitoneal bleeding/hematoma: |
Rectal pain with minimal vulvar visualization of a hematoma. |
|
|
Conservative management of vaginal hematoma: |
Only if non-expanding. Close observation Ice packs Pain management Bladder drainage (if necessary) |
|
|
Management of acutely expanding vaginal hematoma: |
- monitor I/Os - Fluid resuscitate prn - blood prn
Surgical management: - ppx abx - evacuate hematoma - Identify and ligate bleeding vessels - repair defect - Artery embolization if surgical mgmt doesn't work |
|
|
What is fetal lie? |
The relation of the fetal long axis to that of the mother. Can be: - longitudinal - transverse - oblique |
|
|
What is fetal presentation? |
Presenting part is the part of the baby that is closest to the birth canal. Can be: - cephalic - breech - shoulder |
|
|
What is fetal attitude? |
Further defines cephalic presentation. Can be: - vertex - sinciput (anterior fontanel presenting) - brow - face |
|
|
What is fetal position? |
Refers to the relationship of a portion of the fetal presenting part to the right or left of the birth canal. - Vertex: occiput - Face: mentum (chin) - Breech: sacrum |
|
|
What is synclitism vs asynclitism? |
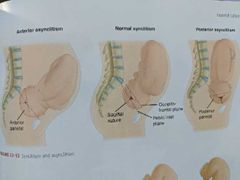
The position of the sagittal suture with relation to the pubic symphisis and the sacral promontory. - Normal is midway between the two. - Anterior asynclitism is sagittal suture closer to sacral promontory (feel more of anterior parietal bone). - Posterior asynclitism is sagittal suture closer to pubic symphisis (feel more of posterior parietal bone). |
|
|
Cardinal Movements of Labor: |
1. Engagement 2. Descent 3. Flexion 4. Internal Rotation 5. Extension 6. External Rotation (Restitution) 7. Expulsion |
|
|
What are the borders of the pelvic inlet? |
Sacral Promontory Pubic Symphisis Linea terminalis (lateral borders) |
|
|
What is the obstetrical conjugate? |
Shortest distance between pubic symphisis and sacral promontory. - Usually >10cm but cannot be measured directly. - measure diagonal conjugate and subtract 1.5-2cm (Diagonal conjugate is the distance between the lowest margin of the pubic symphisis and the sacral promontory) |
|
|
Indications for Cerclage |
1. History: - one or more second trimester losses associated with painless cervical dilation OR - prior cerclage for painless cervical dilation in second trimester
2. Physical Exam: - painless cervical dilation in second trimester
3. Ultrasound: - previous spontaneous preterm delivery <34 weeks and current singleton pregnancy with cervical length <25mm before 24 weeks |
|
|
What is a McDonald cerclage? |
Purse string suture of non-resorbable material inserted into the cervicovaginal junction. |
|
|
What is a Shirodkar cerclage? |
Involves dissection of the vesicocervical epithelium to place the suture as close to the internal os as possible. Use non-resorbable suture. |
|
|
What is a transabdominal cerclage and when is it indicated? |
Suture placed at the cervicoisthmic junction transabdominally (open or laparoscopic). Reserved for previous failed transvaginal cerclage (resulting in second trimester loss) or if can't perform transvaginal cerclage (ie after trachelectomy). Can leave in place for subsequent pregnancies and deliver via cesarean. |
|
|
Risk factors for preterm delivery: |
- Previous spontaneous preterm delivery - short cervix (<25mm) - smoking - previous LEEP/CKC or cervical instrumentation - vaginal bleeding - UTIs - genital infection - periodontal disease (not likely the dental disease itself but other associated traits) |
|
|
Optimal interpregnancy interval: |
18-23 months |
|
|
Lynch Syndrome Cancers |
- Endometrial (16-61% risk by age 70) - Colon (18-61% risk by age 70) - Ovarian (5-10% risk by age 70) |
|
|
Risk Reduction in patients with Lynch Syndrome |
- Colonoscopy q1-2 years starting age 20-25 or 2-5 years before youngest affected family member - Endometrial biopsy q1-2 years starting age 30-35 - menstrual calendar should be kept, if irregular should be investigated! - risk reducing Hysterectomy with BSO at 40-45 or when done childbearing - use progestin or COCs to decrease risk |
|
|
BRCA1 tumor suppressor is on which chromosome? |
Chromosome 17 |
|
|
BRCA2 tumor suppressor is on which chromosome? |
Chromosome 13 |
|
|
What is the breast cancer risk with BRCA1/2? |
45-85% for both
(Male breast cancer seen with BRCA2) |
|
|
What is the ovarian cancer risk with BRCA1 vs BRCA2? |
BRCA1: 39-46% BRCA2: 10-27% |
|
|
When is risk reducing BSO recommended for BRCA carriers? |
BRCA1: age 35-40 BRCA2: age 40-45 (Or when done with childbearing) |
|
|
What are risk factors for Preeclampsia? |
Nulliparity Multifetal gestation Previous PEC CHTN Pregestational diabetes Gestational diabetes Thrombophilia Systemic Lupus Erythematous Pregravid BMI >30 Antiphospholipid Syndrome Age >35 Kidney disease Obstructive Sleep Apnea |
|
|
What are the diagnostic criteria for PEC? |
BLOOD PRESSURE - sBP >140mmHg or dBP >90mmHg on two or more occasions more than 4 hours apart (If sBP >160 or dBP>110 can diagnose within minutes)
PROTEINURIA > 300mg in 24 hours or > 0.3mg/dL protein: creatinine ratio
OR Severe features: - plt <100K - creatinine > 1.1mg/dL (or double baseline) - LFTs twice upper limit of normal - pulmonary edema - persistent headache not responsive to medications and not accounted for by other diagnosis - visual disturbances |
|
|
Fatty Liver of pregnancy: |
Hepatic dysfunction with varying renal failure. - low glucose - liver dysfunction - prolonged PTT - high maternal and fetal mortality |
|
|
What is the antidote to magnesium toxicity? |
Calcium gluconate 1g IV over 2 minutes (Use lasix to increase renal excretion) |
|
|
What are contraindications to magnesium sulfate and what can you use instead for seizure ppx? |
Myasthenia Gravis Pulmonary Edema Can use phenytoin or diazepam. - If use phenytoin, monitor EKG - If use diazepam, make sure able to intubate. |
|
|
Aspirin decreases rates of what two PEC parameters if initiated before xx weeks GA? |
Decrease risk of severe PEC and FGR if started between 12-16 weeks. |
|
|
How should we monitor patients with GHTN/PEC? |
- close BP monitoring (weekly clinic visits) - serial ultrasound for fetal growth (q3-4 weeks) - weekly antenatal testing - weekly labs - urine protein (if GHTN) |
|
|
Contraindications to magnesium sulfate: |
- myasthenia gravis - hypocalcemia - moderate to severe renal failure - cardiac ischemia - heart block - myocarditis |
|
|
At what level are DTRs lost with magnesium toxicity? |
9mg/dL (Respiratory depression at 12mg/dL Cardiac arrest at 30mg/dL) |
|
|
Why can't pregnant women take Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEs) or Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)? |
In first trimester can cause renal dysgenesis and calvarial hypoplasia. Can cause fetal growth restriction later. |
|
|
How should we evaluate chronic hypertensive patients prepregnancy or at initiation of prenatal care? |
Baseline labs: - serum creatinine - BUN - electrolytes (esp K+) - AST/ALT - CBC - spot urine prot ( if <0.15 no need for 24h urine if normal creatinine) - EKG if >4 years disease or concern for long standing hypertension that may have been diagnosed late (echo if EKG abnormal) |
|
|
Doses for oral anti hypertensive medications: |
Labetalol: 200-2400mg daily divided into 2-3 doses Nifedipine XL: 30-120mg daily Methyldopa: 500-3000mg daily divided into 2-3 doses |
|
|
In cases of severe hypertensive intrapartum, how should you monitor BPs once your target BP has been reached (sBP <160 and dBP <110)? |
Monitor BPs - q10 minutes for 1 hour, then - q15 minutes for 1 hour, then - q30 for 1 hour, then - q hour for 4 hours |
|
|
What are contraindications to labetalol use? |
- Asthma - myocardial disease - decompensated cardiac function - heart block and bradycardia |
|
|
Some examples of single gene disorders (inherited in an autosomal recessive manner): |
- sickle cell - cystic fibrosis - Tay- Sachs - alpha or beta thalassemia - phenylketonuria |
|
|
Best genetic test for fetal death/ stillbirth: |
Microarray |
|
|
Pregnancies at increased risk for genetic abnormalities: |
- advanced maternal age - advanced paternal age (>40-50) - paternal carrier of chromosome rearrangement - parental aneuploidy or aneuploidy mosaicism - prior child with structural birth defect - parental carrier of genetic disorders - previous child/fetus with aneuploidy - structural anomalies on sono |
|
|
If a preimplantation genetic test is abnormal, what subsequent test should be performed? |
CVS or amnio due to possibility of error |
|
|
At what gestational age can CVS vs amniocentesis be performed? |
CVS: 10-13 weeks Amnio: 15+ weeks |
|
|
What are the procedure related loss rates of CVS vs amnio? |
~1/500 generally (But really depends on experience of provider) CVS: 0.22% (1 in 455) Amnio: up to 0.27% (1 in 370) |
|
|
What are associated clinical findings of down syndrome (T21)? |
- characteristic facial features - learning disabilities - congenital heart defects (atrioventricular canal defects) - intestinal atresia - seizures - childhood leukemia - early onset Alzheimer's |
|
|
When can FTS be performed and what are the components? |
First trimester screen is done between 10w0d and 13w6d. Components: - nuchal translucency (abnl is >3mm) - serum free bhcg/total hcg - pregnancy associated plasma protein A analyte level (PAPP A) |
|
|
When can quadruple screen be performed and what are its components? |
15w0d - 22w6d (though ideal is 16-18 wks) Components: 1. Hcg 2. Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) 3. Inhibin A 4. Unconjugated estriol (Also consider maternal factors such as age, weight, race, presence of diabetes, number of fetuses) |
|
|
What is sensitivity of quad and FTS for detection of T21? |
~80% FTS 82-87% Quad 81% |
|
|
What are some examples of autosomal dominant genetic disorders? |
- Huntington disease - Marfan syndrome - achondroplasia - osteogenesis imperfecta (types 1-4) - polycystic kidney disease (type 1) - Neurofibromatosis, type 1 |
|
|
What are the X- linked recessive disorders? |
- hemophilia A and B - red/green color blindness - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
|
|
How do we define a prolonged latent phase? |
> 14 hr in multip > 20 hr in nullip |
|
|
How do we define active phase arrest? |
>6cm with ROM and one of the following: - 4hr with adequate contractions and no cervical change (>200 Montevideo units over 10 minutes) - 6hr with inadequate ctxns and oxytocin |
|
|
Factors that influence labor dysfunction: |
Think of 3 Ps: 1. Power 2. Pelvis 3. Passenger
- maternal age - gestational age - parity - prepregnancy BMI - gestational weight gain Obstetric complications like: - PROM - infection - placental abruption - Preeclampsia |
|
|
How do we define second stage arrest? |
- At least 2 hours of pushing for multips - At least 3 hours of pushing for nullips **Add 1 hour if epidural |
|
|
Factors that affect the second stage of labor? |
Parity Delayed pushing Use of epidural Large maternal BMI Large fetal weight OP position Fetal station at complete dilation |
|
|
Maternal risks of a prolonged second stage: |
- infection - PPH - high order perineal laceration |
|
|
What is integrated screening? |
NT + PAPP-A then Quad 96% detection of Down syndrome |
|
|
What is serum integrated screening? |
PAPP-A + quad 88% detection of Down syndrome. |
|
|
What is sequential stepwise screening? |
Offer FTS: If positive - offer diagnostic screen or cell free DNA test If negative - offer second trimester screen 95% detection rate for Down syndrome |
|
|
What is sequential contingent screening? |
Offer FTS: If negative - no further testing If positive - offer diagnostic test or cell free DNA If intermediate - offer quad screen 88-94% detection rate of Down Syndrome |
|
|
Of the soft markers on anatomy ultrasound, which ones should get third trimester follow up? |
- Renal pelvis dilation (pyelectasis) - Short femur and humerus - Echogenic bowel |
|
|
How should you manage an enlarged NT when aneuploidy test is negative? |
Also a/w: - congenital heart disease - skeletal dysplasia - Noonan syndrome |
|
|
Factors contributing to low fetal fraction in cell free DNA test: |
- high maternal BMI - sampling before 10 weeks - fetal aneuploidy |
|
|
Low PAPP-A (<5%ile) is independently associated with which obstetric complications? |
- spontaneous fetal and neonatal loss - fetal growth restriction - preeclampsia - placental abruption - preterm delivery |
|
|
What fetal defects are associated with elevated AFP levels? |
- Spina bifida - anencephaly - abdominal wall defect |
|
|
What obstetric complications have been associated with elevated msAFP levels? |
- Placenta accreta spectrum - low birth weight - fetal to maternal bleeding (ie with Rh incompatibility) |
|
|
If suspect female athletic triad as cause of amenorrhea, what tests should you order in addition to amenorrhea work up? |
Chem profile UA CBC +/- EKG |
|
|
Risk factors for developing endometriosis: |
- Early age of menarche (<11 yr) - Shorter cycles - Prolonged/heavy menses - affected first degree relative |
|
|
Appearance of endometriomas on sono: |
Low-level, homogeneous internal echoes (old blood). |
|
|
What is the FDA approved add-back therapy for GnRH agonist prolonged use? |
Norethindrone 5mg daily |
|
|
What are medical management options for endometriosis? |
- NSAIDs - COCs - norethindrone - provera (oral or Depot) - GnRH agonist - danazol (androgenic) |
|
|
What are ultrasound findings seen in congenital CMV? |
- abdominal and liver calcifications - intracranial calcifications - echogenic bowel and kidneys - ascites - hepatosplenomegaly - microcephaly - hydrops fetalis - growth restriction *(most of these more common with other abnormalities) |
|
|
What is the risk of vertical transmission of CMV? |
30% - more common in third trimester, but more severe if transmission occurs in first trimester |
|
|
What is the vertical transmission rate or parvovirus B19? |
About 25-30% |
|
|
What are potential sequelae of congenital parvovirus infection? |
- spontaneous abortion (1st trimester) - fetal demise, hydrops (2nd and 3rd trimester) |
|
|
What are symptoms of adult parvovirus B19? |
Rash, arthritis, flu-like illness (Many are asymptomatic) |
|
|
How should you manage someone after maternal parvovirus infection confirmed? |
Serial weekly ultrasounds to assess for: - growth restriction - hydrops - cardiomegaly - ascites - increased MCA dopplers
Monitor for 8-12 weeks after exposure/infection. |
|
|
How do you diagnose parvovirus B19 infection? |
Maternal: - check IgM and IgG levels. - If IgG positive but IgM negative, likely previous infection. - If IgM positive, monitor fetus for signs of infection. - if both negative, repeat in 4 weeks if known exposure or suspicion Fetal: - amniotic fluid PCR |
|
|
How much does a normal uterus weigh? |
~60g |

