![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 categories of Rx that may cause MRONJ |
Bisphosphonate monoclonal antibody tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
|
|
IV Bisphosphonates: Indications |
1' - Cancer: Multiple Myeloma, Metastatic bone cancer 2' - osteoporosis: once year dosing |
|
|
Oral Bisphosphonates: Indications |
Osteoporosis |
|
|
Dx of MRONJ |
1. Exposed bone present 2+ mo 2. prior Tx w/ Bisphosphonates 3. No Hx of radiation |
|
|
Name of Osteoporosis Drugs |
-dronate: Fosamax (Alendronate), Actonel (risendronate), Boniva (ibandronate), Skelid (tiludronate), Didronel (etidronate), Reclast (IV: zolendronate), Prolia (denosumab - monoclonal Ab) |
|
|
Stage of MRONJ: pt comes in w/ pain w/o exposed bone |
Stage 0 |
|
|
Stage of MRONJ: pt comes in w/ exposed bone, no pain/symptoms |
Stage 1 |
|
|
Stage of MRONJ: pt comes in w/ exposed bone with infection |
Stage 2 |
|
|
Stages of MRONJ: pt comes in w/ exposed bone w/ pain without infection |
Stage 2: pain AND/OR infection |
|
|
Stages of MRONJ: pt comes in w/ exposed bone w/ pain, infection and pathologic fractures (mand or mx, extra-oral fistula, osteolysis, sinus floor) |
Stage 3 |
|
|
Stages of MRONJ: pt's x-ray shows that the disease is extended into sinus |
Stage 3 |
|
|
Guidelines of MRONJ: pt on IV Bis |
avoid ext or elective bone surgery salvage endo as alt. tx |
|
|
Incidence of ONJ for pts on IV Bis for cancer |
2-14% |
|
|
Practice Guidelines: Pts on oral Bis |
4-2-3: on Bis for 4 yrs: Rx holiday for 2 mos before, 3mo after surgery pt in pain/infection: tx w/o delay |
|
|
Incidence of MRONJ in pts on oral Bis |
low: <1% |
|
|
Practice guidelines for pt on oral Bis: less than 4 yrs but significant immune suppression |
consider Rx Holiday |
|
|
Practice Guidelines: for pt on IV Bis for osteoporosis |
Tx w/o the same concern as pt treat w/ IV for cancer frequency of dosing and cumulative effect is key factor |
|
|
Practice guidelines: risk of MRONJ for pts on IV Bis for osteoporosis |
low |
|
|
Practice guidelines: pts on denosumab/other Rx 1. monthly injections for ca. 2. yearly injections for osteoporosis |
1. Tx like IV Bis pts [delay ext/elective bone surgery] 2. no special precautions yet |
|
|
Routine dental care for pt on Bis: restorative, prophylaxis |
continue for all pt |
|
|
Routine dental care for pt on Bis: implants: IV Bis, oral Bis |
CI for IV Bis pt ok for oral Bis pt (possible Rx holiday) |
|
|
Oncology guidelines for pt on Bis |
stress preoperative dental assessment for all pt prior to Rx w/ anti-resorptive medications |
|
|
MRONJ: Tx strategies: Stage 0 |
pain mng, Abx if necessary |
|
|
MRONJ: Tx strategies: Stage 1 |
daily peridex 0.12% oral rinse and follow q 2mo |
|
|
MRONJ: Tx strategies: Stage 2 |
add systemic Abx, peridex and follow q 2mos |
|
|
MRONJ: Tx strategies: Stage 3 |
pt typically have pain that impacts their quality of life. may need more extensive surgical debridement or resection |
|
|
MoA of Bis |
to prevent osteoclasts from resorbing bone. |
|
|
MoA of Bis is to prevent osteoclasts from resorbing bone: why get destruction in the jawbones |
destruction of osteoblast and osteoclast jawbones are different: higher bone turnover rate |
|
|
3 Hypo-: radiation induced |
hypovascular hypocellular hypoxic |
|
|
H&N finding: pt on radiation therapy |
rock hard area upon palpation severe mucositis, xerostomia, dry skin, lack of hair, trismus |
|
|
is ORN part of infxn of bone? |
no: you may have 2' Infxn but by definition ORN is not infxn of bone (ONJ) |
|
|
when you have radiographic RL/RO lesion, how do to differentiate among: 1. Osteomyelitis 2. MRONJ 3. ORN |
1. Hx of trauma, w/o use of Bis, radiation Tx 2. Hx of Bis 3. Hx of radiation Tx - the bottom line is take through MHx |
|
|
factors involved in ORN |
1. Dose (major: high = 7200 cGy, moderate dose = 6k-6400) 2. Timing 3. type of surgery 4. Oxygen therapy |
|
|
ORN risk vs. time graph contineously increases as time goes up |
No. high at initial stage (early trauma-induced): dips down then continue to go up (spontaneous -> late trauma induced ORN) |
|
|
(T/F) it is recommended Ext shorty before XRT |
F: you want to give chance for soft tissue to completely healed over (wk-mos): no exposed bone, no open wound in the mouth |
|
|
(T/F) It is recommended Ext during XRT |
F: high risk of trauma induced ORN |
|
|
Golden window |
4 mos: if you did not had chance to do ext before XRT, consider doing the tx during Golden window (1st 4 months) |
|
|
what happens after Golden window |
vector crosses threshold -> 3H tissue development (hypovascular, hypocellular, hypoxic = poor healing = necrosis of tissue) |
|
|
prevention of ORN: Tx timing, dose, preventative tx |
at least 21 days prior to XRT, ext teeth w/ - PA pathosis - advanced perio dz - any mand teeth in direct path of radiation of >6000cGy - Fl tx |
|
|
HBO protocol for prevention of ORN: >4mo post XRT |
20/10: 20 sessions of 100% O2 for 90 min prior to Sx 10 sessions post Sx |
|
|
(T/F) repeated Sx in irradiated area would require repeated HBO protocol |
F: Angiogenesis is permanent; Not require repeated HBO |
|
|
Treatment of ORN: Stage 1 |
30/10 HBO 30 sessions of HBO - local debridement - 10 sessions of HBO |
|
|
Treatment of ORN: Stage 2 |
30 sessions follows by surgical debridement then 10 sessions of HBO |
|
|
Treatment of ORN: Stage 3 |
30/surg debridement/10 HBO -> continuity resection, jaw stabilization, soft tissue flap |
|
|
Treatment of ORN: exposed bone w/ pathologic fracture, orocutaneous fistula, or osteolysis to the inferior border of the mand |
straight to Tx of stage 3: 30 sessions before the Sx -> cont. resection, jaw stabilization, soft tissue flap -> 10 after Sx |
|
|
wound healing via HBO is by inducing of |
migrate Macrophages into irradiated area |
|
|
HBO vs. Surgery |
HBO: to tx VITAL radiation-injured tissue Surgery: to remove NON-VITAL bone |
|
|
ORN usually on Mx or Mand |
Mand: less blood supply |
|
|
Tx of ORN diagram |
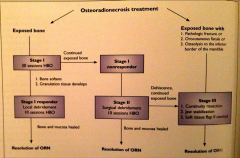
|
|
|
highest risk of developing infxn after __days post chemo when the _____ count drops |
7-10 days Neutrophil |
|
|
Major SE of chemo |
bone marrow suppression |
|
|
Pancytopenia |
anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia |
|
|
(T/F) Myelosuppression is reversible |
T: should return to normal 6-8 wks after stopping of Rx |
|
|
delay even simple tooth ext if platelet count is less than |
50,000/uL |
|
|
Prophylactic Abx prior to Sx on pt w/ central venous catheters for chemo? |
Yes |
|
|
ANC calculation |
ANC = WBC x (% neutrophil + % bands)
bands = immature neutrophils |
|
|
ANC for mild neutropenia and prophylactic Abx uses |
ANC = 1000-1500 Prophylactic Abx not required for minor OS |
|
|
ANC for moderate neutropenia and prophylactic Abx uses |
ANC = 500-999 Prophylactic Abx indicated for invasive procedures |
|
|
ANC for severe neutropenia and prophylactic Abx uses |
ANC = <500 Prophylactic Abx indicated for minor OS |
|
|
common signs of infection |
Fever, swelling, pain, redness, loss of fxn |
|
|
pt comes in and you cannot palpate the inferior border of mand, it indicates which space infxn |
Submandibular & submental space infxn |
|
|
pt comes in w/ elevation of floor of mouth and tongues indicates which space infxn |
Sublingual space infxn: CLASSIC sign! |
|
|
involvement of bilateral submand, submental, and sublingual space infxn is called |
Ludwig's angina |
|
|
dysphonia may indicates which space infxn |
"hot potato voice" indicates bad infxn: compromising how they speak: Ludwig's angina |
|
|
pt comes in w/ trismus, fever. It indicates which space infxn |
Pterygmandibular & submasseteric spaces |
|
|
swelling of the ear region may indicates which space infxn |
parotid space |
|
|
pt comes in w/ dysphagia, and uvula deviated to the one side. it indicates which space infxn |
lateral pharyngeal space |
|
|
Dyspnea may indicates |
multiple space involvement |
|
|
lower molar infxn usually results in which space infxn |
submandibular space |
|
|
inflammatory condition (infxn) of the bone starts where |
in the medullary cavity and havarsian system (marrow) then extend to involve the periosteum |
|
|
formation of the osteomyelitis |
starts at marrow -> compromised local blood supply -> sequester/ischemia formation |
|
|
name that symptom: Compression of neurovascular bundle -> thrombosis, ischemia -> osteomyelitis-mediated inferior alveolar nerve dysfxn |
Vincent's symptom |
|
|
Vincent's symptom involves |
inferior alveolar n. numbness = numbness of lip, chin area |
|
|
acute osteomyelitis: timing |
4wks |
|
|
factors for osteomyelitis: pathogens, virulence factor, host immunity, local tissue perfusion |
inc in # of pathogens, virulence dec in local and systemic host immunity, local tissue perfusion |
|
|
acute osteomyelitis involve: clinical exam |
abscess formation, predominant osteolysis (x-ray), fistular formation |
|
|
as it goes to secondary chronic osteomelitis you'll see: clinical exam |
sequester formation, periosteal rxn neoosteogenesis, predominant sclerosis |
|
|
who are more prone to osteomyelitis |
hx of DM, immunocompromised, malnutrition, leukemia, smokers |
|
|
predisposing factors for osteomyelitis |
trauma (Ext, fractures) acute pericoronitis, PA abscess, intraosseous injection |
|
|
clinical presentation of osteomyelitis |
pain, fever, hypoesthesia/anes of lower lip (IAN) |
|
|
clinical presentation of osteomyelitis if not controlled within 10-14 days of onset |
mobility of teeth (percussion +), purulent discharge, fistular, fetid malodor, regional lymphadenopathy, fever, dehydration, elevated WBC |
|
|
two bacteria that is important for osteomyelitis |
Actinomycosis, Strep |
|
|
radiographs to order when you suspect osteomyelitis |
Pan, CT, MRI |
|
|
Tx for osteomyelitis |
remove any source of infxn, surg debridement, abx (usually IV. rarely only oral) |
|
|
key to surgery in osteomyelitis |
must have bleeding bone in margin: clean out enough bone to have bleeding bone: key is to keep periosteum as close as possible to bleeding bone: ALWAYS do Bx to Dx |
|
|
Tx of acute osteomyelitis |
removal of source of infxn local I&D local curettage (superficial sequestra/saucerization) |
|
|
Tx of secondary chronic osteomyelitis |
surgical debridement of infxed tissue |
|
|
bacteria involved in osteomyelitis |
Actinomycosis |
|
|
Tx of Actinomycosis induced osteomyelitis |
Abx, I&D, excision of the fistulous tract, culture (Bx) to Dx |
|
|
Tx of osteomyelitis: Abx Therapy |
IV Abx 4-6 wk then Oral Abx for 6-12 months (likely to recur) Penicillin (DoC): culture guided Abx |
|
|
first thing to do when pt comes in w/ oral candidiasis |
see if they are immunocompromised/taking long term Abx/steroid/immune suppressin Rx |
|
|
Tx for oral candidiasis |
1. topical 2. if not resolved, systemic pt wo known immunocompromised status check for unDxed dz |
|
|
Two anti-fungal topical agenst |
Nystain clotrimazole |
|
|
systemic tx for candidiasis |
Fluconazole (Diflucan) |
|
|
Dr. Lui lect Summary 1: signs/symptoms of infxn 1. trismus 2. elevation of of Fom 3. Dyphonia 4. Dyphasia 5. inability to palpate inferior border of mand |
1. pterygomanibular/submessenteric 2. sublingual 3. Ludwig's angina 4. lateral pharyngeal 5. submand/submental |
|
|
Dr. Lui lect 1 Summary 2: osteomyelitis Radiographs to order where does it starts causes what (clinical presentation) |
Pan, CT it starts from marrow (path of least resistance. NOT GINGIVA causes ischemia/fenestration |
|
|
Dr. Lui lect 1 Summary 3: Tx of osteomyelitis |
Abx (IV, not just oral), surgical debridement (remove any source of infxn) |
|
|
Dr. Lui lect 1 Summary 4: Tx for Candidiasis, Actinomycosis |
very difficult to tx Actinomycosis: long term Abx Candidiasis: find the cause then tx: MHx |
|
|
Dr. Lui lect 1 Summary 5: who are more prone to osteomyelitis |
DM, immunocompromised pt |
|
|
when you ext Mx molar, pay attention to sinus anatomy, especially |
Superior wall: floor of orbit |
|
|
Where does Mx Sinus drain to |
empties into ethmoid infundibulm: opening into MIDDLE MEATUS - HIATUS SEMILUNARIS |
|
|
respiratory epi of sinus mucosa is composed of |
pseudocolumnar squamous epi goblet cells cilia (which does not renerates fx well when damaged) |
|
|
Duration of acute sinusitis symp < 1wk is almost always _____ |
symptoms for 1-4 weeks symp <1 wk are almost always viral |
|
|
Duration of subacute sinusitis |
symp 4-12 weeks |
|
|
Duration of chronic sinusitis |
symp > 12 weeks |
|
|
Sinusitis Dx: Major factors (8) |
facial pain/pressure facial congestion/fullness nasal drainage/discharge postnasal drip nasal obstruction/blockage hyposmia/anosmia fever (acute only) purulence on endoscopy (automatically diagnostic) |
|
|
Sinusitis Dx: minor factors (7) |
headache mx dental pain cough halitosis fatigue ear pain, pressure, or fullness fever |
|
|
Sinusitis Dx: 3 categories |
2 major factors 1 major factor + 2 minor factors purulence at middle meatus or in sinus cavity |
|
|
most valuable technique for sinus imaging |
CT |
|
|
pt comes in w/ sinusitis for 16 weeks: Dx |
Chronic sinusitis |
|
|
pt comes in w/ sinusitis for 2 weeks |
Acute sinusitis |
|
|
pt comes in w/ sinusitis for 6 weeks |
Subacute sinusitis |
|
|
(T/F) odontogenic bacterial infxn often extends into mx sinus |
F: Rarely extends into mx sinus |
|
|
MC pathogens for acute sinusitis (3) |
Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae Moraxella catarrhalis (rare in adults, 20% in children) |
|
|
MC pathogens for chronic sinusitis |
same as acute: Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae Moraxella catarrhalis + multiple anaerobes |
|
|
ID odontogenic sinusitis |
vitality test, perio probing, exam, x-ray CT Tx: endo/ext, ref OMFS/ENT |
|
|
other (than bacterial) sinusitis etiology (5) |
viral, fungal (rare), genetic, allergy, anatomic predispostion |
|
|
Sinusitis cycle: [inflmmation/stasis/impaired mucociliary clearance/infection] |
IMC (bacterial/viral causing) -> Stasis -> Infxn -> inflm -> more IMC ... |
|
|
Caldwell-Luc operation: how would you get out tooth root that is stuck on anterior wall of sinus |
incision above mucogingival junction ID sinus bone, cut into the bone, get inside, get the tooth root out |
|
|
surgery is for sinusitis |
FESS: functional endoscopic sinus surgery Goal: to restore natural drainage path of sinuses |
|
|
nosebleeds control 1. anterior 2. posterior |
1. easy to control: pinch 2. harder to control: nasal bone is on the way: cauterize, silver nitrates, gauze packing |
|
|
Abx therapy for sinusitis |
Abx for 10-14 day :Clindamycin, Amox, augmentin :cephalosporins, macrolides |

