![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
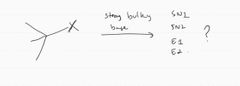
|
E2 hoffman |
|

|
E2 |
|

|
E2 |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
E2 Saytzeff |
|

|
E2 |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
SN1 OR E1 if theres heat |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
SN1/E1 |
|

|
SN1/E1 |
|

|
SN2 |
|

|
SN2 |
|
|
in a protic solvent, what is the trend of nucleophilic strength? |
nucleophile strength increases as you go down |
|
|
in an aprotic solvent, what is the trend of nucleophilic strength? |
it increases as you go up |
|
|
what is the trend of electronegativity? |
up the column, to the right of the row |
|
|
what is the trend of size? |
down the column, the left of the row |
|
|
what is the 4 question line up to determine which pathway to take SN1,SN2,E1 or E2? |
1. Does the question say what your rxn is? 2. What is the positioning of the Leaving group? 3. Is the nuc/base strong or weak? 4. Is the nuc/base bigger or smaller than CH3CH2OH? - If its bigger, then its considered a base - if its smaller, then its a nuc |
|
|
what are the exceptions in measuring whether a molecule is a nucleophile or base? |
acetate, carbanions and sulfur nucleophiles these are considered nucleophiles (go down SN pathway) |
|
|
what is chemical formula for acetate? |
CH3COOH |
|
|
what is the chemical formula for a carbanion? |
-CX3 |
|
|
how do I make sure that an E2 product comes out antiperiplanar? |
you need to make sure the leaving group and H that your about to break off are facing 180 degrees away from each other, u may have to rotate the main bond, switching the placement of molecules |
|
|
for a bulky base, will it go saitsev or Hoffman? |
hoffman |

