![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|

|
. |
|
|
What are the pharmacological receptor targets for Ketamine (4) |
1. NMDA (N-methyl-D-Aspartate) receptors Non-Nmda receptors 2. AMPA receptors are non-Nmda type transmembrane receptors for glutamate that mediate rapid transmission. The antidepressant effect of Ketamine is thought to be due to this. 3. Opioid receptors: Negligible influence on the analgesic effects. K - Opiod receptors >> psychomimetic effect. 4. Modulates function of GABAa receptors. |
|
|
Describe the mechanisms by which Ketamine contributes to the reduction of Pain experienced. 2. |
CNS Action of Ketamine 1. In the Spinal Cord - it inhibits Dorsal Horn wide dynamic range neuronal activity. 2. The S-isomer has mu receptor blocking potential resulting in analgesic and opioid sparing effect of Ketamine 3. Depresses parts of the cortex and thalamus 4. It stimulates the limbic system and depresses transmission in the medullary Reticular formation 5. works on the thalamo-neocortical projection system |
|
|
What class of drug is Ketamine a derivative of? 1.
|
It is an Arylcyclohexylamine. It is structurally related to phencyclidine |
|
|
Elimination half life of Cannabis |
28hrs in chronic user, but it can be 56hrs to a month |
|
|
Withdrawal symptoms of cannabis |
Restlessness, irritability, insomnia, nausea and muscle cramps |
|
|
Medical uses of cannabis |
1. Antiemetic (Nabilone) is effective after chemotherapy. NOT for PONV2. Appetite stimulant3. Decreases intraocular pressure4. Chronic pain (paracetamol may have cannabinoid effect) e.g. Arthritis, cancer & other chronic pain states |
|
|
Cannabis drug interactions in theatre |
1. Increased sedation with benzodiazepines, phenothiazines and barbiturates.2. Potentiates NDMR3. Avoid using it with drugs which increase heart rate e.g. Ketamine, atropine etc4. May be more or less sensitive to opiods. |
|
|
Acute Complications of Cannabis. 4. |
Acute complications In low - moderate doses: 1. Sympathetic stimulation 2. Parasympathetic inhibition
In high doses: 1. Parasympathetic stimulation 2. Sympathetic inhibition |
|
|
Chronic complications of Cannabis. 8. |
1. Addiction 2. Dependance 3. Psychosis, depression and cognitive impairment 4. Cardio - and peripheral vascular disease 5. Respiratory Disease *COPD, upper lobe bullae, pneumothorax *Impaired cilia function *laryngo/Bronchospasm, edematous uvula *increased CO & carboxyhaemoglobin five times more than cigarettes *3 - 4 reefers per day is equivalent to 20 cigarettes per day.
|
|
|
List 2 forms of cannabinoid that have been described and give an example of each. |
1. Endocannabinoids * Anandamide * 2 arachydonyl glycerol (2 AG) 2. Synthetic Cannabinoids Synthetic THC - Dranabinol Synthetic THC analogue - ajulemic acid & Nabilone |
|
|
Name the cannabinoid receptors and give their distribution in humans. |
CB 1 - brain, Spinal Cord, lung, liver, and kidney CB 2 - immune cells, tonsils, thymus, spleen and skin. CB 1 and 2 - heart, eye, stomach, pancreas, digestive tract and bones. |
|
|
Name four classes of NSAIDS & give an example of each 4. |
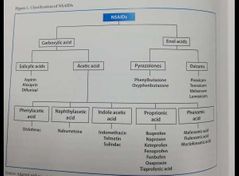
|
|
|
What is the MOA of NSAIDS? |
Cyclooxygenase inhibition They prevent the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins, thrmboxane and prostacyclin. |

