![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What feature separates Cestodes from Nematodes and Trematodes?
A. Cestodes lack a defined central nervous system B. Cestodes are hermaphrodites C. Almost all Cestodes infect mollusks as the first host in the life cycle. D. Cestodes lack an alimentary canal |
D. Instead, nutrients are absorbed through the outer tegument. All three have a CNS. Most cestodes (tapeworms) are hermaphroditic, however so are nematodes(round worms) and trematodes (Flukes). Statement C is true of Trematodes
|
|
|
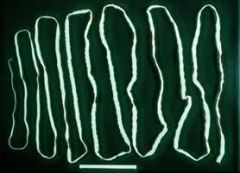
Which statement is false?
A. T. solium is more common in developed countries than T. saginata B. Diphyllobothrium latum and Hymenolepiasis spp. are cestodes. C. Cestode adults dwell in the small intestine. D. Below zero temperatures for several days will kill Taenia found in pork. |
A. Solium is oldworld, saginata is everywhere. Cestode adults dwell in the small intestine. The important cestodes include D. Latum (fish tapeworm), Taeniasis (beef and pork tapeworms), Echinococcus spp. (dog tapeworm) and Hymenolepiasis spp. (dwarf tapeworm and rat tapeworm).
|
|
|
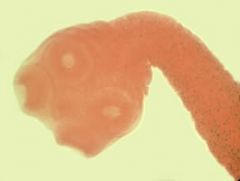
Which is true regarding this organism?
A. It is transmitted by uncooked pork B. Ingestion of the egg form can result in cysticercosis C. The egg form can not be used to differentiate the species D. Infections are fairly common worldwide including developed nations. |
D. This is Taenia saginata (note the four suckers but lack of rostellum and rostellar hooks). T. saginata is present throughout the world and is found in beef; this is partially due to the fact that rare beef ingestion is common. Unlike T. solium, ingesting the egg does not cause cysticercosis.
|
|
|
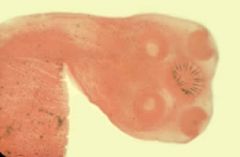
Which is true regarding this organism?
A. Cysticercosis is most commonly seen in the muscles of humans B. Infection is fairly common worldwide, including developed nations C. Ingestion of the larval form does not cause cysticercosis D. Cysticercosis can be avoided by cooking or freezing steak. |
D This is Taenia solium
Note the four large suckers with the added rostellum containing hooks (hooks look like a sun??). Unlike saginata, solium can be systemic after ingestion of the cyst form. The larval form causes disease limited to the intestine. The CNS is most often involved in humans vs. muscle in pigs. Pigs are the reservoir (not steak). |
|
|
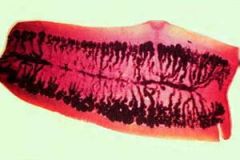
Name this cestode.
A. Taenia saginata B. Taenia solium C. Hymenolepis nana D. Hymenolepis diminuta E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
A. Taenia saginata
Note the number of branches (>12) vs. T. solium that has 12 or less. The other choices look nothing like this picture. |
|
|

Name this cestode.
A. Taenia saginata B. Taenia solium C. Hymenolepis nana D. Hymenolepis diminuta E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
B. Taenia solium
Note the number of branches (12 or less) vs. T. saginata that has >12. (note that t. solium has exactly 12 letters while T. saginata has >12 letters.) The other choices look nothing like this picture. |
|
|
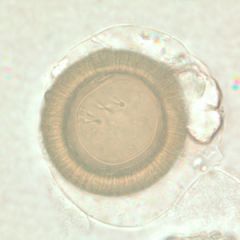
A. Ascaris
B. Taenia C. Hymenolepis D. Diphyllobothrium E. Trichinella |
B. Taenia spp. (Very difficult to differentiate solium from saginata with just the egg).
note the striations and tire-like appearance. Note that echinococcus eggs also look just like this. |
|
|
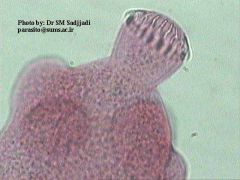
Name this cestode.
A. Taenia saginata B. Taenia solium C. Hymenolepis nana D. Hymenolepis diminuta E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
C. Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm)
Thought to be the most common tapeworm in the world. No intermediate host required. Note the knob-like rostellum with hooks. |
|
|
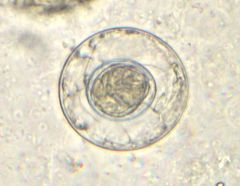
Name this cestode.
A. Taenia spp. B. Hymenolepis nana C. Hymenolepis diminuta D. Diphylidium caninum E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
B. Hymenolepis nana egg (dwarf tapeworm)
~40um with a shell and 6 hooked oncosphere. Note the polar filaments compared to H. diminuta. Taenia has a tire-like appearance. |
|
|
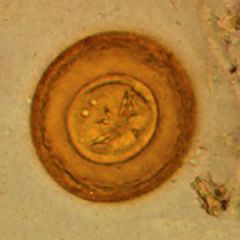
Name this cestode.
A. Taenia spp. B. Hymenolepis nana C. Hymenolepis diminuta D. Diphylidium caninum E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
C. Hymenolepis diminuta
Eggs of H. diminuta are larger (80um) than H. nana and lack the polar filaments. Common in rats and mice (rat tapeworm). Requires an intermediate host, unlike H. nana. (dwarf tapeworm) |
|
|
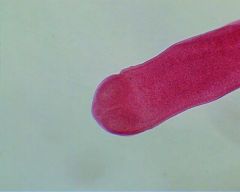
Name this cestode.
A. Taenia saginata B. Hymenolepis nana C. Hymenolepis diminuta D. Taenia solium E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
C. Hymenolepis diminuta scolex
Like H. nana, it has a knob-like rostellum and 4 suckers but has no hooklets. |
|
|

Name this cestode.
A. Taenia saginata B. Taenia solium C. Hymenolepis nana D. Hymenolepis diminuta E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
E. Diphyllobothrium latum
|
|
|
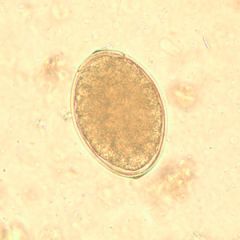
Which statement is false?
A. This species needs two intermediate hosts, crustaceans and fish. B. Most infections are asymptomatic C. Adult of this species have two characteristic longitudinal grooves. D. Infection is caused by ingestion of this form (the egg). E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
D. These are Eggs of Diphyllobothrium latum. (Operculum without opposite end thickening.) The egg form is found in the stool however infection in humans is caused by eating the larva form found in fish.
Most infections are asymptomatic except in uncommon cases where vitamin b12 deficiency is seen |
|
|

Name this cestode.
A. Taenia saginata B. Taenia solium C. Hymenolepis nana D. Hymenolepis diminuta E. Diphyllobothrium latum |
E. Diphyllobothrium latum scolex with two shallow longitudinal grooves. Adult is 4-10 meters. Found in crustaceans which are eaten by fish ---> raw ingested fish. Chiefly parasites of fish-eating mammals, birds and fish. Causes human disease when uncooked. B12 deficiency.
|
|
|
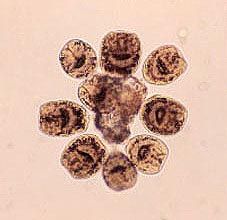
Where was this sample likely obtained from?
A. Stool sample B. Brain biopsy C. Subcutaneous biopsy D. Liver FNA E. gastric lavage |
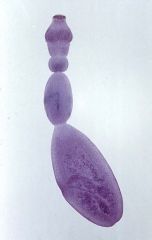
D. It is "hydatid sand". It is the contents of an expanding echinococcus cyst. These cyst are most often seen in the liver and cause disease by either slow expansion with impingement or rupture and either disseminated disease or anaphalaxis. This photo is of the worm which is trisegmented and photos have appeared on boards.
|
|
|
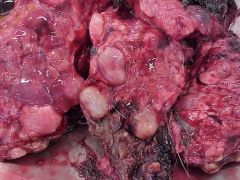
Which statement is false regarding the cause of these liver lesions?
A. Disease is most often found in the liver. B. The egg is indistinguishable from taenia spp. C. Dogs and foxes are the definitive hosts. D. Disease is self limiting except in the immunocompromised |
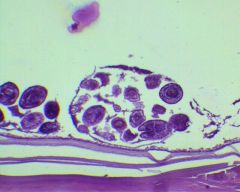
D. This is echinococcus spp. Ingestion of the egg --> disseminates to the liver --> Hydatid cysts form and slowly fill with fluid until they either burst --> causing anaphalaxsis and potential diseminated disease. It is potentially infectious in all persons.
|
|
|
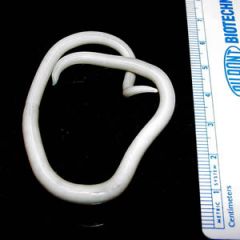
Identify this worm.
A. Ascaris lumbricoides B. Lumbricus terrestris C. Trichuris trichiura D. Enterobiasis vermicularis E. Brugia malayi |
A. Ascaris lumbricoides worm
-Has tapered ends and is 15 to 35 cmin length. B is the common earthworm which is segmented. C is commonly referred to as whip-worm due to its whip-like appearance. D is pinworm which is much smaller. E is the 2nd leading cause of elephantiasis and is very small. |
|
|
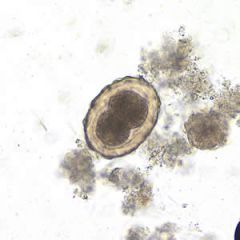
Regarding this species
A. It initially infects by penetrating the skin B. It is a common cause of rectal pruritis C. It is acquired through ingestion of infected fish D. It is transmitted via the mosquito E. High numbers can cause bowel obstruction, esp. in children |
E. Ascaris lumbricoides egg - note the distinct outer shell.
largest round worm of human intestine; found in tropics in the soil. Infection is via ingestion of the egg (larva penetrate duodenum) ---> circulation --> heart/lungs --> up trachea to esophagus --> bowel; in total, a 3 month process. |
|
|
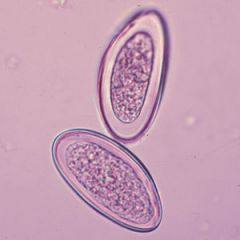
Pick the false statement.
A. The adult form has ala toward the head. B. Appendicitis is a well established sequela of this organism. C. Infection is acquired through ingestion of the egg. D. This is an Enterobius vermicularis egg. |
B. This is Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm). The worm is usually found incidentally in the appendix; there is not proven relationship with appendicitis.
|
|
|
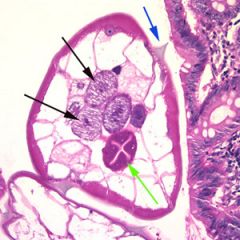
Name the organism.
A. Strongyloides stercoralis B. Ascaris lumbricoides C. Enterobius vermicularis D. Trichuris trichiura |
C. Enterobius vermicularis worm. AKA. pinworm. Note the alae (blue arrow)
|
|
|
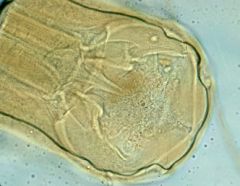
Name the species.
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
A. Necator americanus (new-world hookworm) head
Note the lack of teeth. It has a "cutting plate, unlike Ancylostoma duodenale which has 4 teeth. |
|
|
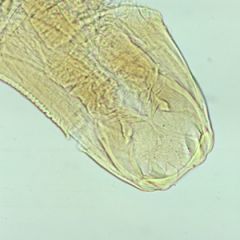
Name the species.
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
B. Ancylostoma duodenale (old-world hook worm) head
Note the 4 teeth -N. americanus has a "cutting plate" rather then teeth. |
|
|
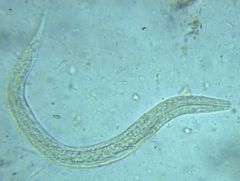
Name the species.
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
D. Hookworm larvae. Not the long (thin) buccal cavity. The head (presence or absence of teeth or cutting plate will differentiate them). Strongyloides has a shorter buccal cavity.
|
|
|
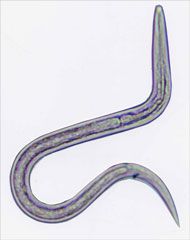
Identify this larvae.
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
D. This is the filariform stage. Hookworm has an esophageal-intestinal junction that is 1/3 the distance from the head while Strongyloides is midway.
|
|
|
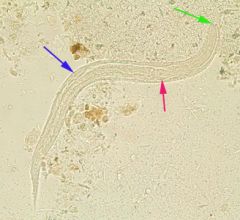
Name the species.
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
C. Strongyloides stercoralis larvae. This has a short buccal cavity vs. hookworm which has a long (thin) cavity. Dx can be confirmed using fluorescent antibody.
|
|
|
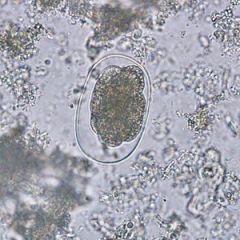
This stage is infectious. What species is this?
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
B. Hookworm egg (Necator americanus vs. Ancylostoma duodenale)
N. americanus infects through the skin while A. duodenale can infect through the skin or by ingestion of the egg. Hookworm is the 2nd most common helminthic infection after ascariasis. |
|
|
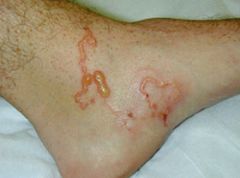
What is the cause of cutaneous larva migrans?
A. Ancylostoma braziliense B. Ancylostoma caninum C. Ancylostoma duodenale D. Toxocara canis E. A and B |
E. A. braziliense and A. caninum hookworms can penetrate human skin but are unable to complete their migratory cycle. They migrate in the subQ until they die causing much host response. Toxocara canis is the cause of visceral larval migrans.
|
|
|
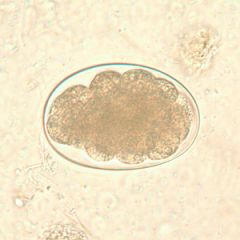
Name the species.
A. Necator americanus B. Ancylostoma duodenale C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Hookworm, cannot subclassify |
D. Hookworm egg. It is either Ancylostoma duodenale or Necator americanus, but this cannot be determined in the egg. The larva penetrates the skin, go to the heart, climb the pharynx and are swallowed; causing intestinal disease. A. duodenale egg can be infectious by ingestion.
|
|
|
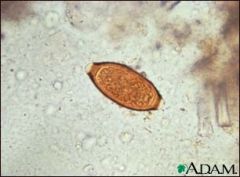
Name the species.
A. Ancylostoma duodenale B. Strongyloides stercoralis C. Trichuris trichiura D. Dirofilaria immitis |
C. Trichuris trichiura (whipworm). It is acquired through ingestion of the egg. It rarely causes symptoms. It is common in the tropics. Note that D is the name for dog heartworm which has shown up on boards!
|
|
|
|
Which of these can cause respiratory symptoms? (>1)
A. Ancylostoma duodenale B. Necator americanus C. Strongyloides stercoralis D. Trichuris trichura E. Schistosoma haematobium |
A, B, C and E- ABC, The life cycle of these three involves migration of the larva through the circulatory system and up the pulmonary tree with potential for respiratory symptoms. E- Eggs get deposited in the lungs leading to fibrosis and possible cor pulmonale.
|
|
|
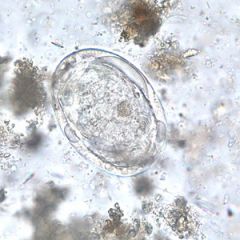
Name the organism.
A. Schistosoma haematobium B. Schistosoma japonicum C. Schistosoma mansoni |
B. Schistosoma japonicum egg The adult dwells in the branches of the superior mesenteric vein. The female deposits its eggs in small venules close to the intestinal lumen.
Note the lack of hook (is small) Snail intermediate host, penetrates skin, circulation to liver, adult worms sheds eggs in stool. |
|
|
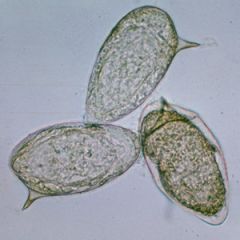
Name the organism.
A. Schistosoma haematobium B. Schistosoma japonicum C. Schistosoma mansoni |
C. Schistosoma mansoni egg
Note the side "hook". The adult dwells in the branches of the inferior mesenteric vein. Eggs are deposited near the intestinal luman and are shed in the urine. Snail intermediate host, penetrates skin, circulation to liver, shed in stool or urine. |
|
|
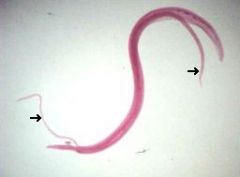
This photo shows the unique mating of what species?
A. Schistosoma spp. B. Ascaris spp. C. Hookworms D. Strongyloides spp. |
A. Schistosoma spp. They supposedly mate for life. The female sits in the gynocophoral canal of the male.
|
|
|
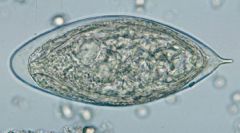
Name the organism.
A. Schistosoma haematobium B. Schistosoma japonicum C. Schistosoma mansoni |
A. Schistosoma haematobium egg
Note the forward "hook". The worm lives in blood vessels near the bladder. Eggs are deposited in the wall of the bladder. Snail intermediate host, penetrates skin, circulation to liver, adult sheds eggs in stool (or urine, unlike other schistosoma). |
|
|
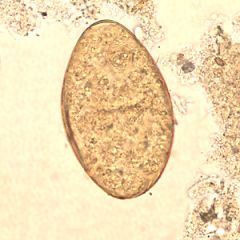
Which statement is false regarding this Fasciolopsis spp?
A. This organism can invade the larger bile ducts and gall bladder. B. The adult form is up to 7cm long. C. It is found primarily in Asia. D. The infective larva are found on bamboo and water chestnuts |

A. It is Fasciolopsis buski (picture above is the adult) not to be confused with fasciola hepatica whose egg looks remarkably similar. The life cycle is similar for both organisms however. Snails --> pigs --> humans. It lives in the upper small intestine.
|
|
|
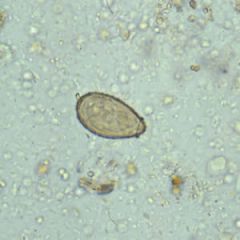
Name this organism.
A. Fasciolopsis buski B. Fasciola hepatica C. Clonorchis sinensis D. Paragonimus wetermani |
This is Clonorchis sinensis. The defining feature is that it is a small egg with operculum. Fluke of snails --> raw fish --> cyst ingestion. The fluke climbs up the bile ducts and causes inflammation and obstruction of the ducts. Seen in Asia. Only heavy infection cause disease and possibly associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
|
|
|

This organism was found in a bile duct. Which statements is false?
A. There is an association with hepatocellular carcinoma B. It is found in Asia and has been reported in Hawaii C. Snails and fish are hosts D. It reaches the bile ducts via the peritoneal cavity. |
D. This is clonorchis sinensis. It reaches the bile ducts via the ampulla of vater (fasiola fits letter D). Only heavy and ongoing infections cause disease.
|
|
|
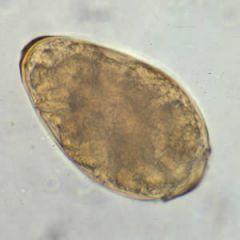
Name this parasite egg
A. Diphyllobothrium latum B. Paragonimus westermani C. Hymenolepis nana D. Schistosoma haematobium |
B. Paragonimus westermani egg.
Note the operculum with thickening on the opposite end. Fluke of crustaceans |
|
|
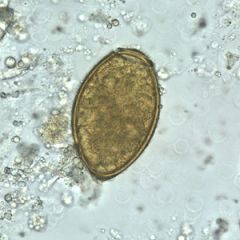
How is this Trematode most like to be a cause of infection?
A. Eating raw crab in Brazil B. Eating raw crayfish in China C. Rafting in the Nile D. Eating water chestnuts in Japan E. Swimming in freshwater in Peru |
B. This is a Paragonimus westermani egg.
Note the operculum with thickening on the opposite end. It is found primarily in Asia and parts of Africa. It is acquired through ingestion of the metacercaria found in raw crayfish or crab. |
|
|
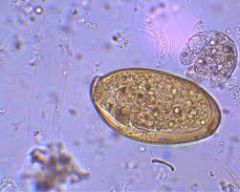
Regarding Fasciola hepatica, which statement is false.
A. The egg cannot be easily differentiated from Fasciolopsis buski B. It is found primarily in Asia C. The worm reaches the bile ducts via the peritoneal cavity D. Infection follows consumption of aquatic vegetation. |

B. Unlike the other major flukes, Fasciola hepatica is found in France, Algeria, Cuba and Latin America. The Fluke is large (3cm) so even light infections are symptomatic.
|
|
|
|
Which of the following species does not infect via unbroken skin penetration?
A. Schistosoma mansoni B. Necator americanus C. Ancyclostoma duodenale D. Ascaris lumbricoides |
D. Ascaris infects via ingestion of the egg. B and C are both hookworms. D, Schistosoma are the only species of Trematode that infect via the skin (maturation takes place in the liver).
|
|
|
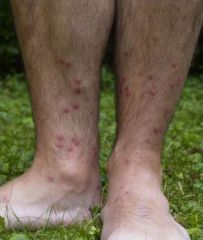
What is the cause of swimmer's itch?
A. Schistosoma spp. B. Hymenolepis spp C. Trichostrongylus spp D. Sigmodon spp. E. Echinococcus spp. |
A. It is a papular eruption caused by penetration of the skin by cercariae of various schistosome parasites of lower animals.
|
|
|
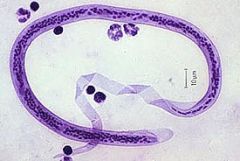
Name the species depicted.
A. Wuchereria bancrofti B. Loa loa C. Brugia malayi D. Onchocerca volvulus |
A. Note that it is sheathed and that the sheath extends well past the tail. Also, the nuclei do not extend all the way to the end of the tail. Loa loa is similar except the nuclei entend to the tail. B. malayi has evenly spaced single nuclei at the tail. O. volvulus has no sheath.
|
|
|
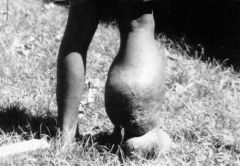
Regarding the process, which statement is false?
A. The organism often has the same vector as malariae B. W. Bancrofti enters the peripheral blood at night. C. Brugia malayi can cause this. D. The organism spends part of its life cycle in the hepatic sinusoids. |
D. Especially, note that B has shown up on board exams in the past; the idea being that mosquitoes are more active at night so going peripheral at night makes sense to infect the mosquitoes. Also note that C is true; it is the 2nd leading cause of elephantiasis.
|
|
|
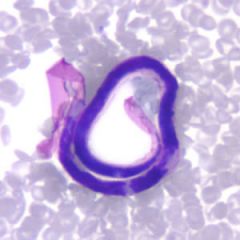
Found in the blood of someone in Indonesia.
A. Wuchereria bancrofti B. Loa loa C. Brugia malayi D. Onchocerca volvulus |
C. This is admittedly difficult. History may be of more help here. The tail is tapered, with a significant gap between the terminal and subterminal nuclei.
|
|
|
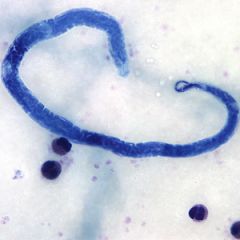
Worm found traversing someone's eye.
A. Wuchereria bancrofti B. Loa loa C. Brugia malayi D. Onchocerca volvulus |
C. Similar to W. bancrofti except the nuclei extend all the way to the tip of the tail.
|
|
|
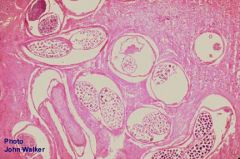
This is taken from a firm nodule just under the skin surface. What does it most likely represent?
A. Wuchereria bancrofti B. Loa loa C. Brugia malayi D. Onchocerca volvulus |
D. Onchocerca volvulus. The worm wanders the SubQ until it forms a fibrous tissue nodule. Eyes are sometimes involved. It is found in Africa and south/central America.
|
|
|
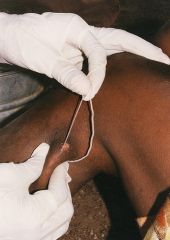
How is this worm contracted?
A. Eating infected crayfish B. Mosquito bite C. Contact with infected water D. Ingestion of infected water |
D. This is the Guinea worm (Dracunculus medinensis). The larvae is ingested, then the larvae makes its way to the deep connective tissue. The female deposits its eggs in ulcers which are released with water contact.
|
|
|
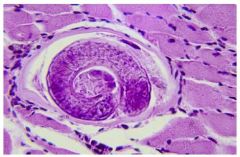
Name the organism
A. Strongyloides stercoralis B. Ascaris lumbricoides C. Enterobius vermicularis D. Trichuris trichiura |
D. Ingested from undercooked pork. Settles in muscles. Used to be quite common in the US (1930's) but is now rare and reportable.
|
|
|
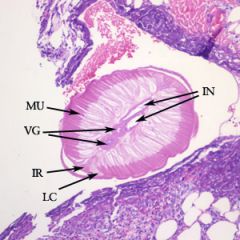
This is taken from a firm nodule in the pulmonary artery. What does it most likely represent?
A. Wuchereria bancrofti B. Loa loa C. Dirofilaria immitis D. Onchocerca volvulus |
C. Dirofilaria immitis
Followup Question: What is the vector and normal host? |
Mosquito is the vector
Host is the dog. AKA dog heart worm. This has been on boards as recent as 09' |

