![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
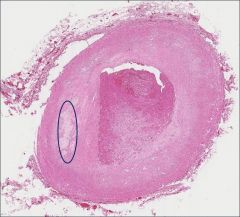
What pathology is shown in the circle?
|
Thickened intima resulting from atherosclerotic plaque.
|
|
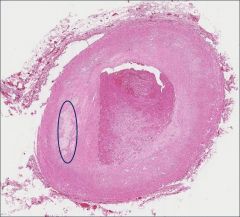
What molecules are key to the process occurring within the circle? How do these molecules relate to the occlusion of the vessel?
|
LDLs and necrotic cells are present within the circled area.
LDLs cause injury to the vessel which leads to endothelial activation. Endothelial activation results in an inflammatory response and the generation of a thrombus. |
|
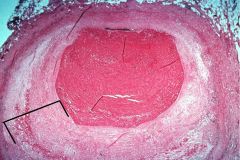
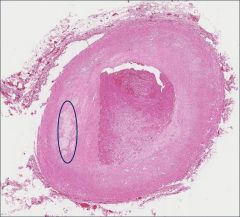
What pathology/ pathological process is associated with the bracketed area?
|
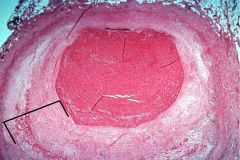
Atherosclerosis
|
|
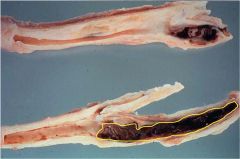
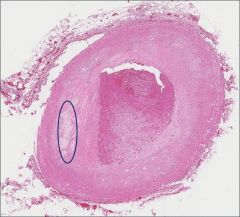
What is pathology seen in the area outlined in yellow?
How is the location relevant to the pathology |
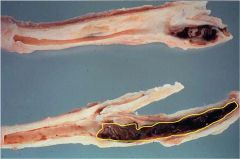
Thrombus
Thrombi often form near bifurcations of vessels because there is increased turbulence at the branch points. |
|
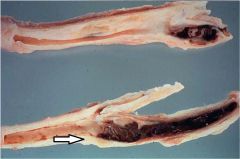
What is the pathology shown at the tip of the arrow?
|
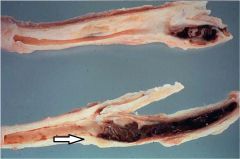
Atherosclerosis
|
|
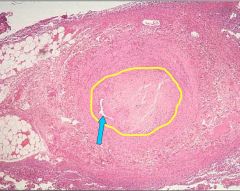
What process is occurring inside the yellow circle?
What related process is occurring at the tip of the blue arrow? |
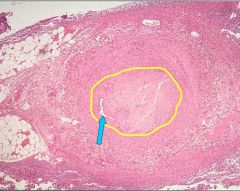
The yellow circle shows organization of a thrombus.
The blue arrow is pointing to recanalization. Recanalization is occurs as part of organization. |
|
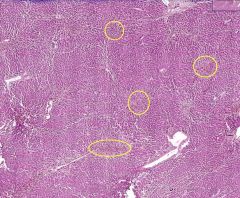
What type of tissue is this?
What are the areas in the yellow circles an example of? |
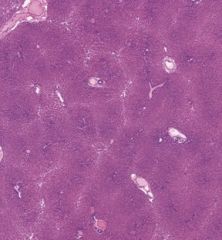
Liver
Hemorrhage into the central lobule. Image above shows what the central lobules look like normally -- normally there is an empty space in the center. |
|
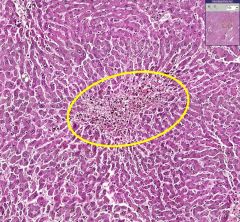
What is shown above?
What type of cells would are seen in the yellow circled area? |
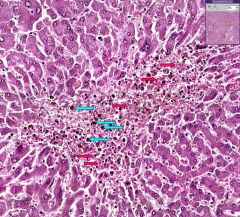
Hemorrhage into the central lobule of the liver.
RBCs (indicated by red arrows) and macrophages (indicated by blue arrows) that are filled with pigment from the RBCs. |
|
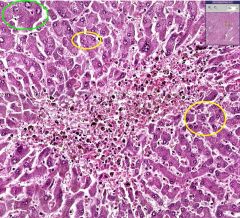
What is the difference between the cells circled in yellow and those circled in green?
|
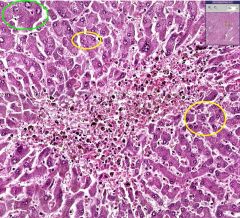
The cells circled in yellow are atrophic while those circled in green are more normal.
|
|

What is the name given to the pathology shown?
|
Nutmeg liver
|
|
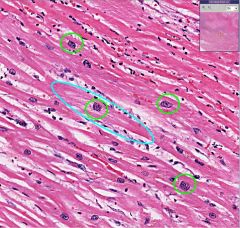
What type of cell is this?
What is the response to injury associated with the blue circled region? What name is given to the green circled nuclei and how do they relate to the response to injury? |
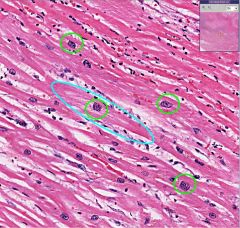
Cardiac Myocytes
The cell circled in blue has hypertrophied in response to injury to surrounding cells. The green circled nuclei are called "boxcar" nuclei and are associated with cardiac myocytes undergoing hypertrophy. |
|
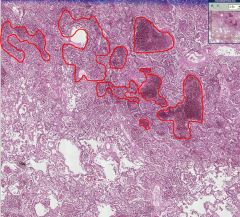
What type of tissue is this?
What is occurring in the areas circled in red (how are these areas different from the part of the image at the bottom)? |
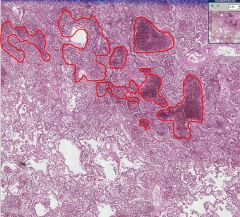
Lung (alveoli)
Hemorrhage into the alveolar tissue. The bottom area is normal (alveoli are empty). |
|
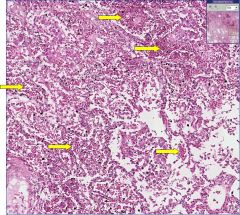
What type of tissue is this?
What type of cell is indicated by the arrows? |
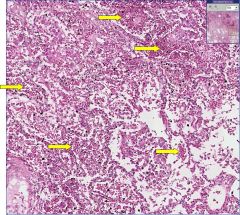
Lung (alveoli)
RBCs |
|
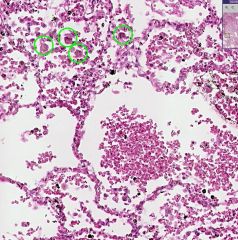
What type of cells are shown in the green circles?
What organ is this? |
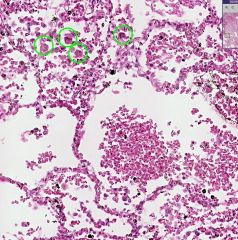
Heart Failure Cells
Lungs |
|
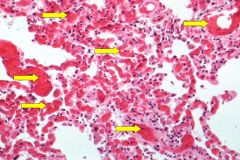
What pathology are the yellow arrows pointing to?
What is a likely possible cause of this pathology? |
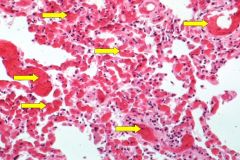
Congested capillaries
Acute pulmonary congestion due to increased hydrostatic pressure. |
|
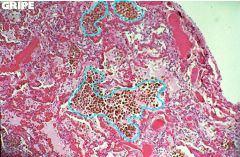
What type of cells are shown inside the blue circles?
|
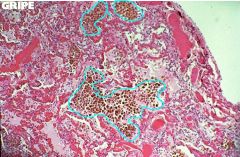
Heart failure cells
|
|
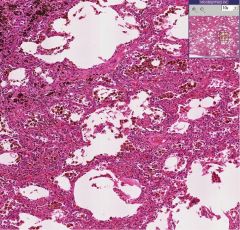
What process is seen in the image and is it acute or chronic?
|
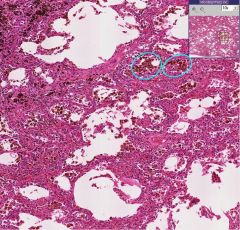
Chronic pulmonary congestion (indicated by the fact that the interstitium is thickened). Heart failure cells are indicated by the blue circles.
|
|
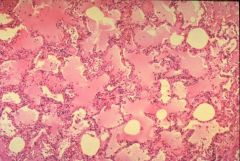
What pathological process is shown in the image?
|
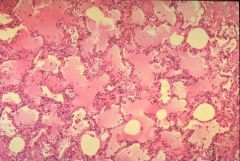
Edema of the lungs
|
|
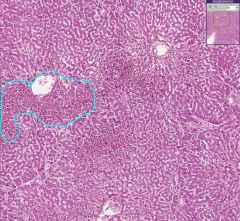
What is shown in the blue area?
|
Congestion surrounding a central lobule in the liver
|
|
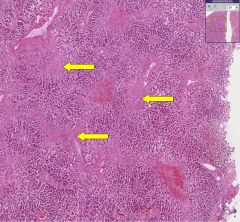
What process has occurred in the areas indicated by the yellow arrows?
Why does this process occur? What term is given to this pathology? |
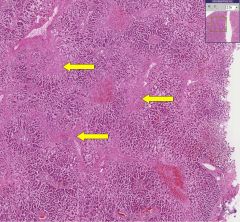
Fibrosis surrounding central veins in the liver.
Chronic hypoxia leads to necrosis of the hepatocytes in the central lobules. Termed cardiac cirrhosis. |
|
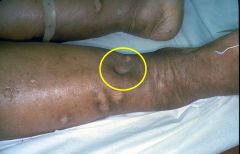
What is occurring in this image (ideal example indicated by yellow circle)?
What underlying pathology/ cause is associated with this? |
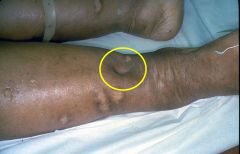
Pitting Edema
Right sided heart failure, which leads to increased venous hydrostatic pressure. |

