![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 7 Classes of Diuretics? Examples?
Use of diuretics? |
What are the 7 Classes of Diuretics? Examples?
1. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: ACETAZOLAMIDE, DORZOLAMIDE 2. Osmotic diuretics: MANNITOL 3. Loop diuretics: FUROSEMIDE, Bumetanide, Toresemide, Ethacrynic acid 4. Thiazides: HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE, METOLAZONE, Bendroflumethazide, Chlorthalidone, Hydroflumethiazide, Inadapamide, Polythiazide 5. K+ Sparing: (a) AMILORIDE, TRIAMTERENE (b) SPIRANOLACTONE 6. Natriuretic Peptides: Nesiritide 7. ADH Antagonists: Use of diuretics: (1) Edematous states: CHF, Kidney disease, Hepatic cirrhosis, Pulmonary edema (2) Non-edematous states: HTN, Nephrolithiasis, Hypercalcemia, Diabetes insipidus (3) Miscellaneous: Intoxications |
|
|
Acetozolamide: Use?
|
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR
(1) Alkalinisation to promote excretion of weak acids (e.g. uric acid, cysteine, aspirin) (2) Mountain sickness prophylaxis (3) Metabolic alkalosis [2nd line if standard procedures are contraindicated] (4) Systemic application in emergency lowering of IOP in glaucoma |
|
|
Acetozolamide:
Route? Onset & Duration? Excretion? Effect on CNS? |
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR
Route: Oral, IV Onset & Duration: Effective in 30min, Persist for 12h Excretion: Via proximal tubule, Enhanced NaCl reabsorbtion downstream may reduce effectiveness of diuretic CNS Effect: Decreased rate of CSF fluid formation [no clinical significance listed] |
|
|
Acetozolamide: MOA/PD?
|

CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR
|
|
|
Acetozolamide: AE?
|
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR
(1) Metabolic acidosis (2) Renal stones due to enhanced phosphaturia, calciuria, decreased solubility in alkaline urine, & decreased secretion of solubilizing factors [e.g. citrate] (3) Renal K+ loss |
|
|
Acetozolamide: Contra?
|
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR
Hepatic cirrhosis b/c urine alkalinization causes reversal of NH4+ trapping in acidic urine leading to hepatic encephalopathy |
|
|
Dorzolamide: Use?
|
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR
USE: Topical application for treatment of glaucoma |
|
|
Dorzolamide: MOA/PD?
|
CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR:
(1) Blocks sodium bicarbonate secretion (2) Decreased rate of aqueous humor formation |
|
|
Mannitol: Use?
|
OSMOTIC DIURETIC
(1) Water diuresis in preference to sodium excretion to maintain tubular flow [TEST dose in non-responders] (2) Reduce ICP/IOP |
|
|
Mannitol:
Route? Onset, Duration, & Excretion? |
OSMOTIC DIURETIC
Route: IV Onset, Duration, & Excretion: Immediate onset & excreted via GFR within 30-60min |
|
|
Mannitol: MOA/PD?
|
OSMOTIC DIURETIC
Retains water within tubule, Some increase in natriuresis |
|
|
Mannitol: AE?
|
OSMOTIC DIURETIC
(1) Extracellular volume expansion [CHF, pulmonary edema] (2) Headache, nausea, vomiting (3) Dehydration (4) Hypernatremia |
|
|
Furosemide: Others in same class?
|
LOOP DIURETICS
Bumetanide, Torsemide ; Ethacrynic acid |
|
|
Furosemide: Use?
|
LOOP DIURETICS
(1) Edematours conditions, especially emergencies [Acute pulmonary edema/CHF] (2) Acute hypercalcemia/hyperkalemia (3) Acute renal failure adjustment of oligurea, enhancement of K+ secretion [oliguric renal failure --> nonoliguric renal failure], "flushing of bubbles" (4) Anion overdoes, combined with saline infusions [bromide, fluoride, iodide] (5) Forced diuresis (6) HTN/CHF [2nd line for refractory cases] |
|
|
LOOP DIURETICS
Furosemide: Route? Onset & Duration? Elimination? |
Route: Oral, IV
Onset & Duration: Instant onset, Duration 2-3h Elimination: Through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion |
|
|
Furosemide: MOA/PD?
|

LOOP DIURETICS
(1) Inhibition of the coupled Na+/K+/Cl- transport system in thick ascending limb (2) Has direct effects on blood flow [e.g. renal, pulmonary] |
|
|
Furosemide: DI?
|
LOOP DIURETIC
DON'T use with aminoglycosides b/c increase ototoxicity [both drugs are ototoxic] |
|
|
Furosemide: AE?
|
LOOP DIURETICS
(1) Hypokalemia [can cause metabolic acidosis] (2) Ototoxicity usually reversible (3) Hyperuricemia [gouty attack] (4) Hypomagnesaemia (5) Allergic rxn to sulfonamide moiety |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide: Use?
|
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
(1) HTN [inexp, effective, safe, one daily dose, no dose titration needed] (2) CHF (3) Kidney stones due to IDIOPATHIC hypercalciuria [e.g. Ca2+ hyperabsorbers, Leakers, Phostphate leakers] (4) Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide:
Route? Onset? Excretion? |
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Route: Usually oral Onset: Diuresis last 3-7days, It takes 1-3 weeks to stabalize HTN due to long acting vasodilation Excretion: Organic acid secretory system |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide: MOA/PD?
|
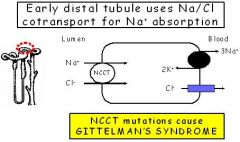
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Inhibit NaCl- symporter in DCT, Enhance calcium reabsorb [mech unknown] |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide: AE?
|
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Mostly similar to loop diuretics but less pronounced: (1) Hypokalemia [can cause metabolic acidosis] (2) Hyperuricemia [gouty attack] (3) Hypernatriuria (4) Impaired carb tolerance (5) Hyperlipidemia (6) Allergic rxn |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide: Contra?
|
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Not absolute, require monitoring: (1) Arrhythmias (2) Diabetics |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide: DI?
|
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Since they compete for the organic acid secretory system they will reduce the excretion of other organic acids |
|
|
Amiloride/Triamterene: Use?
|
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
Given w/ thiazides or loop to improve K+ retention |
|
|
Amiloride/Triamterene:
Excretion [Amiloride/Triamterene]? |
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
(1) Amiloride [renal secretion only] (2) Triamterene [hepatic metab & renal secretion] |
|
|
Amiloride/Triamterene: MOA/PD?
|
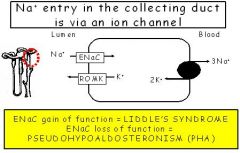
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
Block ENac in in collecting duct [unlike spironolactone have diuretic activity even in people w/ Addison disease] |
|
|
Amiloride/Triamterene:
AE [Amiloride/Triamterene]? |
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
(1) Hyperkalemia [can cause metabolic acidosis] (2) Triamterene can cause acute renal failure [+ indomethacine], kidney stones |
|
|
Amiloride/Triamterene: DI?
|
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
Hyperkalemia aggravated by B-blockers and ACE inhibitors |
|
|
Metolazone: Use?
|
THIAZIDE DIURETIC:
(1) HTN [low dose and combo therapy] (2) Edema (3) Instead of other thiazides in combo treatment of furosemide [loop diuretic] resistance |
|
|
Metolazone:
Route? Duration? Special? |
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Route: Oral bioavail good Duration: 12-24hr Special: Unlike other thiazides also effective at GFR < 30mL |
|
|
Metolazone: MOA/PD?
|
THIAZIDE DIURETIC
Similar to thiazide diuretics [Inhibit NaCl- symporter in DCT] |
|
|
Spironolactone/Canreonate: Use?
|
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
(1) Diuretic of choice in hepatic cirrhosis & secondary hyperaldosteronism (2) Given w/ thiazides or loop to improve K+ retention (3) Heart failure [prevents remodeling] |
|
|
Spironolactone/Canreonate: Excretion [Spironolactone/Canreonate]?
Onset? |
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
Route: Spironolactone [oral], Canreonate [IV prodrug] Onset: Delayed |
|
|
Spironolactone/Canreonate: MOA/PD?
|
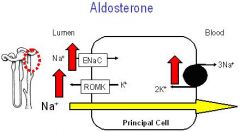
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
Aldosterone antagonist --> Mild increase NaCl excretion in late distal tubule & collecting duct |
|
|
Spironolactone/Canreonate: AE?
|
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
(1) Hyperkalemia [can cause metabolic acidosis] (2) Gynaecomastia |
|
|
Spironolactone/Canreonate: DI?
|
POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETIC
Hyperkalemia aggravated by B-blockers and ACE inhibitors |
|
|
Nesiritide: Use?
|
NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE:
Infusion in acute severe heart failure |
|
|
Nesiritide:
Route? Half life? |
NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE
Route: IV [peptide drug] Half-life: t1/2 = 18min |
|
|
Nesiritide: MOA/PD?
|
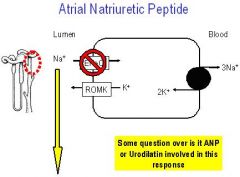
NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE
(1) Activate guanylyl cyclase in many tissues --> smooth muscle relaxation (2) Multiple functional and interlinked antagonism for renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone, ADH --> Increased GFR and decreased tubular Na+ absorption |
|
|
Diuretics: DI w/ any diuretics?
|
(1) Tetracycline w/ any diuretic can increase BUN
|

