![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Interference |
When waves from two sources meet and a new wave is produced. The displacement produced at any point by this wave is the algebraic sum of the displacements that each wave would produce on its own |
|
|
Refraction |
The changing of direction of a wave when it enters a region where its speed changes. The bending of a ray of light when it goes from one medium to another. |
|
|
Diffraction |
The sideways spreading of waves into the region beyond a gap or around an obstacle. Happens when the size of the gap is near in size to the wavelength of the wave |
|
|
Coherence |
Two sources of periodic waves are said to be coherent if they are in phase or if there is a constant phase difference between waves from each of the sources (Therefore the sources also both have the same frequency) |
|
|
Dispersion |
The separating out of the different wavelengths present in light |
|
|
Laws of reflection of light |
1 the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane 2 the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection |
|
|
A real image |
Is one formed by the actual intersection of light rays |
|
|
A virtual image |
Is an image formed by the apparent intersection of rays |
|
|
Laws of refraction |
1 the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the refracted ray all lie in the same plane 2 sin(i)/sin(r)=n |
|
|
Snell's law |
Sin(i)/Sin(r)=n where n is the refractive index |
|
|
Critical angle |
Where light traveling from a denser medium to a rarer one and the angle of incidence = a corresponding angle of refraction is 90° |
|
|
Total internal reflection |
When light going from a denser to a rarer medium hits the rarer with an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle and is reflected back in |
|
|
Power of a lense |
P=1/f |
|
|
Transverse wave |
The direction of vibration is perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is traveling |
|
|
Longitudinal wave |
The vibration is parallel to the direction the wave is traveling |
|
|
Constructive interference |
When waves from two sources meet and the amplitude of the resulting wave is greater than the amplitudes of each of the individual waves |
|
|
Destructive interference |
When waves from two sources meet and the amplitude of the resulting wave is less than the amplitudes of each of the individual waves |
|
|
Polarisation |
Where the vibration of a transverse wave is restricted to one plane |
|
|
Doppler effect |
The apparent change in frequency due to the relative movement of the source or the observer |
|
|
Sound intensity at a point, unit |
Is the rate at which sound energy is passing through unit area at right angles to the direction in which the sound is travelling at that point I=P/A W/m² |
|
|
Overtones |
Frequencies which are multiples of a certain frequency |
|
|
The loudness of a sound wave depends on |
The amplitude Greater amplitude, greater loudness |
|
|
The pitch of a note depends on |
The frequency. High frequency, high pitch |
|
|
The quality of a musical note |
Depends on the number of overtones present and the relative strengths of the different overtones |
|
|
Frequency limits of audibility |
20Hz-20,000Hz |
|
|
Resonance |
When a body vibrates with a large amplitude due to the application of a periodic force that has a frequency close to the natural frequency of the body |
|
|
Stationary wave |
The wave formed by the meeting of two periodic travelling waves of the same frequency and amplitude moving in opposite directions |
|
|
Threshold of hearing |
The smallest sound intensity detectable by the human ear at a frequency of 1kHz Value: 1×10-¹² W/m² |
|
|
Scale for sound energy for human ears |
Sound intensity level measured in decibels dB |
|
|
Secondary colour |
When two primary colours are mixed in equal intensity |
|
|
Complementary colour |
A primary and secondary colour that when mixed give white |
|
|
Primary colours |
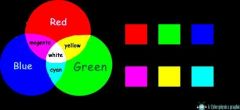
Red, green, blue |

