![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does a narrow beam pneumbra look like
|
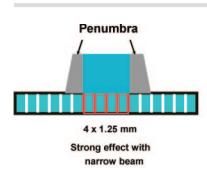
|
|
|
Why do cardiac CTs have high dose for the area covered
|
lower pitch
|
|
|
What are some typical effective doses for CT
|
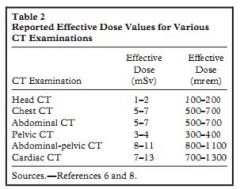
|
|
|
What are 3 techniques to reduce radiation during cardiac CT exams
|
tube current modulation
cardiac phase-specific scanning increased pitch |
|
|
how does current modulation work
|
x-ray tube current can be modulated, or varied,
while the gantry spins around the patient. The tube current thus can be decreased when the beam crosses areas of the body with less tissue o lower tissue density, thereby lowering the total overall dose of radiation needed |
|
|
how much dose reduction can be achieved by current modulatoin
|
In general
CT examinations, dose reductions on the order of 20%– 40% have been achieved with these ap-proaches |
|
|
How does cardiac phase specific scanning work
|
CT is to decrease the x-ray tube current during
phases of the cardiac cycle that are expected to contain fairly large amounts of motion. Images acquired during these phases are expected to be of lower quality and of less value for interpreta- tion; thus, the radiologist may choose that they not be captured for use in image reconstruction. Dose reductions of up to 50% have been achieved with this feature |
|
|
What are 4 standard reformatting methods
|
sagital
coronal oblique curved refomatting |
|
|
What are 3 reformatting techniques that change the thickeness of slices
|
maximum intensity projection
minimum-intensity projection variable thickness viewing |
|
|
What are 2 methods for reformatting axial images into 3 dimensional views
|
volume rendering
surface rendering |
|
|
What is a type of physiologic imaging performed with CT
|
CT perfusion
|
|
|
What 2 CT acquisition parameters have the most effect on the quality of the image processing result
|
section thickness
section images |
|
|
The the pitch have an effect on post processing image quality
|
yes, but not as much as slice thickness and slice spacing
|
|
|
What kind of artifact can an increased pitch introduce
|
higher pitches can introduce artifacts, such as ze-
bra-type striping |
|
|
What is reconstruction
|
The reconstruction process, especially in CT, refers to a very specific procedure that converts raw projection data into an axial image
|
|
|
What is reformatting
|
Reformatting, on the other hand, merely
displays the images produced from the original reconstruction process in an orientation other than how they were originally produced. |
|
|
Is reconstruction and refomatting terminology often confused
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the axis' of a pt undergoing CT
|
the x direction of an axial image plane is
along the patient’s right-left axis, the y direction of an axial image plane is along the patient’s ante-rior-posterior axis, and the z direction of the axial image plane is along the patient’s superior-infe-rior axis |
|
|
What is very very important when reformating images
|
isotropic voxels
|
|
|
What are 2 areas of the body that may benefit from oblique images
|
pancreatic and hepatic regions
|
|
|
What are two things that are accentuated by max-intensity projections
|
bone
enhancing areas such as vessels |
|
|
how does a maximum intensity projection work
|
viewing rays are traced from the expected position of the operator through the object to the display
screen, and only the relative maximum value de- tected along each ray path is retained by the computer This method tends to display bone and contrast material–filled structures preferen-tially, and other lower-attenuation structures are not well visualized |
|
|
how does a minimum image projection image work
|
minimum-intensity
projection involves detecting the minimum value along the ray paths in each view. |

