![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a system and what happens when a system changes ? |
An object or group of objects When a system changes there are changes in the way energy is stored e.g roller coaster transfers energy between gravitational and kinetic energy |
|
|
Eqaution for kinetic energy |
Kinetic energy = 0.5 x mass x (speed)2
|
|
|
Equation for gravitational potential energy |
GPE = mass x gravitational field strength x height
|
|
|
Equation for elastic potential energy |
Elastic potential energy = 0.5 x spring constant x (extension )2 |
|
|
Equation for change in thermal energy |
Change in thermal energy = mass x specific heat capacity c temperature change |
|
|
What are the three things that can happen in energy transfer |
Can be transferred into another energy Stored Or dissipated (spread out to the surroundings |
|
|
What are the three ways unwanted energy transfers can be reduced |
Lubrications which reduces friction - less heat energy Tightening loose parts - prevents unwanted vibration - sound waste Thermal insulation - reduces heat loss |
|
|
Characteristics of a solids particles |
Fixed pattern and have a fixed size and shape |
|
|
Characteristics of a solids particles |
Fixed pattern and have a fixed size and shape |
|
|
Characteristics of liquids particles |
Fixed size but contain particles that are free to move allowing them to change shape and fit to the container |
|
|
Characteristics of gas particles |
Large gaps between particles making them compressible and enabling them to change size and shape |
|
|
Equation for density |
Mass / volume |
|
|
Equation for a change in state |
Mass x specific latent heat |
|
|
What is latent heat of fusion ? |
The energy needed for a substance to change from solid to liquid (melt) |
|
|
What is latent heat of fusion ? |
The energy needed for a substance to change from solid to liquid (melt) |
|
|
What is latent heat of vaporisation |
The energy needed for a substance to change from liquid to gas (evaporate ) |
|
|
What is sublimation ? |
When a substance changes from a solid to gas without having a liquid phase |
|
|
What is the radius of an atom ? |
1 x 10 ^-10 |
|
|
Periodic table element structure |
Mass number —4 He Atomic number —2 Mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons Atomic number is hfs protons |
|
|
What are isotopes ? |
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons |
|
|
Plum pudding model facts |
Discovery of electron by j Thompson in 1897 led to lim pudding mode Atom is ball of pushed charge with electron scattered in it |
|
|
What did Geiger and marsden do ? |
They carried out gold foil experiment with alpha particles (Rutherfords experiment ) Some particles got deflected meaning there had to be a concentrated area of positive charge |
|
|
What did Niels Bohr and James Chadwick do ? |
Niels Bohr developed the modern nuclear model of having electrons orbit the centre and found the proton James Chadwick found the neutron |
|
|
What do unstable atom nuclei do ? |
Unstable atom nuclei give out radiation to become more stable - the type of radiation depends on the nucleus |
|
|
How do you measure the activity of a radioactive source ? |
In becquerels (Bq) which is the rare at which the source decays e.g 1Bq = I count per second |
|
|
How do you measure the activity of a radioactive source ? |
In becquerels (Bq) which is the rare at which the source decays e.g 1Bq = I count per second |
|
|
What are the three main types of radiation ? |
Alpha , beta and gamma |
|
|
How do you measure the activity of a radioactive source ? |
In becquerels (Bq) which is the rare at which the source decays e.g 1Bq = I count per second |
|
|
What are the three main types of radiation ? |
Alpha , beta and gamma |
|
|
Properties of alpha radiation and how to stop it |
Strong ionising power Absorbed by a few centimetres of air or a thin sheet of paper |
|
|
How do you measure the activity of a radioactive source ? |
In becquerels (Bq) which is the rare at which the source decays e.g 1Bq = I count per second |
|
|
What are the three main types of radiation ? |
Alpha , beta and gamma |
|
|
Properties of alpha radiation and how to stop it |
Strong ionising power Absorbed by a few centimetres of air or a thin sheet of paper |
|
|
Properties of beta and how it’s stopped |
Reasonable ionising power Beta passes through air and paper but is absorbed by a few millimetres of aluminium |
|
|
How do you measure the activity of a radioactive source ? |
In becquerels (Bq) which is the rare at which the source decays e.g 1Bq = I count per second |
|
|
What are the three main types of radiation ? |
Alpha , beta and gamma |
|
|
Properties of alpha radiation and how to stop it |
Strong ionising power Absorbed by a few centimetres of air or a thin sheet of paper Two neutrons and two protons |
|
|
Properties of beta and how it’s stopped |
Reasonable ionising power Beta passes through air and paper but is absorbed by a few millimetres of aluminium A high speed electron Ejected from nucleus as neutron and turns into a proton |
|
|
Properties of gamma and how to stop it |
Poor ionising power Very penetrative and need many centimetres oh lead or many metres of concrete to absorb most of it Electromagnetic radiation Emitted from nucleus |
|
|
What is radioactive contamination ? |
The unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on materials |
|
|
What is irradiation? |
Process of exposing an object to nuclear radiation Doesn’t cause object to become radioactive |
|
|
The half love of a radioactive isotope is ? |
The average time if game for half of the nuclei to decay The time it takes for the count rate or activity to drop by 50% E.g the count rate takes 25 minutes to fall from 80-40 so it’s half life is 25mins |
|
|
What happens when a alpha particle is emitted ? |
The mass number of the element is reduced by 4 The atomic number is reduced by 2 This is because 2 protons and 2 neutrons are emitted from the nucleus |
|
|
What happens when a alpha particle is emitted ? |
The mass number of the element is reduced by 4 The atomic number is reduced by 2 This is because 2 protons and 2 neutrons are emitted from the nucleus |
|
|
What happens with beta decay ? |
The mass number does not change The atomic number increases by 1 This is because the neutron turns into a proton and an electron - electron is emitted as beta particle |
|
|
What happens with the emission of gamma rays ? |
The gamma ray does not cause a change in mass of the charge of the nucleus |
|
|
Electric circuit symbols |
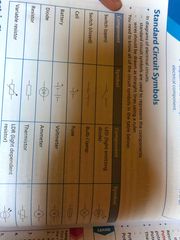
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Electric circuit symbols |
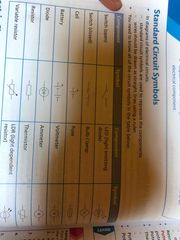
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is current ? |
The flow of electrical charge -greater the rate of flow the higher the current |
|
|
What is current ? |
The flow of electrical charge -greater the rate of flow the higher the current Measured in amps |
|
|
Equation for charge flow |
Charge flow = current x time |
|
|
Equation for charge flow |
Charge flow = current x time |
|
|
What is resistance |
The resistance of a component is how it resists the flow of charge - higher resistance lower the current Measured in ohms |
|
|
What is potential difference |
The difference in electrical potential from one point in a circuit to another - greater the potential difference the greater the flow of charge and current |
|
|
Equation for potential difference |
Current x resistance |
|
|
Equations for power |
Potential difference x current (Current)2 x resistance |
|
|
What is the difference between direct and alternating current supply’s |
Direct is always a positive or negative with the same constant direction - supplies through cells and batteries Alternating ,alternates which direction the current is going and supplied through the mains |
|
|
What is the difference between direct and alternating current supply’s |
Direct is always a positive or negative with the same constant direction - supplies through cells and batteries Alternating ,alternates which direction the current is going and supplied through the mains |
|
|
Properties of mains electricity |
230V and changes direction 50 times a second -50hz Used three wires Live wire - brown Neutral wire - blue Earth wire - green and yellow stripes |
|
|
Role of earth wire |
The live wire carries the potential difference and the neutral wire completes the circuit -therefore the earth wire is a safety wire which stops exterior of appliances becoming live |
|
|
Another equation for power |
Energy transferred / time Work done / time Measured in watts |
|
|
Another equation for power |
Energy transferred / time Work done / time Measured in watts |
|
|
Equation for efficiency |
Useful energy transfer / total energy transfer |
|
|
Equations for energy transferred |
Power x time Charge flow x potential difference |
|
|
What is the national grid |
A system of cables and transformed which link power stations to homes and businesses |
|
|
Course electricity takes through national grid |
Power station - 25,000V Step up transformer Transmission cables - 400,000V Step down transformer Houses and shops - 230V |
|
|
What is an exothermic reaction |
When the heat is given out to the surroundings |

