![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

stanza
|
a stanza is a group of two or more lines that form a unit in a poem. A stanza is comparable to a paragraph in prose. each stanza may have the same number of lines, or the number of lines may vary
|
|
rhythm
|
rhythm is a pattern of stressed and understand syllables in a line of poetry. poets use rhythm to bring out the musical quality of language, to emphasize ideas, to create new moods, to unify works, and to heighten emotional responses.devices such as alliteration, rhymes, assonance, consonance, and parallelism often contribute to creating rhythm
|
|

foot
|
The 'Foot' in Literary Terms refers to two or more syllables that together make up the smallest unit of rhythm in a poem. For example, an Iamb is a foot that has two syllables, one unstressed followed by one stressed. an Anapest has three syllables, two unstressed followed by one stressed.
|
|

Meter
|
is the basic rhythmic structure of a verse or lines in verse. Many traditional verse forms prescribe a specific verse meter, or a certain set of meters alternating in a particular order.
|
|

sight rhyme
|
is a rhyme in which two words are spelled similarly but pronounced differently and have come into general use through "poetic license" also known as artistic license. An example is the pair slaughter and laughter; although they look similar, and should rhyme based on the visual aspect, when they are spoken there is no rhyming quality.
|
|
slant rhyme
|
is consonance on the final letters of the words involved. Many slant rhymes are also mouth rhyme.
|
|

identical rhyme
|
Identical rhyme definition, rhyme created by the repetition of a word.
|
|

end rhyme
|
rhymed on the terminal syllables of the verses.
|
|

internal rhyme
|
A rhyme involving a word in the middle of a line and another at the end of the line or in the middle of the next.
|
|

rhyme scheme
|
the pattern of rhymes used in a poem, usually marked by letters to symbolize correspondences, as rhyme royal, ababbcc.
|
|
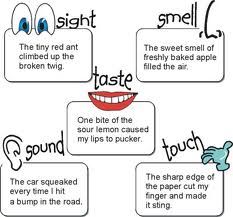
imagery
|
Imagery is the name given to the elements in a poem that spark off the senses.
|
|

symbolism
|
many poets used symbolism to deepen the meaning of their poem.
|
|

alliteration
|

Alliteration is the repetition of the same or similar sounds at the beginning of words such as tongue twisters.
|
|

simile
|
A Simile is a figure of speech in which two things are compared using the word "like" or "as" to draw attention to similarities about two things that are seemingly dissimilar.
|
|

metaphor
|
A metaphor is a pattern equating two seemingly unlike objects.
|

