![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Characteristics of living systems |
Metabolism- cata & ana Responsiveness Mvmt Growth & differentiation Reproduction |
|
|
Levels of structural organization |
Chemical Cellular Tissue Organ Organ system Organismic |
|
|
Scientific method |
Observation Hypothesis/prediction Experimental testing Analysis & conclusion Develop new hypothesis |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Body's internal environment remains relatively constant w/ in physiological limits |
|
|
Physiological limits & viability |
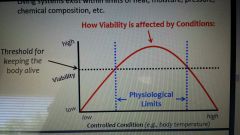
|
|
|
Negative feedback |
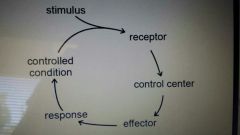
Most systems in body Original stimulus reversed Used for conditions that need frequent adjustment (body temp, blood sugar levels, blood pressure) |
|
|
Positive feedback |
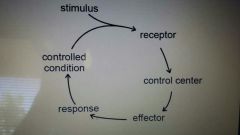
Not as common Original stimulus intensified Seen during normal childbirth |
|
|
Equilibrium |
Constant state achieved w/out energy expenditure |
|
|
Covalent bonds |
Share electrons |
|
|
Ionic bonds |
Attractive force of electrical charge |
|
|
Potential energy during chemical rxn |
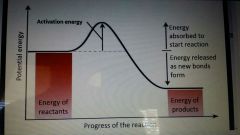
|
|
|
Effect of catalysts on chemical rxn |
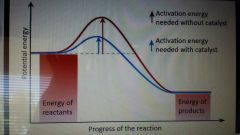
|
|
|
Carbs |
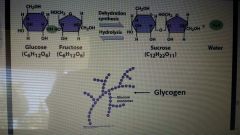
|
|
|
Protein |
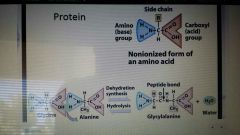
Comprised of linear sequence of amino acids |
|
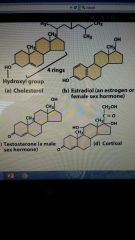
Lipids |
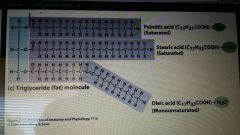
|
|
|
Nucleic acid (DNA,RNA) |
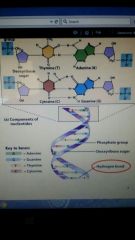
|
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Interaction surface between cell and outside world |
|
|
Nucleus |
Genetic material |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Everything between membrane and nucleus ICF(cytosol) Organelles |
|
|
Membranous organelles |
Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Mitochondria Golgi complex |
|
|
Non membranous organelles |
Cytoskeleton Proteasomes Ribosomes |
|
|
Integral protein |
Extend into/crosses cell membrane Amphipathic |
|
|
Peripheral proteins |
Attached to inner or outer surface of cell membrane and are easily removed |
|
|
Membrane fns |
Barrier Organization Transport Rxn/response |
|
|
Passive transport |
Down concentration gradient No energy input Simple diffusion,channel mediated facilitated diffusion,carrier mediated facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Active transport |
Against concentration gradient Uses ATP |
|
|
Diffusion |
Net proportional to concentration gradient Occurs rapidly over short distances |
|
|
Simple diffusion |
Hydrophobic: gasses, fatty acids, steroid hormones, fat soluble vitamins |
|
|
Osmosis |
Water through channels (aquaporins) |
|
|
Channel mediated facilitated diffusion |
Ions |
|
|
Carrier mediated faciliateted diffusion |
Glucose, fructose, galactose, some vitamins |
|
|
Primary active transport |
hydrolysis of atp chgs shape of carrier protein and pumps sub across membrane against concentration gradient |
|
|
Secondary active transport |
Energy stored in NA+ or H+ gradient used to move other sub against concentration gradients |
|
|
Bulk transport |
Endocytosis, exocytosis, transcytosis Vesicles |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Vesicular transport of something into cell |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Vesicular transport of something out of cell |
|
|
Transcytosis |
Vesicular transport of something from outside of one side of cell to outside of other side of cell |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Microtubules |
|
|
Microfilaments |
Strands of protein (actin) Connects organelles to membrane Influence cell motility and shape |
|
|
Intermediate filaments |
Keratins Structural stability |
|
|
Microtubules |
Strands of tubulin Influence cell structure and shape Motility- mvmt (cilia & flagella) |
|
|
Centrioles/centrosomes |
Cell motility/cell division |
|
|
Cilia & flagella |
Cell motility |
|
|
Microvilli |
Increase surface area of plasma membrane |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Site of protein synthesis |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Major site of cell energy metabolism |
|
|
Oxidative phosphorylation |
Enzyme controlled breaking of bond Consumes O2 Produces CO2 Efficient production of ATP |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Lipid&protein synthesis Storage (protein;Ca2+) Transport within cell Detoxification Rough and smooth |
|
|
Rough er |
Protein synthesis & storage |
|
|
Smooth er |
Lipid synthesis & Ca2+ storage |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Site of packaging and processing of protein products for secretion |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Contains digestive enzymes for recycling old cellular material |
|
|
Peroxisomes |
Contain enzyme for detoxification of byproducts of metabolism |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Nucleic acid (histones) Made of DNA |
|
|
Composition of nucleic acids |
Sugar, phosphate, 1of 4 diff nitrogenous bases Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine |
|
|
Codon |
Triplet of 3 bases that rep 1 of 20 diff amino acids |
|
|
Gene |
Sequence of codons rep encodes (single polypeptide) protein |
|
|
Chromatin |
Typical condition of DNA Dispersed DNA |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Cell dividing Condensed DNA |
|
|
Transcription |
Synthesis of RNA from DNA synthesis of complementary strand of RNA using base sequence of DNA as template Occurs in nucleus Produces mRNA Alt splicing of exons produce distinct mRNAs from 1 gene |
|
|
Translation |
Synthesis of protein from RNA Synthesis of protein using base sequence of RNA as template Occurs in cytoplasm Involves mRNA,rRNA,tRNA Produces protein |
|
|
Promoter |
DNA sequence upstream to start of gene which RNA polymerase binds |
|
|
Transcription factors |
Proteins bind to promoter to augment binding of RNA polymerase |
|
|
Mitosis |
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
Prophase |
Condensation of DNA to chromosomes |
|
|
Metaphase |
Alignment of chromosomes along center line or plane |
|
|
Anaphase |
Sep of sister chromatids to daughter cells |
|
|
Telophase |
Formation of 2 new nuclei |

