![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Motivation to study attention to speech |
To determine the efficiency with which we can divide attention whilelistening to more than one message at a time To determine the extent to which we can selectively focus on one speech stream to the exclusion of others |
|
|
Cocktail Party Phenomenon |
The ability to attend to one conversation while being surrounded by so much noise, yet being sensitive to other conversations. |
|
|
What questions do the cocktail party scenarios raise? |
others around us? How much do you retain of the other conversations that we do not pay attention to? How are we able to focus attention on just one conversation and disentangle it from others around us?How much do you retain of the other conversations that we do not pay attention to?Do we not completely shut up other conversations while attending to our name, and instead listen to them in at least a superficial manner? |
|
|
Dichotic listening |
Presentation of auditory stimuli binaurally to each ear. Selective attention studies: subjects attention and put in just one ear and ignore input to the other ear Divided attention studies: subjects attend inputs in both ears at the same time |
|
|
Shadowing, phrase shadowing, phonemic shadowing |
Shadowing: repeating aloud an attended message as heard Phrase shadowing: repeating entire phrases as heard Phonemic: repeating each sound is heard |
|
|
Findings of dichotic listening studies |
Efficiently processed the meaning of the attended messages they had shadowed, but remember very little about the meaning of the unintended messages Found little or no memory of the unattended messages meaning but some memory of the messages sensory properties |
|
|
Does presenting speech to the left ear or right ear make a difference? |
People remember better when presented to the right ear Maybe because language area is in left hemisphere in most people, contralateral connections in brain |
|
|
Broadbent (1950s) |
Proposed first attention model, known as the early selection model. Y-tube gating mechanism: 2 information channels providing input to a single channel, only limited capacity can get through at a time. |
|
|
Early selection model |
Proposed by Broadbent Selection based on sensory properties of speech streams, speech meaning plays no role in guiding filter mechanism Sensory input buffer → filter mechanism, selects one input → limited capacity channel receiving input → module representing higher-level cognitive analysis Attended speech → sensory buffer → Attentional selection → semantic analysis → long term memory |
|
|
Why was the early selection model so appealing? |
Limited analysis of unattended inputs, analyzing all inputs with lead to brain overload Parsimonious (efficient) |
|
|
Why was Boadbent's early selection model incorrect? |
Too simple Didn't explain cocktail phenomenon Too rigid |
|
|
How did late selection model come about? |
Leaks in broadbent's model → new model needed If they only allow one speech stream, how is it we noticed our name being said in unattended conversation |
|
|
Late selection model |
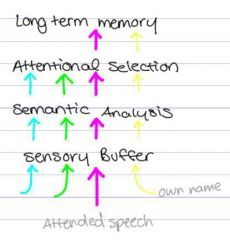
Suggest all inputs undergo semantic analysis then depending on importance some inputs go to long-term memory/ consciousness
|
|
|
Linguistic expectancy |

|
|
|
Split-span experiment |
Broadbents experiment, where three pairs of digits were presented in sequence. Subject were required to split their attention span and listen to inputs to both ears. When asked to recall the digits as heard, subjects did not report them in the pair by pair presentacion order but instead reported them in the ear by ear order. Suggested recall order must reflect the initial order in which the digits were encoded |
|
|
Structural limit of selection |
Selective attention is a necessary consequence of limits on our capacity to process information imposed by information channel capacity |
|
|
Y-tube model |
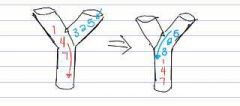
Structural bottleneck mediates selective attention by limiting the amount of information that can pass through communication channels |
|
|
Why was Broadbents early selection models so important |
Played large role in legitimization of the psychological study of cognitive processes after the behaviorist era It was a catalyst for attention research |
|
|
Semantic analysis |
Processing the meaning of speech |
|
|
In the early selection model what happens to inputs that do not go on to semantic analysis |
They remain in the sensory buffer until they decay |
|
|
Can unattended words affect the meaning of the speech of attended message? |
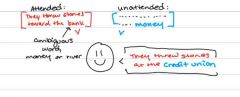
|
|
|
Who developed the late selection model ? |
Deutsch and Deutsch |
|
|
Explain the GSR study |
Stage 1 classical conditioning of GSR List of words + shock = GSR (sweating) List of words → sweating Stage 2 dichotic listening unattended message with word list → sweating Favors the late selection model |
|
|
How was late selection better than early selection? |
Can account for findings that unattended speech is processed for meaning |
|
|
What are some limitations to the late selection model |
too extreme not efficient |
|
|
Intermediate selection model |
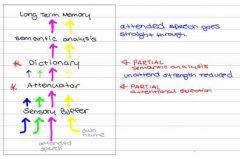
Proposed by Treisman as a compromise between late and early selection Some but not all unattended input undergo semantic analysis
|
|
|
How are Broadbent and Treismans model different? how are they the same? |
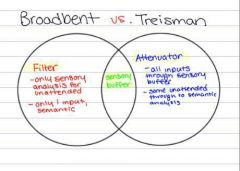
|
|
|
Explain the use of thresholds, dictionaries and activation level in the intermediate selection model |
Dictionary: store of words each associated with an activation threshold Once node in dictionary is activated, associated meaning is passed along for further semantic analysis and then to long term memory Words that are more important to us ie. our names, have a lower threshold Lower threshold don't require as much input strength to grab our attention |
|
|
What does the attenuator do in the intermediate selection model |
Reduces the signal strength of unattended message. Attended and unattended messages make it through to the second stage of attentional selection, but physical intensity of unattended has been reduced |
|
|
What are the advantages of the intermediate selection model |
It's a compromise between the late and early Flexible More efficient than the late |
|
|
Neuroimaging of attention to speech |
ERP studies found attention works really quickly, reaction in 150 ms But we don't start processing words until + 300ms Doez not favor the late selection because attentional filter happens before semantic analysis |

