![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Age of Adolescence |
1900-1940, 60% more adolescents in school |
|
|
School funding |
Only 5% from federal government Local and state level legislation and funding |
|
|
Secondary Education in Industrialized European Countries |
College preparatory, Vocational School, Professional school |
|
|
Size Matters for Effective Schools |
Large: Diverse courses and extracurriculars Small: Less diversity, more likely to participate in extracurriculars. Optimum school size: 500-1000 students |
|
|
6-3-3, 5-3-4, 8-4 |

|
|
|
School Climate |
How s and t interact, expectations of s and t, and methods used in the classroom. |
|
|
Optimum School Climate |
Supportive teachers, dedicated to the students, Firm-but-fair discipline, High expectations for student performance and conduct |
|
|
Engagement |
Being psychologically committed to learning Engagement has gone down steadily since 1983 |
|
|
Family Environment & Schools |
Parents have high expectations for achievement -> Better grades and more involvement. Linked to parenting styles Important and helpful to engage parents in school |
|
|
The Role of Socioeconomic Status |
Higher SES is strongly related to academic achievement. |
|
|
Peers, Friends, and School |
Friends influence consistency of class attendance, time spent doing homework, effort put into schoolwork, and grades more than parents. |
|
|
Work Hours and School Performance |
Beyond 10 hours a week, the more an adolescent works, the lower their school performance. |
|
|
Steinberg 1996 |
Socializing with friends was an adolescents most common activity, Engagement, School Climate, |
|
|
Ethnic Differences in Achievement |
Cultural perspectives on academic success being due to effort or ability, Issues of social class/access, Variations in parenting practices, Friends' influence |
|
|
Gifted Adolescents Traditional criterion= IQ of ≥130 AP classes available |
Gifted programs recognize special talents Four characteristics of giftedness: Precocity Independence Drive for mastery Excellence in information processing. Issues: may become bored and alienated/ socially isolated. |
|
|
Adolescents with Disabilities Speech handicaps, mental retardation, emotional disorders, and learning disabilities. |
About 10% of adolescents in American schools have a learning disability, reading being the most common source of difficulty. Boys are twice as likely to have a disability. |
|
|
ADHD |
50% comorbidity rate with adolescents who have learning disabilities. Boys are 4x more likely to be diagnosed Nearly 50% of diagnosed have an immediate relative with ADHD Nearly 9/10 treated with Ritalin or other medication. |
|
|
AdhD Observational Research in Europe (ADORE) Study |
1,500 participants (ages 6-18) in 10 countries. Pediatricians and child psychologists collected observational data at seven points over 2 years. |
|
|
ADORE study findings |
Higher rates of ADHD among boys than girls, Symptoms similar among both sexes, Girls more likely to have additional emotional problems and be bullied by peers Boys more likely to have additional conduct problems Frequent problems in relationships Frequent stresses reported by parents due to child's ADHD behavior |
|
|
Adolescents with Disabilities: The Tracking Strategy |
Tracking (Stratified Levels): Upper- College preparatory level General- For average students Remedial/Special Education- For students academically behind their peers Some schools have a vocational track for technical or trade preparation. |
|
|
High School Drop Out Rates |
Highest among Latinos, then Blacks, then Whites. |
|
|
College Attendance |
Less than 5% in 1890, 70% in 2010. Females more likely than males to enter college. In America, 90% of Asian Americans enter college after HS, compared to 71% of Whites and 60% Blacks and Latinos |
|
|
College Life (Clark & Trow, 1966) |
Four Subcultures: Collegiate Vocational Academic Rebel |
|
|
College Life: Collegiate |
Fraternities, Sororities, dating, drinking, campus sports, fun. Learning is not a first priority. |
|
|
College Life: Vocational |
Practical view of college to help get a better job |
|
|
College Life: Academic |
Aligned with the educational mission of college- all about ideas, knowledge, and connecting with professors and the material |
|
|
College Life: Rebel |
Deeply engaged with ideas in classes, but are also nonconformists, engaged with ideas, but skeptical of professors and their experiences. |
|
|
Adolescent Work in Traditional Cultures |
Hunting, Fishing and Gathering (men), Farming and Care of Domestic Animals (fathers and sons), Child Care and Household Work (women). |
|
|
Adolescent Work Before 1900 |
Common for adolescents to work in farming and care of domestic animals in the 17th century and earlier. Industrialization in the 18th century moved adolescent workers to factories. |
|
|
The Adolescent Workplace |
Most American girls baby-sit, boys to yard work. Retail or restaurants make up the majority of jobs for older adolescents. The average Sophomore works 15 hours a week, Seniors is 20 a week. |
|
|
Hours of Work a Week |
≤10 is no related to psychological symptoms
>10: Anxiety, depression, less sleep, disruptive to eating and exercise habits. >20: Problems become considerably worse |
|
|
Working and Problem Behaviors |
Adolescents who work are more likely to smoke, drink, and do drugs BUT correlation does not assume causation. |
|
|
The Forgotten Half (1988) |
Those who didn't go to college, going straight to work. Loss of manufacturing jobs that used to provide well-paying jobs for unskilled workers. Follow up report in 1998 states that prospects for the forgotten half had become worse. |
|
|
New Basic Skills (Murnane & Levy, 1997) |
Six basic skills needed for success at office and factory jobs now available to high school graduates: Reading and math at ≥9th grade level, Solving semi-structured problems, Communicating orally and in writing, Using a computer for word processing and other tasks, Collaborating in diverse groups. |
|
|
The Typical American Adolescent |
4 hours of music a day 2 hours of tv a day 50% go to a movie at least once a month 70% of girls read popular magazines 90% have access to computers and the Internet 93% own a digital device |
|
|
Theories of Media Influence |
Cultivation Theory and Social Learning Theory |
|
|
Cultivation Theory |
Watching tv gradually shapes or cultivates a person's worldview so it becomes like the worldview frequently depicted on tv. |
|
|
Social Learning Theory |
People are more likely to imitate behavior they see frequently modeled [in the media] and that behavior is rewarded (or at least not punished) |
|
|
Uses & Gratification Approach |
Two principles: 1. People make individual decisions about which media to consume based on their individual differences and characteristics 2. People that consume the same media product will respond to it in different ways depending on their individual characteristics. |
|
|
Media Practice Model |
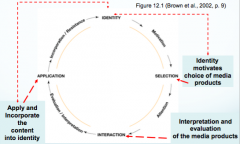
|
|
|
Five Uses of Media |
Entertainment (To have fun) Identity Formation (Forging who I am) High Sensation (Seeking intense and new thrills) Coping (Relaxation and De-stressing) Youth Culture Identification (Connecting to others) |
|
|
Media and Socialization |
More technology = more availability & diversity of media Media is market driven. |
|
|
Television and Aggressiveness |
Majority of violent crimes committed by males 15-25 Most of the research is correlation |
|
|
Gaming |
97% of us middle school students reported playing electronic games (Olson et al., 2008) Of the computer game players, 31% played every day and additional 21% played 3-5 times a week. A study in 10 European countries and Israel found that children 6-16 played more than 30 minutes a day on average |
|
|
Computer Games: Players' Perspectives (Olson et al., 2008) |
12-14 year old boys interviewed about eh effects of playing violent computer games Used games to experience fantasies of power and fame, explore exciting new situations, to play and talk with their friends, and to work through feelings of anger or stress (cathartic effect) They did not believe that playing the games had negative influences. |
|
|
Computer Games and Aggressiveness |
Playing violent computer games is related to heightened aggressiveness, hostility and anxiety Recently games involving sports and music have become popular |
|
|
Sexual Portrayals on TV: Males |
"Boys will be boys" Actively seek sex Always "ready and willing" Recreational attitude toward sex |
|
|
Sexual Portrayals on TV: Females |
Girls better be prepared for the guys Sexual gatekeepers (Yes or no is on us) Recreational attitude toward sex |
|
|
Sexual Portrayals on TV (Cope-Farrar and Kunkel, 2002) |
82% of programs had sexual content Sexual behavior more frequent than sexual talk Sexual behavior between partners with established relationships (not married) Kisses and hugs; intercourse and nudity infrequent at 7% Not much discussion or sexual risk` |
|
|
Music TV |
USA in 1981, now worldwide Rap began in the late 1970s, MTV devoted to rap in 1988 2/3 of 12-18 year olds listen to rap/hiphop Female rap artists Rap is highly popular in many places around the world Impact of "gangsta rap" & women controversial Violence, racism, sexism and promotion of homophobia in lyrics |
|
|
Music: Heavy Metal |
Started in the late 1960s with Led Zeppelin, Iron Maiden and Black Sabbath, peaked in 1980s Hard rock/heavy metal is the third most popular music among adolescents after hiphop and alternative rock (Roberts et al., 2005) Violence is also a common theme in heavy metal songs. Metalheads or headbangers tend to have a dark view of the world. Cathartic effect |
|
|
Big Tobacco and Advertising |
Cigarettes are the second most heavily promoted consumer product int he US, totaling 6 billion dollars/year. 90% of smokers start by 18, Ads present images of youthful fun and vigor, independence, and "coolness". The effects of advertising on brand choice was 3x as strong for adolescents as adults. 3 most popular brands are the most heavily promoted |
|
|
Internet Benefits |
Access to information- potential to enhance education Can be a source of positive social interactions- opportunities to practice communication, engage in "identity play," and find answers to problems |
|
|
Internet Cautions |
Chat rooms sometimes frequented by sexual predators seeking to victimize children and adolescents Academic cheating via downloading or purchasing pre-written papers Promote social isolation (displacement effect) |
|
|
New Internet Forms |
Social networking websites 73% of 13-17 year olds regularly use them 72% of 18-29 year olds Users construct profiles and use sites to keep in touch with friends and family |
|
|
Social Networking |
In constructing a profile, users are allowed to maintain and expand their social networks Adolescents and emerging adults use these sites mainly to keep in touch with friends and make new ones |
|
|
Blogging |
Blog- A public internet journal of a person's thoughts, feelings and activities. 1/4 adolescents 12-17 have a blog in the US Half read others' blogs Adolescents are more likely than adults Most common content is daily activities Can be an area for identity explorations as bloggers reflect of their feelings and experiences They are private and public, personal and social |
|
|
Mobile Phones and Texting |
Most popular among adolescents and emerging adults. Adolescents use cell phones for texting more than talking. |
|
|
Media and Globalization |
Western Media appeals to adolescents because they've grown up with it and are more capable of exploring the environment outside the family than younger children. |
|
|
Two Broad Problem Types: Externalizing |
Externalizing: create difficulties in a person's external world. Tend to go together More common among males Often motivated by desire for excitement, not necessarily underlying unhappiness or psychopathy. "Undercontrolled" |
|
|
Two Broad Problem Types: Internalizing |
Internalizing: primarily affect a person's internal world Tend to go together More common in females Associated with experiencing distress "overcontrolled" |
|
|
Externalizing Problems: Risky Driving |
16-24: Highest rates of auto accidents, injuries, & fatalities, leading cause of death for age group Reasons? Driving while Impaired, aggressiveness, driver inexperience, sensation-seeking personality, lack of parental monitoring, belief that friends approve of risky driving. Optimistic Bias |
|
|
Shope's Model of Young Driver Crash Risks (2002) |
The social environment & driver characteristics influence the driving behaviors & driving environment, which influence the likeliness of a crash, which can lead to injury and fatality. |
|
|
Prevention of Auto Accidents: Driver's Ed |
Generally hasn't worked well Get your license faster |
|
|
Prevention of Auto Accidents: Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) |
More effective Address a variety of risk factors Restrict the conditions under which novices can drive 3 Stages of License: Learning- getting driving experience under supervision of experienced driver Restricted- can drive unsupervised, restricted to reduce crashes (e.g. driving curfews) Full- After 1 year of restricted |
|
|
Externalizing Problems: Substance Use in the US (2008) |
Alcohol- 14% of boys, 12% of girls Cigarettes- 7% of boys, 9% of girls Illegal drugs. |
|
|
Sequence of Substance Use |
Drinking beer and wine Smoking cigarettes and drinking hard liquor Smoking marijuana Using "hard" drugs (e.g. cocaine, LSD) |
|
|
Externalizing Problems: Substance Use- Reasons for Use |
Experimental (See what it's like) Social (At parties and such) Medicinal (To relieve unpleasant emotional state) Addictive (Dependency, either physical or psychological) |
|
|
Externalizing Problems: Crime |
Delinquency- when "juveniles" commit crimes Status Offense- Only a violation of the law because committed by juvenile (e.g. drinking) Index Crimes- Serious crimes at any age (e.g. violent crimes, property crimes) Non-index Crimes- Less serious offenses (e.g. gambling) |
|
|
Two Types of Delinquency: Life-course-persistent delinquents (LCPDs) |
Pattern of problems "from birth" on up Originate in neuropsychological deficits (difficult temperament, learning disabilities) Likely to grow up in high risk environment |
|
|
Two Types of Delinquency: Adolescent-limited delinquents (ALDs) |
No signs of problems in infancy or childhood Period of occasional criminal activity between ages 12-25 (e.g. vandalism, illegal drug use) |
|
|
Preventing Crime & Delinquency: Varied Strategies |
Individual therapy Group therapy Vocational training Outward Bound type programs Scared Straight "Boot Camp" (Doesn't work) Multi systemic Approach (met with some success) |
|
|
Problems with Preventing Crime & Delinquency |
Participation is typically non-voluntary or against one's will Prevention comes too late (in adolescence) after behavior patterns have been established. Possible peer contagion |
|
|
Factors of Risk Behaviors |
Individual characteristics and socialization influences |
|
|
Socialized and Unsocialized Delinquents |
Socialized: Involved with gangs, stealing in groups. A pack delinquent Unsocialized: assault, usually being a lone delinquent (not cooperating with others) |
|
|
Culture and Risk Behavior (Schlegel and Barry 1991) |
In traditional cultures, boys, not girls, tend to engage in risk behavior during adolescence. Evidence of antisocial behavior in less than half of the cultures studied USA has highest rates of violent crimes Less risky driving in Western countries other than the USA |
|
|
Death Rates (2012) |
US has 3 times more homicides than suicides, and 3 times more homicide than the second highest rate, with USA homicides at ~22,000 persons and suicides at ~6,500 persons. |
|
|
Levels of Depression |
Depressed mood: enduring period of sadness without any related symptoms Depressive syndrome: addition of symptoms such as frequent crying, feeling guilty, lonely or worried. Major depressive disorder: episode includes ≥5 symptoms during a two-week period and disrupts functioning |
|
|
Diathesis-stress model |
When predispositioned vulnerability meets stress from life experiences |
|
|
Suicide: Risk factors and facts |
Risk Factors: Depression, family disruption, substance abuse problems, relationship problems outside the family, result of serious of difficulties over time. 3rd more common cause of death ages 15-19 Women attempt more, men succeed more Americans grades 9-12, 24% report thinking of suicide, 3% attempt Current rate in US is 4x the rate in the 1950s Highest among Native American youth Higher in White adolescents and emerging adults |
|
|
Eating disorders |
Anorexia Nervosa (intentional self-starving) Bulimia Nervosa (binge eating & purging) Cultural ideal of thinness Puberty and body changes More common among upper and middle SES, girls who read "Seventeen" magazine Linked with warm and controlling parent styles Occurs most often among females in teens, early 20s |
|
|
Resilience: Protective Factors |
Most adolescents who grow up in high-risk environments exhibit resilience Protective factors: High intelligence Authoritative parenting styles Strong religious faith A caring adult "mentor" outside the family |

