![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When are EM radiations assumed to behave as a wave? |
They exhibits phenomenia such as diffraction and interference. |
|
|
When are EM radiations assumed to behave as particles? |
In experiments such as: 1. The photoelectric effect 2. Atomic line spectra |
|
|
What are the fundamental particles which make up all forms of electromagnetic radiation? |
Photons are fundamental particles which make up all forms of electromagnetic radiation. |
|
|
What is a photon? |
A photon is a massless "packet" or a quantum(particle) of electromagnetic energy. |
|
|
Learn |
Each proton carries a specific amount of energy, and transfers this energy all in one go, rather than supplying a consistent amount of energy. |
|
|
State the formula to calculate the energy of a photon. |
E = hf h- Planck's constant (Js) f- frequency (Hz) |
|
|
Einstein showed that a photon traveling in a vacuum has momentum, despite it having no mass. |
Learn |
|
|
State the formula for the momentum(p) of a photon. |
p= E/c E - energy of photon c- speed of light |
|
|
What is the electronvolt? |
The electron volt is a unit which is commonly used to express very small energies |
|
|
State the definition of an electrovolt. |
An electrovolt is the energy gained by an electron travelling through a potential difference of one volt. (1 ev= 1.6 × 10^-19 J) |
|
|
State the speed of an electron in terms of eV. |

v = Sqrt((2*eV)/m) |
|
|
What is the photoelectric effect? |
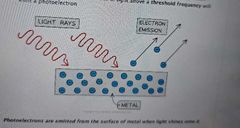
The photoelectric effect is the phenomena in which electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal upon the absorption of electromagnetic radiation. |
|
|
What are photoelectrons? |
Photoelectrons are the electrons that are emitted from the surface of a metal upon the absorption of electromagnetic radiation. (during the photoelectric effect ) |
|
|
State the evidence shown by the photoelectric effect that proves light is quantised, or carried in discrete packets. |
Each electron can absorb only a single photon. This means only the frequencies of light above a threshold frequency will emit a photoelectron. |
|
|
What is the definition of threshold frequency? |
The threshold frequency is defined as the minimum frequency of incident electromagnetic radiation required to remove a photoelectron from the surface of a metal. |
|
|
State the definition of threshold wavelength. |
Threshold wavelength is defined as the longest wavelength of incident electromagnetic radiation that would remove a photoelectron from the surface of a metal. |
|
|
State the equation for the energy of an incident photon. |
Energy = threshold energy + Ek of photoelectron hf = Φ + 1/2 mv^2 max |
|
|
Learn |
EKmax of the photoelectrons depend only on the frequency of the incident photon, not the intensity of the radiation. |
|
|
What is the work function Φ, or threshold energy, of a material? |
It is the minimum energy required to remove a photoelectron from the surface of a material. |
|
|
Why placing the UV light source closer to the metal plate causes the gold leaf to fall more quickly? |
The intensity increases and thus the number of photoelectrons emitted per second increases, Therefore the gold leaf loses negative charge more rapidly. |
|
|
Why using a higher frequency light source does not change how quickly the gold leaf falls? |
Only the Ek of the photoelectrons increases with frequency of the incident radiation. Energy and frequency are independent of the intensity of the radiation. |

