![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
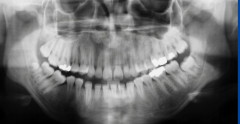
|
hyperdontia -distodens -"fourth molar" |
|
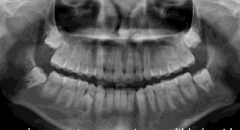
|
hyperdontia peridens (premolar) -most common in mandible
|
|
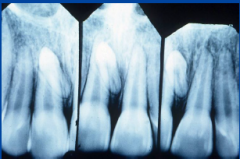
|
hyperdontia -mesiodens *most common single supernumerary tooth
(midline) |
|
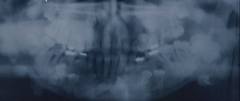
|
conditions associated with supernumerary teeth: Gardner's |
|
|
Syndromes associated with supernumerary teeth? |
-Gardner's -cleidocranial dysplasia |
|
|
hypodontia (missing 1/few teeth)
-retained decid. and missing premolar |
|
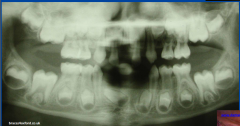
|
hypodontia (missing 1/few teeth) |
|
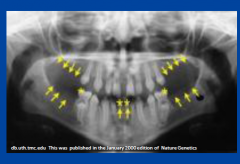
|
oligodontia -missing 6+ teeth |
|
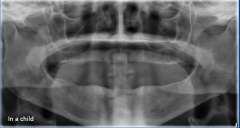
in a child |
anodontia |
|
|
Syndromes assoc. with missing teeth |
-ectodermal dysplasia
also can see in: -downs -cleft lip/palate! -hemifacial microsomia -rad to jaws in kids |
|

|
ectodermal dysplasia -AD condition -at least 2 ectodermal structures are missing |
|
|
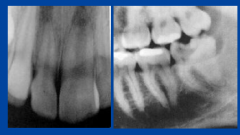
macrodontia M |
|
|
Macrodontia may be associated with: |
-vascular abnormalities -hemihypertrophy of face -pituitary gigantism
*could be confused with gemination/positioning errors |
|
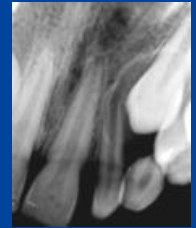
|
microdontia
|
|
|
Microdontia may be assoc. with: |
-may be syndromic -CHF, progeria, downs |
|

|
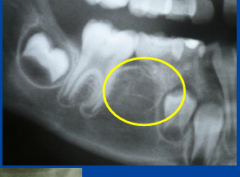
impaction (canine) |
|

|
impaction (molars) |
|
|
Most common places for impaction? |
canines and molars -teeth encased in bone/soft tissue -tooth "fails" to erupt |
|

|
CBCT bony window -impaction |
|

|
transposition -most common in permanent canine and first premolar -teeth switch places |
|

|
ankylosis |
|
|
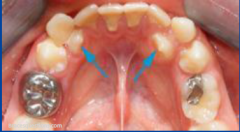
Anyklosis could be caused by: |
Fusion to bone could be caused by: -infection -trauma -abscence of permanent tooth |
|
|
ectopia |
|

|
gemination -cleft/invagination of crown -single pulp chamber -normal number teeth -more common in primary teeth -common in insors and canines
|
|

|
gemination |
|

|
twinning -complete division of the tooth bud
don't confuse with fusion; count teeth! (same number teeth) |
|

|
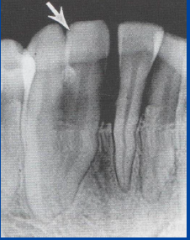
fusion
|
|
|
fusion |
|
|
How do you know you have a case of fusion? |
-No pdl space between -one fewer tooth in arch
2 pulp chambers; dentin fused together |
|

|
concrescence -teeth fused by cementum |
|

|
concrescence -no alv. bone or pdl between teeth |
|

|
taurodontism -long trunk, short root -normal crown
|
|
|
What is associated with taurodontism? |
-Downs -Amelogenesis imperfecta |
|
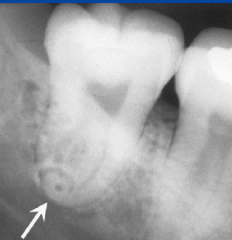
|
dilaceration -b/l places roots look like bull's eye |
|
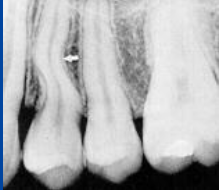
|
dilaceration |
|

|
dens in dente -radicular
*folding of hertwig's -line by cementum -rare |
|

|
dens in dente -coronal
*folding inwar of enamel organ -lined with epith |
|

|
dens in dente -invag. |
|

|
enamel pearl |
|
|
Dens in dente may result in? |
-necrosis -rarefying osteitis (aka granuloma or cyst) |
|
|
Diff. dx of enamel pearl |
-calculus -pulp stone |
|
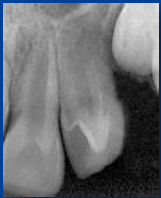
|
talon cusp |
|
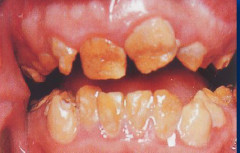
|
amelogenesis imperfecta -enamel hypoplasia due to incomplete defective formation of enamel matrix
-normal dentin |
|
|
In amelogenesis imperfecta, enamel is... |
-laminated, prismatic -resistant to caries
|
|

|
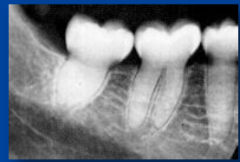
dentinogenesis imperfecta
-sometimes assoc. with osteogenesis imperfecta *with this, blue sclera, multiple fractures and scars (type 1) |
|
|
dentinogenesis imperfecta type 2 -bulbous crown, constricted at CEJ |
|
|
Talk about dentin dysplasia |
Rare -"rootless teeth"
type 1: -radicular
type 2: -coronal |
|
|
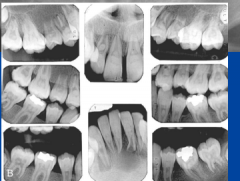
Type 1: dentin dysplasia |
-short roots, conical -ROOTLESS TEETH -W shape |
|
|
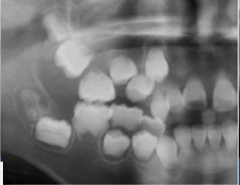
Type 2: dentin dysplasia |
-normal roots -pulp chambers flame-shaped |
|
|
dentin dysplasia type 1 -w roots |
|
|
dentin dysplasia type 2 -flame pulp |
|

|
dentin dysplasia type 2 |
|

|
regional odontodysplasia -large pulp chambers -thin enamel -ghost teeth |
|
|
Attrition clinical presentation |
-physiological wearing -wear facets -dentin exposure
pathologic: bruxism |
|
|
Attrition on Rx |
-shortened height -secondary dentin -widened pdl -sometimes hypercementosis |
|
|
Abrasion clinically and Rx |
-"v" shaped
rx = semi-circular shape with increasing r-opacity (white) |
|
|
Erosion clinical and Rx |
-chronic vomit/acid reflux -lingual and palatal surfaces affected -lesions look rounded on edges, smooth, glistening depressions on enamel |
|
|
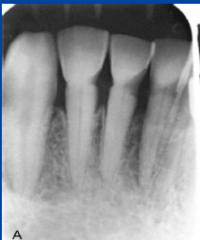
External resorption of tooth structure |
-root surface, involves dentin and cementum -smooth resorption, bone and lamina dura follow the resorbing root |
|
|
floss abrasion *appear as r-lucent grooves *if deep, obliteration of pulp and 2 dentin formation |
|

|
floss abrasion followed by 2 dentin formation -2 dentin formed by odontoblasts |
|

|
pulp stones; no tx |
|

|
hypercementosis |
|
|
Hypercementosis is assoc with? |
-pagets -hyperpituitarism (gigantism)
|
|

|
stafne bony defect (non-odontogenic) -mn lingual surface -usually below inf. alv. canal -usually at angle of mn
-aka dev. salivary gland defect |
|

|
stafne bony defect (non-odontogenic) -mn lingual surface -usually below inf. alv. canal -usually at angle of mn |
|

|
palatal tori/enostosis |
|

|
mandibular tori/inostosis |
|

|
condylar agenesis (condyle gone) |
|
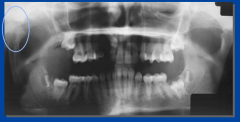
|
condylar hyperplasia |
|

|
bifid condyle |
|
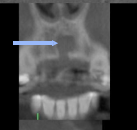
|
invasive canal cyst -well circumscribed -r-lucent
|
|

|
invasive canal cyst -well circumscribed -r-lucent |
|
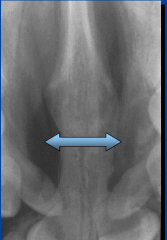
|
cleft palate -can be unilat. or bilat. |
|

|
cleft palate -w/ cleft, could see supernumerary teeth |
|

|
mx sinus agenesis |
|
|
Things to know about cleidocranial dysplasia |
1. delay in eruption of permanent teeth 2. SUPERNUMERARY TEETH 3. DENTIGEROUS CYSTS MAY DEVELOP |
|
|
Cleidocranial dysplasia pts look: |
-large head w/ frontal and parietal protuberance/bossing -skull flat/missing clavicle -high arche palate -small sinus -small maxilla |
|
|
Craniofacial dysplasia pts look: |
-beaten metal appearance -cranial markings; look like digital impression -early closure of sutures |
|

|
craniofacial dysplasia |
|
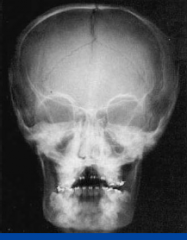
|
cleidocranial dysplasia |

