![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Deep Sulcus Sign
|
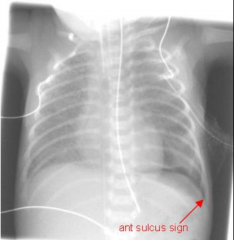
- Occurs in pneumothorax
- When lying supine, air goes to highest part in thorax --> deep sulcus. |
|
|
Aunt Minnie's Sign
|
Collapsed Lung - look at lateral
|
|
|
Obscured heart outlines
|
Pneumonia/involvement of right middle lobe or left upper lobe/lingula. Lower lobes do not obscure heart outlines.
|
|
|
Pneumomediastinum
|
Can be 2/2 small pleural bleb (spontaneous resolution), esophageal tear, pneumothorax, high inspiratory/expiratory pressures in asthma/COPD
|
|
|
Aortic Dissection
|
Type A - Ascending (requires surgery)
Type B - Descending |
|
|
D-Dimer
|
- Detects fibrinogen products
- Used most often for PE ddx - Very sensitive (negative result excludes PE) - Best in "healthy" outpatient patients |
|
|
V/Q Scan
|
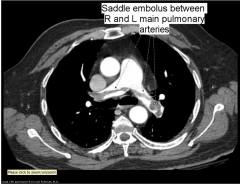
- Used to dx PE
- Performed by injecting technetium labeled macroaggregated albumin particles intravenously - these 'stick' in the smaller pulmonary capillaries and remain there for several hours until phagocytosed. Distribution of the particles provides us with a perfusion map of the lungs. |
|
|
Colonic Edema
|
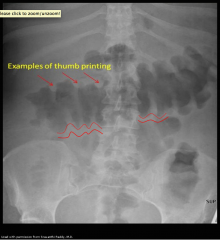
- "Thumbprinting" sign
- When colon wall thickened, protrudes into bowel. - IBD |
|
|
"Apple Core" Lesion
|
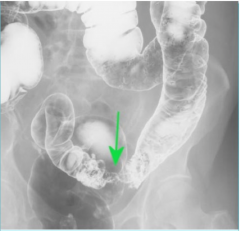
Seen in patients with colon carcinoma
|
|
|
SBO + Ileus
|
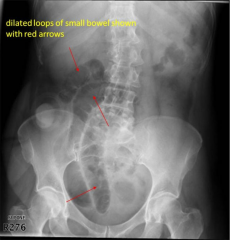
|
|
|
Gallstones
|
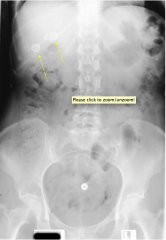
|
|
|
Kidney Stones
|
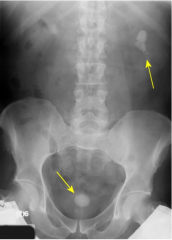
Non-contrast CT scan is the best modality. US better for pregnant patients.
|
|
|
Gallbladder + Cystic Duct
|
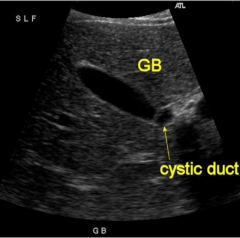
Normal cystic duct is 6 mm.
|
|
|
Pancreas + Surrounding Vasculature
|

|
|
|
Appendicitis
|
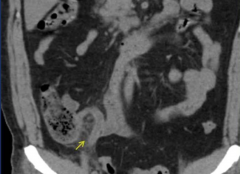
|
|
|
"Tram Tracking"
|
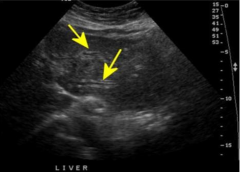
Dilated intrahepatic bile duct adjacent/parallel to portal vein branch.
|
|
|
MRCP
|
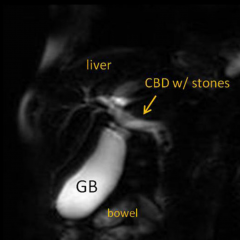
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreaticogram
|
|
|
ERCP
|
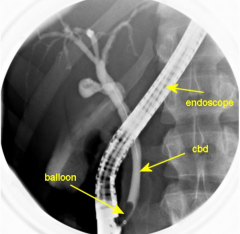
- Endoscopic Retrograde CholangioPancreaticogram
- More therapeutic than diagnostic |
|
|
Ultrasound > CT Scan
|
- Cheaper, faster, and can better visualize gallbladder wall thickening and stones within.
- Better for f/u of renal stone. |
|
|
CT Scan > Ultrasound
|
- Needed to visualize pancreatitis --> whenever you have painless jaundice.
- Gold standard of kidney stone eval. |
|
|
Acalculus Cholecystitis
|
- Inflammation of gallbladder w/o presence of stones.
- Associated with anorexia nervosa. |
|
|
Pancreatitis
|
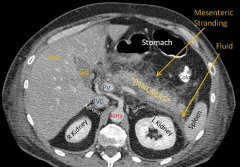
Associated with painless jaundice.
|
|
|
"Colon cut-off sign"
|
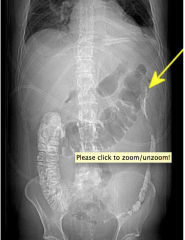
Inflammation from the pancreatitis causes inflammation and spasm of the adjacent bowel and may result in a partial pseudoobstruction at the splenic flexure.
|
|
|
Pancreatic Mass
|
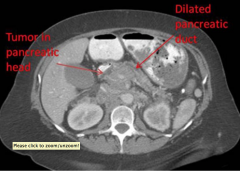
|
|
|
Renal Stone
|
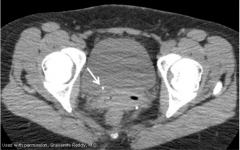
- On non-contrast CT, gold standard imaging modality.
- Located at the URETEROVESICULAR junction |
|
|
Renal obstruction coronal
|
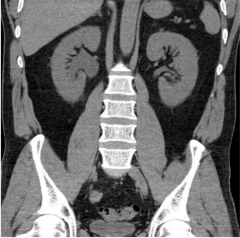
Right hydronephrosis, renal enlargement, and perinephric stranding.
|
|
|
Renal obstruction transverse
|
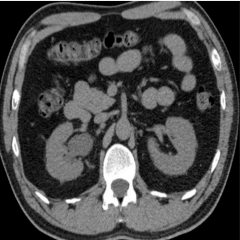
Right hydronephrosis, renal enlargement, and perinephric stranding.
|
|
|
Ureterovesicular Junction
|
Where ureter inserts into bladder.
|
|
|
Ureteropelvic Juntion
|
Where ureter inserts into renal pelvis
|
|
|
Ureteral Jets
|
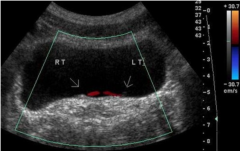
Doppler U/S shows urine jets from ureter into bladder bilaterally. Kind of like a cysto.
|
|
|
Pyelonephritis
|
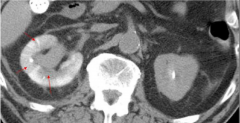
Image taken 8 minutes after contrast injection. Left kidney cleared it all, looks normal. Right, infected kidney retained the contrast and looks swollen. Arrows point to area of patchy/striated nephrogram. This is an UNcomplicated case.
|
|
|
Emphysematous Pyelonephrosis
|
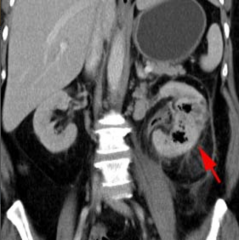
Requires drainage.
|
|
|
Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
|
- Occurs in up to 40% of patients with underlying renal failure (elevated creatinine levels)
- Prophylactic therapies include hella hydration and/or NaHCO3 and/or N-acetylcysteine - Acetylcysteine mechanism of action: scavenges O2-derived free radicals and improves endothelium vasodilatation. - Treat with supportive therapy |
|
|
Renovascular Hypertension
|
- Caused by increased renin release.
- More renin released because kidneys need higher forward pressure. - Kidneys often need higher forward pressure 2/2 renal artery stenosis. ie a vicious cycle. |
|
|
Renal Artery Stenosis
|
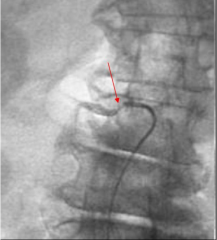
Diagnosed with angiogram
|
|
|
Hematuria
|
- Glomerular: with proteinuria = problem with the neprhron.
- Extraglomerular (isolated hematuria): without proteinuria = malignancy, stones, trauma, infection, meds. |
|
|
Renal Cyst U/S
|
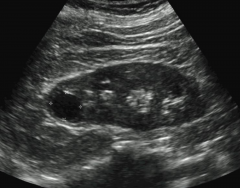
|
|
|
Renal Cyst CT
|
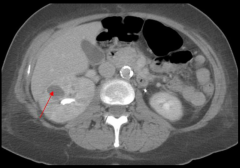
|
|
|
Simple Renal Cyst on U/S
|
- Anechoic (black)
- Round/oval - Increased through transmission - Smooth walls, no septations - No internal vascularity |
|
|
Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
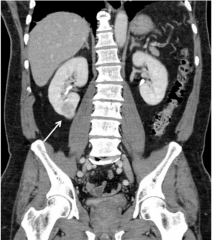
- Classic Triad: flank pain, hematuria, fnalk mass
- Surgery is main treatment |
|
|
Pelvic Trauma X-Ray
|
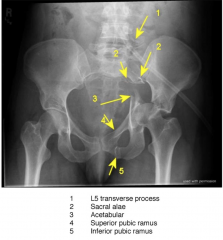
|
|
|
Chest Trauma CT
|
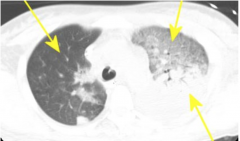
- Right lung normal.
- Left lung anterior = "ground glass" appearing contusion - Left lung posterior = atelectasis and effusion |
|
|
Abdominal Trauma CT
|
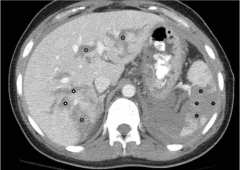
Stars = hematomas
|
|
|
Free abdominal gas
|
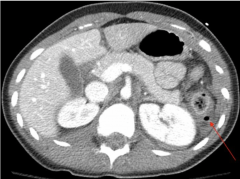
|
|
|
Duodenal Leak
|
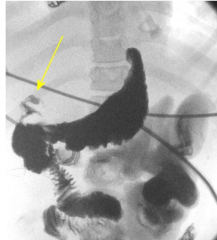
|
|
|
Bladder Rupture
|
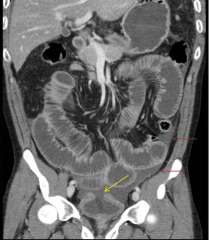
Yellow arrow shows rupture. Red arrows shows where urine leaked into abdomen.
|
|
|
Head CT w/o Contrast
|
Primary and 1st modality used for head trauma.
|
|
|
Epidural Hemorrhage
|
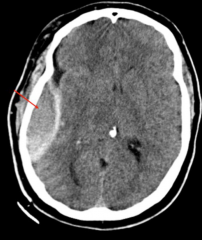
- Do NOT cross skull bone suture lines
- Arterial in origin (middle meningeal) - Patients lose consciousness, have lucid interval, then rapid decompensation. |
|
|
Subdural Hemorrhage
|
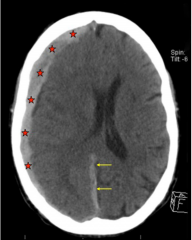
- Occur b/w dura and arachnoid.
- Due to tearing of bridging cerebral veins - Crescent shaped - Do NOT cross flax |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
|
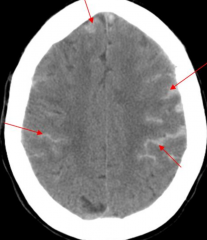
- Tearing of cerebral vessels
- Rupture of aneurysm or trauma or AVM - Lumbar puncture will show elevated opening pressure, elevated RBC count, and xanthochromia (pink tint) |
|
|
Clay Shoveler's Fracture
|
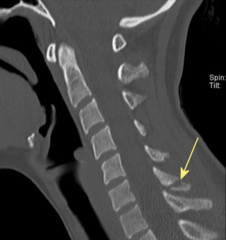
- Avulsion of spinous process 2/2 pulling from trapezius muscle.
- Treatment = pain meds and phys. therapy |
|
|
Decompensation 2/2 Brain Bleed Tx
|
- In epidural hemorrhage, you can get cerebral herniation and rebleed
- In subarachnoid, you can get vasospasm |
|
|
Brain Herniation 1
|
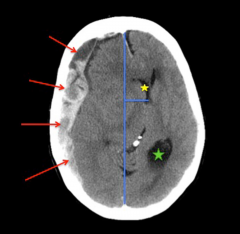
- Red arrows point to subdural collection
- Yellow star shows compressed RIGHT lateral ventricle - Blue line is midline and shift from - Green star shows dilated occipital horn of LEFT lateral ventricle |
|
|
Brain Herniation 2
|
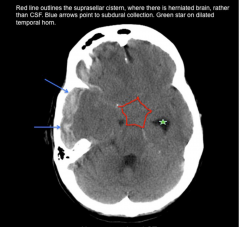
Suprasellar Cistern (in red) should be black/liquid... filled with brain.
Suprasellar cistern is where the cavernous sinus is? |
|
|
Brain Herniation Overview
|
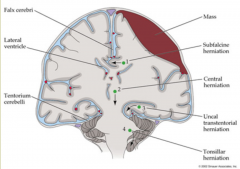
|
|
|
Diffuse Axonal Injury
|
White matter damage
|
|
|
Acute Subdural Hemorrhage
|
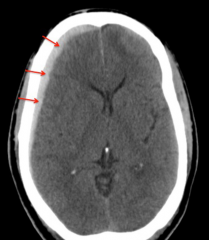
- < 3 days, generally hyperdense.
- Subacute (3 days-3 weeks) are isodense - Chronic ( > 3 weeks) are hypodense |
|
|
CT Angiography
|
Diagnosis and evaluation of aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
|
|
|
Lumbar Puncture
|
Should always follow a negative non-contrast CT scan in the setting of increased ICP headache.
|
|
|
Aneurysm Incidence
|
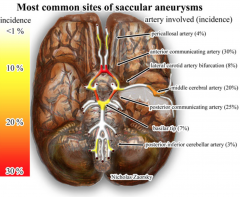
- Anterior Communicating (30%)
- Posterior Communicating (25%) - Middle Meningeal (20%) |
|
|
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage 2/2 ruptured aneurysm
|
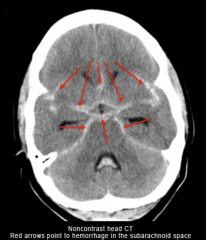
|
|
|
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
|
- Caused by JC Virus
- CD4 < 100 - Rapid demyelinating disease |
|
|
Neurocysticercosis
|
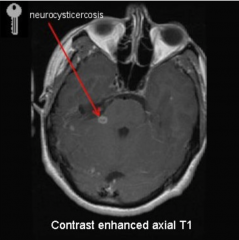
- No edema in imaging
- Infection from eggs of Taenia solum (pork tapeworm) - Eggs must be ingested independently of the actual tapeworm - infection by the latter only causes abdominal problems. |
|
|
Toxoplasmosis General
|
- Reactivation of Latent Disease
- Prophylactic treatment once CD4 < 100 |
|
|
Toxoplasmosis Imaging
|
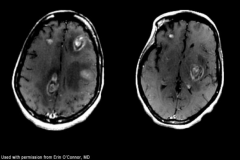
- Multiple lesions
- Abundant edema - Hyperintense center w/ T2 imaging - Involvement of deep gray matter (Basal Ganglia) |
|
|
Primary CNL Lymphoma
|
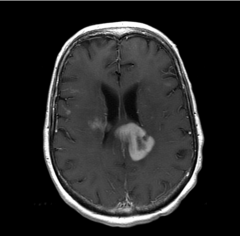
- Solitary lesion
- Subependymal (by ventricles) enhancement - Encasement of ventricles - Hypointense center w/ T2 imaging |
|
|
Pyogenic Absecess
|
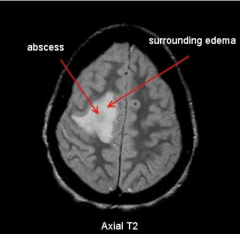
- Appears bright on diffusion weighted imaging
|
|
|
Cerebral Mets
|
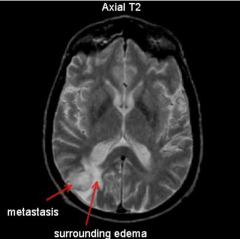
- Plenty of edema
|
|
|
Intussusception
|
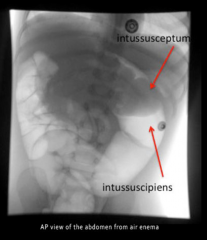
- Currant Jelly stools (stool mixed with mucous and blood).
- Paroxysms of pain - Vertically oriented mass - Treat and see with AIR ENEMA |
|
|
Upper GI Series
|
Fluoroscopic study that uses radio-opaque contrast to look at the entire GI tract.
|
|
|
Mid-Gut Volvulus
|
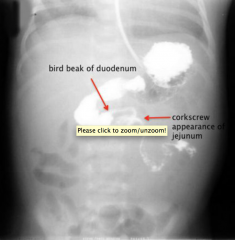
|
|
|
RSV
|
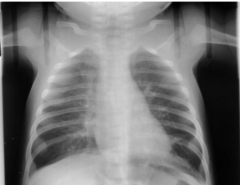
- Causes hyperinflation and perivascular markings
- Perivascular markings 2/2 bronchial wall thickening and edema. - Hyperinflation caused by peripheral air trapping when central airways collapse 2/2 edema. |
|
|
Torus (Buckle) Fracture
|
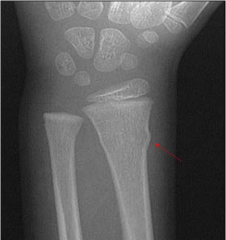
- 2/2 compressie force
|
|
|
Joint Effusion in Child
|
- Most common cause is transient synovitis
- Also consider septic arthritis |
|
|
Metaphyseal Corner Fracture (Bucket-Handle Fracture)
|
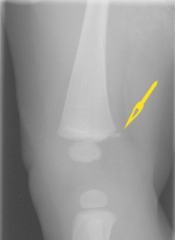
- Happens with shaking/grabbing
- Pathognomonic for child abuse - Other child abuse fractures: posterior ribs, humeral head dislocation, Type V salter harris fracture (crush fracture) |
|
|
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
|
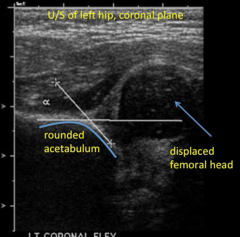
- Shallow acetabular development
- Predisposition to Subluxation and dislocation of hip - Ultrasound is best in 2 month olds because not enough calcifications yet for radiograph. |
|
|
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
|
- Seen in premature infants
- Gas gets trapped under submucosal layers of intestines and causes necrosis to mucosal layers |
|
|
Epiglottitis
|
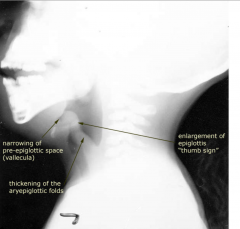
- Caused by HIB (Haemophilus influenzae type B)
|
|
|
Croup
|
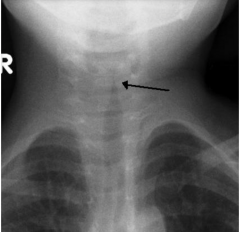
- Steeple Sign
- Subglottis infection |
|
|
Air Bronchogram
|
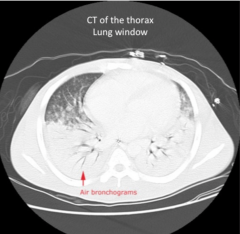
Visualizing the airways when the entire lung is consolidated 2/2 pneumo
|
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
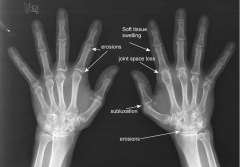
- Stiff joints in the morning
- MCP and PIP joint involvement - Swan neck and boutonniere deformities |
|
|
Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) Scan
|
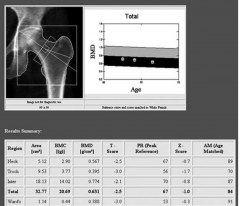
- Osteoporosis screening
- Can be used in osteopenia, too (precursor to osteoporosis). - T-score > -1 = normal. - T-score < -2.5 = osteoporosis |
|
|
Fibroadenoma
|
MCC of breast mass in women < 30
|
|
|
Hysterosalpingogram
|
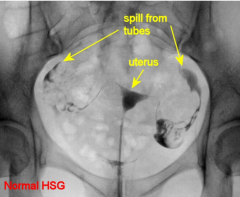
Fill uterus with contrast, let it pour through tubes. Will show you the contours of the uterus as well as the patency of the fallopian tubes.
|
|
|
Sonohysterogram
|
Fill uterus with saline and you can evaluate uterus for thickening... but you cannot see tube patency.
|
|
|
Breast Mass
|
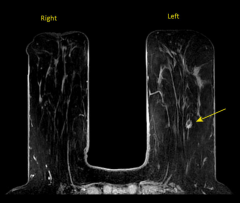
- First do ultrasound.
- If cystic, you're good. If not clear, do ultrasound guided core biopsy of mass. - If biopsy positive, do MRI to see if any other focal lesions present. |
|
|
Tamoxifen
|
- Anti estrogen receptor
- Increases risk of endometrial cancer and endometrial hyperplasia |
|
|
Ankle anatomy
|
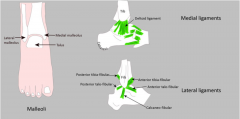
|
|
|
Injured Ankle
|
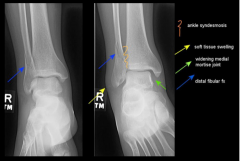
|
|
|
Fracture Adjectives
|

|
|
|
Knee Injury 1
|
|
|
|
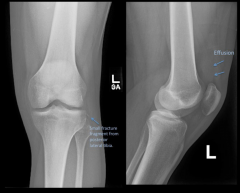
Knee Injury 2
|
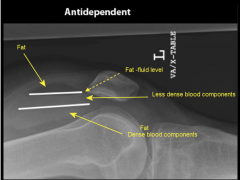
- Lipohemarthrosis (mixture of fat and blood within joint capsule 2/2 trauma)
- Intraarticular frature --> fat and blood released from marrow space |
|
|
MRI Normal Knee
|

|
|
|
Femoral Neck Insufficiency Fracture
|
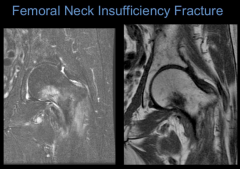
|
|
|
Right Wrist Fracture
|
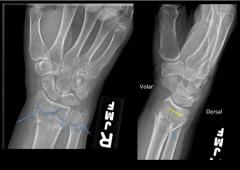
|
|
|
Hill-Sachs Fracture
|
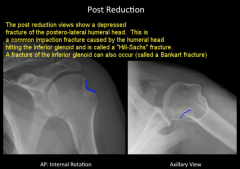
- During dislocation, happens when humeral head hits the glenoid
|
|
|
Elbow Injury
|
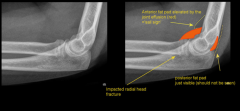
|

