![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Erection is due to parasympathetic stimulation via what nerve? |
Pelvic nerve - nitric oxide here causes vasodilation and blood fills penis |
|
|
Vagina muscles in wall cramp up when touched, and that's really painful, then they cramp more and become more painful. Vestibulitis is if you touch bartholin glands at opening of vagina and patients have a TON of bruning pain even though you're just touching (allodynia) |
Prevents cGMP breakdown that leads to corpus cavernosum smooth muscle relaxation, so the vessels fill |
|
|
Which nerve mediates the sympathetic response of sperm "emission" - where it moves from testes to the prostatic urethra? |
hypogastric nerve |
|
|
Which nerve involved with ejaculation? |
Pudendal nerve - ejaculation is sympathetic! |
|
|
Which ligament connects uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries to side wall? this ligament is ligated in hysterectomies |
Broad ligament |
|
|
Suspensory ligament connets the ovaries to the ____. The ovarian ligament connects the ovaries to the _____ |
Pelvic wall, uterus |
|
|
Which ligament contains uterine vessels? Which one contains ovarian vessels? |
Cardinal ligament, suspensory ligament of ovary |
|
|
Vagina histo? Cervix histo? Fallopian tubes? Ovary? |
Stratified squamous, simple columnar, ciliated columnar, simple cuboidal |
|
|
Pudendal nerve block occurs at ischial spine, happens during deliveries often |
Just know this |
|
|
Why is a vericocele more common on left rather than right scrotum? |
because right scrotom has less pressure b/c it brings blood RIGHT INTO IVC, left drains into left renal vein then IVC |
|
|
Ovaries and testes lymphatic draining into |
Para aortic lymph nodes |
|
|
Indirect inguinal hernia and direct hernia - relationship to inferior epigastric artery. How about femoral hernias? |
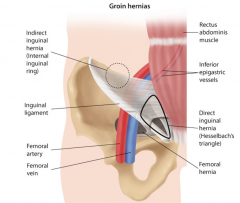
Indirect is lateral to this artery through inguinal ring. Direct hernia is MEDIAL to inferior epigastric artery through hesselbach's triangle (made up of inguinal ligament, lateral border of rectus abdominus, and inferior epigastric artery). FEMORAL HERNIAS below lignuinal ligament |
|
|
Mesonephric duct goes on to become male genitalia if acted on by testosterone. Paramesonephric duct (mullerian) makes female genitalia unless inhibited by mullerian inhibiting factor |
just know that |
|
|
If two paramesonephric ducts don't fuse, what happens? |
Bicornuate uterus - leads to infertility and stuff |
|
|
SRY gene codes for |
testis determining factor, which will make sertoli cells (which make MIF - mullerian inhibiting factor), Leydig cells - make testosterone (act on mesonephric ducts to make internal male genitals). Also makes 5 alpha reductase - converts testosterone to DHT which makes male external genitalia |
|
|
What is exstrophy of the bladder? What congenital condition is it associated with? |
Congenital gap in anterior bladder wall and abdominal wall infront of it. Interior of bladder is open to outside world
-Associated w/ epispadias |
|
|
Sertoli cells stimualted by ____. They secrete ____ , ____ and _____ |
FSH. Stroll cells secrete: 1. MIF 2. Inhibin (decreases FSH) 3. ABP - androgen binding protein (which maintains level of testosterone in seminiferous tubules to help maturation of spermatogonia) |
|
|
Finasteride what kind of drug? What do we use finasteride to treat?
--------------------- Flutamide is what kind of drug? What do we use flutamide to treat? |
Finasteride slowly reduces DHT levels, used to treat BPH ------------------ Flutamide is a competitive inhibitor at testosterone receptor and used in prostate cancer |
|
|
Ketoconazole and spironolactone used in PCOS, how does each work?
S/Es of these 2 drugs? |
Ketoconazole inhibits desmolase, Spiro inhibits steroid binding
S/Es: gynecomastia, amenorrhea |
|
|
Females with rudimentary vagina but 46 XY. Testes in labia majora
---------------
|
Androgen insensitivity - you don't have upper portion of vagina but you have lower portion, testes found in labia majora |
|
|
Hypogonadic gonadism with olfactory bulb defect |
Kallmann syndrome - female with primary amenorrhea or males with small testes |
|
|
High riding testis with long axis oriented weirdly with absent cremasteric reflex |
Testicular torsion |
|
|
Failure of testis to descend into scrotum |
Cryptorchidism |
|
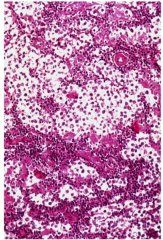
Testicular tumor with watery cytoplasm/fried egg appearance
(similar histologic appearance to oligodendrogliomas)
--------------------- Late mets & good prognosis |
seminoma |
|
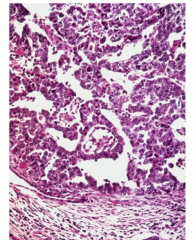
Malignant tumor with painful, palpable mass in the scrotum and eleveated hCG
Histology is more glandular |
Embryonal carcinoma |
|
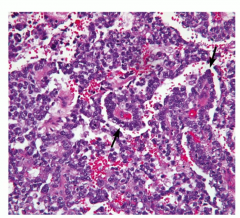
Most common testicular cancer in children < 3 Elevated AFP, with schiller-duval bodies in testes (look like glomeruli) |
Yolk sac tumor (aka aneodermal sinus tumor) |
|
|
Lab values: Which tumors have increased...
1. AFP 2. hCG ----------------------------------------------------
Teratomas in males vs teratomas in females |
1. AFP -- Yolk sac tumor 2. hCG -- choriocarcinoma, Embryonal carcinoma ----------------------------------------------------
Teratomas in males = MALIGNANT Teratomas in females = benign |
|
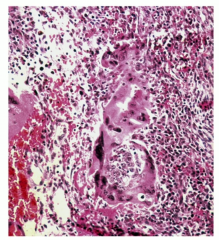
Testicular cancer, Elevated hCG , tumor of trophoblasts, can metastasize hematogenously |
Choriocarcinoma |
|
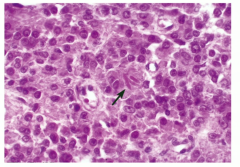
Ranke crystals, androgen producing tumors of testes and can cause gynecomastia or percocious puberty |
Leydig cell tumor (a non-germ cell tumor) |
|
|
These benign testicular tumors secrete estrogen and can cause gynecomastia, can be associated with puetz jeghers syndrome or carney syndrome |
Sertoli cell tumors (a non-germ cell tumor) |
|
|
Metastasis to testes, common in older men |
testicular lymphoma |
|
|
1. Fluid in scrotum due to incomplete fusion of processus vaginalis
--------------------- 2. Dilated epididymal ducts |
1. Hydrocele
---------------
2. Spermatocele |
|
|
Dilated veins in pampiniform plexus and can cause infertility with "bag of worms" fealing in scrotom |
Varicocele |
|
|
Spermatocele |
dilated epididymal duct |
|
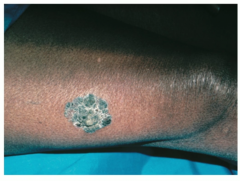
Greyish blue weird scap on genitalia that can progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma in some patients |
Bowen's disease |
|
|
Angulation/bent penis, painful erections |
Peyronie disease - due to inflammation and fibrous tissue formation of tunica albuginea |
|
|
Prostatitis in younger man?
Older man? |
Young people - think chlamydia/gonorrhea (sexual),
Older think UTI bugs (ecoli, kelbsiella, proteus, enterobacter).
Tx older people with fluoroquinolones and TMP/SMX |
|
|
How does prazosin/doxazosin/terazosin help with BPH?
Side effects of these drugs? --------------------------------
What is tamulosin? |
relaxes prostate smooth muscle and improves urine flow
S/Es: Dizziness, postural hypotension, fatigue --------------------------- Selective alpha1AD blocker
Fewer side effects than the -osins (nonselective alpha1 blockers)
Tamulosni does not affect the alpha1b receptors in blood vessels so you get NO antihypertensive effect |
|
|
Where does prostate cancer metastasize to commonly? How do you treat it? |
Bone (you'd see increased alk phos).
Treat with flutamide/resections
--Flutamide is a testosterone receptive competitive antagonist |
|
|
Estrone vs estradiol vs estriol
Remember the 1 + 2 = 3 (man + woman = baby) |
Estrone is made in periphery by fat cells via aromatase.
Estradiol - made in ovaries, abundant in women and gives women female characteristics.
Estriol found in placenta |
|
|
Which two layers of endometrium are shed during menstruation? |
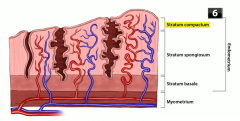
Stratum compactum and stratum spongiosum (but stratum basalis stays) |
|
|
What is mittelschmerz? |
Mid cycle pelvic pain associated with ovulation; caused by peritoneal irritation caused by serous fluid release |
|
|
Primary oocytes (diploid) arrested in ____ -------------------------------------------------------- Seconary oocytes (haploid) arrested in ____ |
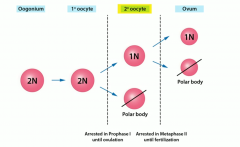
Prophase I until ____. ovulation
Metaphase II until ("egg MET sperm" |
|
|
Hormonal birth control supresses ovulation (because no LH surge occurs) and thickens cervical mucus (progesterone) and thins endometrium (progesterone) |
just know that |
|
|
Avoid OCPs in these women |
Patients with history of clot/stroke, smokers > 35, or those who have migraines with auras |
|
|
Clear cell adenocarcinoma of vagina with anatomic abnormalities of genital tract due to in utero exposure to |
DES - diethylstilbestrol |
|
|
This form of birth control is associated with bone mineral density loss, especially long term |
Medroxyprogesterone (depo-provera IM shot) |
|
|
IUDs are contraindicated in these patients |
STDs - because you can push the infection into the wall and cause it to spread |
|
|
Which vaginal wall tears correspond to a cystocele? Rectocele? Enterocele? |
(1) anterior wall, bladder bulges into vagina - cystocele. (2) Posterior wall - rectum bulges through - rectocele. (3) Tear at tope of vagina - small intestines bulge through, that's an enterocele |
|
|
What is vaginismus? what is vestibulitis? |
Vagina muscles in wall cramp up when touched, and that's really painful, then they cramp more and become more painful. Vestibulitis is if you touch skene ducts or bartholin glands at opening of vagina and patients have a TON of pain even though you're just touching (allodynia) |
|
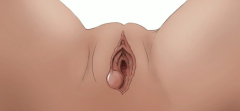
Balloon/ball of inflammation at opening of vagina? |
Bartholin duct or skene duct cyst
What do these glands do? -- vaginal lubrication production |
|
|
VIN? VAIN? |
Vulvar and vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia - very similar to CIN (all of these are pre-cancerous) but vulvular or vaginal. Associated with HPV (16, 18, 31, 33) |
|
|
HPV genes that can cause cancer? |
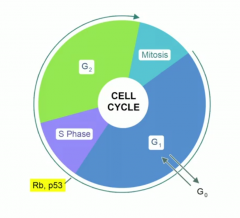
E6 and E7.
E6 - degrades p53, E7 inhibits Rb
|
|
|
What do you see on histology for CIN/VIN/VAIN? |
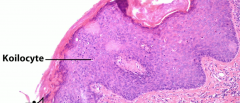
Koilocytes - look like a fried egg like oligodendrocytes
|
|
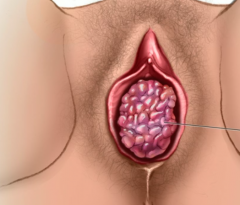
Vaginal cancer in girls < 4,
with spindle shaped cells and "grape like" appearance of tumor in vagina.
Also has positive desmin stain ------------------------------------------------- Associated w/ DES (synthetic estrogen) exposure in utero |
Sarcoma botryoides - these arise from bladder or vaginal wall
------------------------------------- Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina |
|
|
How does cervical cancer spread? What changes can you see w/ advanced disease? |
- Spreads locally
- Clinically staged
- Lateral invasion can block ureters, leading to renal failure |
|
|
Endometrial tissue found outside uterus? ---------------------------------------------------------
Chocolate cysts, severe pain related to menstruation |
Endometriosis
---------------------------------
Endometrioma or endometriosis in general |
|
|
Theories for endometriosis pathogenesis? |
Retrograde menstrual flow, hematologic/lymphatic spread, direct spread, or metaplasia |
|
|
Tx for endometriosis |
1. OCPs 2. Leuprolide (continuous GnRH agonist) as well 3. Danazol - mild androgenic medication to counteract estrogen and supress endometrial tissue |
|
|
Endometrial tissue found within myometrium? What is this and what would you see on histology? |
Adenomyosis - smooth muscle with endometrial glands inside of it on histology |
|
Benign smooth muscle tumor in uterus that is estrogen sensitive and have a whorl pattern on histology?
-Increased rates in black women
-Stain positive for design |
Leimyoma (fibroid)
-Either asymptomatic or can cause bleeding |
|
|
Tx for leimyomas? aka fibroids |
OCPS, leuprolide (continuous GNRH analog), ablation or hysterectomy |
|
|
Bulky, irregular shaped tumor with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage in uterus
Arises de novo
increased rates in black females
also stains positive for desmin stain |
Leiomyosarcoma |
|
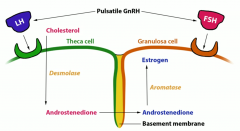
LH acts on theca cells to make ____ via _____ (enzyme). This product crosses over into granulosa cells through the basement membrane.
In the granolas cells, aromatase converts it to estradiol when activated by FSH |
Makes androstenedione from cholesterol via desmolase |
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for PCOS |
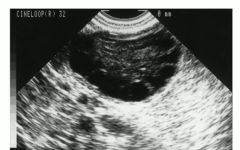
2 of the following 3 are necessary for diagnosis
- oligo/anovulation - hyperandrogenism, - polycystic ovaries on ultrasound |
|
|
Increased LH/FSH ratio |
PCOS
1. LH stimulates theca cells to make androgens (that's why you get hirsutism)
2. That stimulates estrogen production from granulosa cells (which feed back and inhbit FSH production) - that's why your ratio is greater (LH/FSH)
----------------
ANVOLUTION results from the dysregulation of these hormones |
|
|
Insulin resistance and obesity are also involved with PCOS - one of the mainstays of treatment is weight loss and metformin.
What do you use to treat hirsutism and estrogen overload? |
Spironolactone and OCPs or progesterone, or leuprolide in pulsatile fashion |
|
|
Clomiphene -- what's it used for? What's its mechansim of action?
Side effects? |
Clinical use: anovulation, PCOS
MOA: Partial agonist at estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus --> relatively decreases the negative feedback of estrogen, therefore increases FSH
Side effects: hot flashes, vision changes, ovarian hyperstimulation & enlargement |
|
|
CA-125 |
marker for ovarian cancer, but not specific, so mainly used to monitor disease |
|
|
Gene mutations associated with family history of ovarian cancer?
What are some additional risk factors? |
BRCA1, 2, and lynch syndrome
- Uninterrupted ovulatory cycles - Nulliparity |
|
|
What are the 4 categories of ovarian tumors? |
Epithelial, germ cell, stromal, and metastatic |
|
|
What are the types of epithelial ovarian tumors? |
Serous, mucinous, endometrioid, clear cell, Brenner, mixed |
|
|
Benign ovarian tumor/cyst lined by fallopian tube (ciliated) epithelium |
Serous cystadenoma |
|
|
Malignant ovarian tumor with psammoma bodies |
serous cystadenocarcinoma |
|
|
Ovarian tumor with cells that look like intestine, filled with mucine |
mucinous cystadenoma or cystadenocarcinoma |
|
|
Pseudomyxoma peritonei |
This is intraperitoneal mucinous material that characterizes mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, also seen with cancers of the appendix |
|
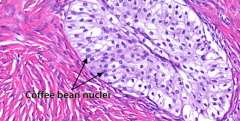
Ovarian tumor that's benign, solid, encapsulated, and looks like transitional epithelium of the bladder with "coffee bean" nuclei |
Brenner tumor |
|
|
What are the ovarian germ cell tumors? |
teratoma, dysgerminoma, endodermal sinus (yolk sac), and choriocarcinoma |
|
|
Teratoma in patients with hyperthyroid? Are teratomas in females benign or malignant? What about males? |
Struma ovarii teratoma - can have functional thyroid tissue in it
- Teratomas in men = malignant - Teratomas in women = benign |
|
|
Ovarian tumor equavalent of seminoma in males.
Made of undifferentiated germ cells - "sheets of uniform cells".
May produce LDH and hCG and associated with Turner syndrome |
Dysgerminoma |
|
|
Elevated AFP, with schiller-duval bodies in ovaries (look like glomeruli)
---------------------
Common site of mets for choriocarcinomas? |
Yolk sac tumor aka endodermal sinus tumor
----------------------------------
Lung |
|
|
What are the three types of stroma/sex cord ovarian tumors?
------------------------------------
|
Fibromas, granulosa-theca cell, sertoli-leydig cell
--------------------- Sertoli-leydig tumor details:
-Rare, large -Contain testicular structures that produce androgens --> virilization
|
|
|
Meig's syndrome |
Fibroma (benign ovarian tumor), ascities (fluid in abdominal cavity), and pleural effusion (hydorthorax) |
|
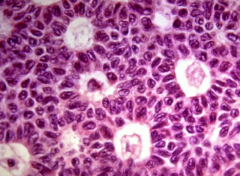
Call exner bodies - eosinophilic fluid-filled spaces between granulosa cells
Further clues: malignant, secretes estrogen/progesterone/inhibin
-can cause endometrial hyperplasia or percocious puberty |
Granulosa cell tumor |
|
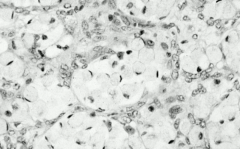
Musin-secreting signet ring cells in ovaries |
Krukenberg tumor metastasizing from GI (gastric cancer usually) |
|
|
Cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts - what do they do? |
They are the fetal component of the placenta.
Cytotrophoblasts are the inner layer and contain stem cells.
The syncytiotrophoblasts make bHCG and they're the outer layer, important for nutrient and waste transmission |
|
|
Decidua basalis |
Base layer of endometrium making up the maternal component of the placenta |
|
|
What is the urachus? What happens if it doesn't close? |
Connects fetal bladder to yolk sac. If it doesn't close you can have urine coming out of belly button, or outpouching of bladder into it |
|
|
What is the vitelline duct? What happens when it doesn't obliterate? |
Connects fetus midgut to yolk sac. If it doesn't obliterate, you get meckel diverticulum or a fistula to the belly button |
|
|
Trisomy 21 vs Trisomy 18 on quad fetal screening (AFP estriol and hCG - which ones are low and high in each?
------------------ Side note... what is the mCC of abnormal serum screening? |
In trisomy 18 - ALL ARE LOW
In trisomy 21, hCG is high, AFP & estriol are low ---------------------
MCC of abnormal serum screening is incorrect dating |
|
|
What would you see on quad screen (fetal testing) with neural tube defects, abdominal wall defects, or multiple gestations (twins)? |
Increased AFP |
|
|
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome happens when twins share a placenta - what is this? |
Anastamosis leads to shunting of blood - donor baby is anemic, pale, growth restricted. Recipient baby has polycythemia, fatter, and has heart failure |
|
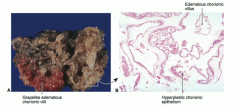
Edmeatous/grapelike chorionic villi are the buzzword for |
hydatiform mole pregnancy |
|
|
Complete vs partial hydatiform mole pregnancy |
Complete: 46xx or 46xy - REALLY REALLY HIGH hCG - Large uterus
Partial : 69xxy or xxx or xyy - not as high hCG - normal uterine size - can have some fetal parts - lower risk of choriocarcinoma or malignant trophoblastic disease |
|
|
Early uterine rupture is pathognumonic for |
Complete mole pregnancy |
|
|
"honeycomb" or "snowstorm" appearance of uterus on ultrasound |
Mole pregnancies |
|
|
what is placenta previa?
What's the worst type? How does this present and what's the "cure"? |
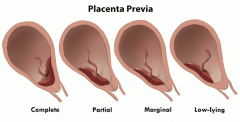
It's abnormal placement of the placenta.
Placenta attaches over or near the cervix so we can get a "preview" of the placenta in the cervical os
Complete is the worst, where it covers the cervix completely and baby can't be delivered through there - so have to do C section.
Mom's present with painless vaginal bleeding |
|
|
What is vasa previa? |
fetal blood vessels covering cervix - massive risk of fetal hemorrhage if these tear |
|
|
Painful vaginal bleeding in third trimester |
placental abruption - trauma/smoking/cocaine increase risk of this happening |
|
|
Why is fetal esophogeal or duodenal atresia associated with polyhydramnios?
Why is renal agenesis or posterior urethral valves associated with oligohydramnios?
------------------------------------------------------
Important association w/ polyhydramnios is: |
Normal flow of amniotic fluid goes out of the baby (pee) and is swallowed by the baby, so if you have esophogeal issues or atresia, you can't swallow it and it builds up.
If you can't pee it out, you have oligohydramnios
----------------------------------------------------
Maternal diabetes is a huge predisposing risk factor for polyhydramnios
|
|
|
Oligohydramnios, limb/facial deformities, and pulmonary hypoplasia |
Potter syndrome |
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for preeclampsia? For eclampsia? |
Preeclampsia - hypertension and proteinuria. Eclampsia = preeclampsia + seizures
----> see edema in face & upper extremities! (not diagnostic criteria, but a good tip) |
|
|
What is HELLP syndrome? |

**COULD SEE FIBRINOID NECROSIS IN PLACENTA VESSELS** |
|
|
Treatment for eclampsia? Side effects of this treatment?
|
Deliver baby and give IV magnesium sulfate for seizure risk
S/Es of Mg: - Decreased DTRs - Pulmonary edema - Altered mental status - Cardiac conduction defects |
|
|
Pathogenesis of gestational diabetes?
First line drug for gestational diabetes?
------------------------------------------------------------- Type I or Type II diabetes while pregnant are associated w/ which fetal anomalies? |
HPL - human placental lactogen - this is physiologically important because it increases maternal insulin resistance to leave more glucose in blood for baby, but when this is extreme, you get gestational diabetes.
Baby can have macrosomia and risk of stillbirth
First line -- try weight loss. Then use insulin
------------------------------------- - Congenital heart defects -- transposition of the great vessels - Neural tube defects - Caudal regression syndrome -- poor formation of the lower spine w/ problems in bladder control |
|
|
Positive hCG, abdominal pain like appendicitis during first trimester and vaginal bleeding |
Ectopic pregnancy -- where is most common location?
Fallopian tube
Symptoms?
- Occurs in 1st trimester - Positive hCG - Abdominal pain (b/c of bleeding)
Risk factors? ... anything that can cause scarring - Infertility - Salpingitis, PID - Ruptured appendix - Endometriosis - Prior tubal surgery |
|
|
Categories A, B, C, D, and X of drugs in pregnancy |
A - safe. B - presumed safety based on animal studies. C - no studies show adverse effect, D - human risk but benefits may outweigh risk, X - contraindicated, risk clearly outweights benefits |
|
|
Diseases in pregnancy and medications we use to treat - (1) Hypertension (2) Diabetes (3) Epilepsy (4) Hyperthyroidism (5) Anticoagulation |
(1) Hyertension - methyldopa, hydralazine, labetalol
(2) Diabetes - insulin
(3) Epilepsy - AVOID VALPROIC ACID, but can use anything else but supplement with increased folic acid to prevent neural tube defects
(4) Hyperthyroidism - PTU in 1st trimester, MMU in 2nd/3rd
(5) Anticoagulation - heparin or enoxaparin |
|
|
Tocolytics are used to delay pregnancy - what are these?
Which drugs do we usually give with these drugs? |
Indomethicin (cox inhibitor preventing stimulatory PGE formation),
Nifedipine - calcium channel blocker causes myometrial relaxation
Terbutaline, Ritrodine - B2 agonist on uterus and relaxes myometrium
Magnesium sulfate for seizure prophylaxis
-------- Give GCs (betamethasone, dexamethasone) to help increase fetal lung development |
|
|
What do you use to promote labor in somebody to help with contractions/cervical dilation? |
Prostaglandin anologs - dinoprostone, misoprostol and oxytocin |
|
|
Mifepristone - this is used in medical abortions with 2 other drugs - name those drugs and the mechanisms of action of all of them |
Synthetic steroid that's a competitive inhibitor of progesterone receptors
Used for abortions in addition to misoprostol (makes you contract) and methotrexate |
|
|
name the teratogenic properties of these drugs (1) Ace inhibitors, (2) aminoglycosides (eg gentamicin), 3 - Fluoroquinolones, 4- tetracyclines, 5- chlormphenicol, 6 - valproic acid, 7 - lithium, 8 - isotretinoin, 9 - DES (diethylstilbestrol), 10 - statins, 11 - thalidomide (used to treat multiple myeloma and other cancers) |
1) Ace inhibitors - renal malformations, (2) aminoglycosides (eg gentamicin - ototoxicity ), 3 - Fluoroquinolones - cartilage damage, 4- tetracyclines - discolored teeth , 5- chlormphenicol - gray baby syndrome, 6 - valproic acid - neural tube defects , 7 - lithium - ebstein anomaly, 8 - isotretinoin - spontaneous abortion or really bad birth defects (category X) , 9 - DES (diethylstilbestrol) - vaginal clear cell adenocarcinoma 10 - statins - CNS/limb defects 11 - thalidomide - limb defects , |
|
|
Which drugs can cause gynecomastia? |
Some Drugs Cause Awesome Knockers - Spiro Digoxin Cimetidine Alcohol (chronic) Ketoconazole |
|
|
Non-proliferative breast changes can either be |
Fibrosis - hyperplasia of breast stroma, or cysts (aka "blue dome cysts" - fluid filled) |
|
|
Caffeine and dietary fat can cause benign proliferative changes in breasts |
just know that |
|
|
Proliferative, benign, increased acini and intralobular fibrosis and calcifications without atypia in breast tissue |
Sclerosing adenosis |
|
|
Complex sclerosing lesion with radial scar on mammogram |
Looks like fat necrosis, scar with irregular shape, but it's benign but proliferative |
|
|
What are the three benign breast tumors to know? |
Fibroadenoma, Intraductal papilloma, Phylllodes tumor |
|
|
Small, firm breast tumor with regular edges. Mobile, common in women under 25, and increases in size with estrogen exposure |
Fibroadenoma - NOT a precursor for breast cancer |
|
|
Small breast tumor, benign (but small cancer risk) found inside of lactiferous ducts, and causes serous/bloody nipple discharge |
Intraductal papilloma |
|
|
Large benign bulky tumor of the breast with leaf like projections on histology |
Phyllodes tumor |
|
|
Most important prognostic factor of breast cancer? |
Lymph node involvement |
|
|
Two general types of breast cancer? |
Ductal - arises from duct epithelium, Lobular - arises from lobules (glands) |
|
|
DCIS - ductal carcinoma in situ - what are the subtypes? -------------------------------------
What is the characteristic finding of DCIS on mammography? |
(1) Comedocarcinoma - caseous necrosis, solid, cribiform, papillary, micropapillary
---------------------------- Dystrophic calcification |
|
|
Eczema-like patches on nipple and areola suggesting underlying carcinoma |
Paget disease of breast - assocated with UNDERLYING DCIS |
|
|
Signet ring cells in this breast cancer.
These cancers are ALWAYS ER+ and PR +
Relatively lower risk of progression to invasive carcinoma |
LCIS - lobular carcinoma in situ |
|
|
MC type of invasive breast cancer - Firm, rock hard, immobile breast mass with sharp margins, often arises from DCIS |
Invasive ductal carcinoma |
|
|
Generally multiple & bilateral Inactivation of E-cadherin genes, ER+ and PR+ breast cancer, and also has signet ring cells |
invasive lobular carcinoma |
|
|
What is tamoxifen? How does it work?
Tamoxifen activity in breast tissue vs endometrial tissue? |
Tamoxifen = selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
- Antagonist at ER in breast, - Agonist in endometrial tissue, so increases risk of endometrial cancer |
|
|
Alternative to tamoxifen - estrogen agonist in bone, antagonist in breast, and does NOT cause increased endometrial cancer risk |
Raloxifene |
|
|
Anastrozole is also used to treat breast cancer - how does this work? Who is it commonly used in and what side effect is it assocaited with? |
Inhibits aromatase -- thus inhibiting production of estrogen
Used in post menopausal women with breast cancer.
Side effect - osteoperosis due to antagonistic effect on bones |
|
|
MC breast tumor in women under 25 |
Fibroadenoma |
|
|
MC breast mass in postmenopausal women |
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma |
|
|
MC breast mass in premenopausal women |
Fibrocystic change of the breast |
|
|
Loss of e-cadherin adhesion gene on chromosome 16 |
Invasive lobular carcinoma |

