![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Salmonella Shigella Agar
|
Salmonella Shigella Agar is a modification of the Desoxycholate Citrate Agar described by Leifson.
Is a selective and differential medium widely used in sanitary bacteriology toisolate Salmonella and Shigella from feces, urine, and fresh and canned foods. |
|
|
Salmonellosis
|
Typhoid fever, caused by Salmonella typhi, ischaracterized by fever, headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and can result in fatal respiratory, hepatic, andor neurological damage.1This infection can result from the consumption of raw, undercooked, or improperlyprocessed foods contaminated with Salmonella spp.
|
|
|
Shigellosis
|
caused by Shigella spp., is an intestinal illness characterized by abdominal pain, fever, and watery diarrhea. When associated with outbreaks, shigellosis is usually transmitted through contaminated food and/or water.
|
|
|
Why it is superior |
Salmonella Shigella Agar is superior to a number of other media for the isolation of Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp.
|
|
|
Recommended for
|
Salmonella Shigella Agar is recommended for testing clinical specimens and food testing for the presence of Salmonella spp and some Shigella spp
|
|
|
Principle of media |
The basis for differentiation on SS Agar depends on the fermentation of lactose and the absorption of neutral red as the bile salts precipitate in the acidic condition.
Neutral red turns red in the presence of an acidic pH, thus showing fermentation has occurred. The inclusion of bile salts, sodium citrate, and brilliant green serve to inhibit gram-positive and coliform organisms. Sodium thiosulfate is added to the medium as a hydrogen sulfide source, and ferric citrate is added as an indicator for hydrogen sulfide production. |
|
|
Media Composition |
Beef Extract - 5 g
Enzymatic Digest of Casein - 2.5 gEnzymatic Digest of Animal Tissue - 2.5 g Lactose - 10 g Bile Salts 8.5 g Sodium Citrate - 8.5 gSodium Thiosulfate -8.5 gFerric Citrate - 1 g Brilliant Green - 0.00033 g Neutral Red - 0.025 g Agar - 13.5 g |
|
|
Final pH
|
7.0 ± 0.2 at 25oC
|
|
|
Precaution |
While make media Don't autoclave ,Heat with frequent agitation and boil for one minute to completely dissolve the medium. Due to its strong inhibitory power, SS Agar can be streaked with a heavy inoculum |
|
|
Expected Result |
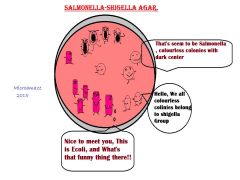
Salmonella spp and Shigella spp arenon-lactose fermenters and form colorless colonies on Salmonella Shigella Agar.
H2S positive Salmonellaspp produce black-center colonies. Some Shigella spp. are inhibited on Salmonella Shigella Agar. E. coliproduces pink to red colonies and may have some bile precipitation. |
|
|
Limitations |
Salmonella Shigella Agar is highly selective and not recommended as the primary isolation of Shigella. Some Shigella spp. may be inhibited.
A few nonpathogenic organisms may grow on Salmonella Shigella Agar. These organisms can bedifferentiated by their ability to ferment lactose and other confirmatory tests. |
|
|
For more information |
microamaze.blogspot.com
|

