![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
194 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The distinction between goods and services is not always perfectly clear but their primary difference is the property of ______. |
intangibility |
|
|
It is defined as objects, devices, or things. |
Goods |
|
|
a ______ implies that the consumer's benefits contained nothing but components supplied by service. |
pure good |
|
|
It is defined as deeds, efforts, or performances. |
Services |
|
|
a _____ contains no tangible elements. |
pure service |
|
|
It refers to both goods and services |
Products |
|
|
Reflects the view that the intangible aspects of products are becoming the key features that differentiate products in the marketplace |
Service Imperative |
|
|
The scale that displays a range of products along a continuum based on their tangibility. |
Scale of Market Entities |
|
|
Goods that possess physical properties that can be felt, tasted, and seen prior to the consumer’s purchase decision. |
Tangible Dominant |
|
|
Services that lack the physical properties that can be sensed by consumers prior to the purchase decision. |
Intangible Dominant |
|
|
There is no such thing as a pure good or pure service. True or False |
True |
|
|
Condition of firms that produce tangible products and overlook the service aspects of their products. |
Service Marketing Myopia |
|
|
A conceptual model of the relationship between the tangible and intangible components of a firm's operations. |
Molecular Model |
|
|
_______ products, goods "knowledge" is obtained by focusing in on the physical aspects of the product itself. |
Tangible dominant |
|
|
It provides the direction necessary for service companies to create a compelling service experience. |
Servuction Model |
|
|
Is improved through the actual service itself, through the experience of receiving it. In the end, when a customer when someone pays for a service, they are really paying for an experience! |
Service Knowledge |
|
|
Is the encapsulation of the benefits of a product in the consumer's mind |
The Benefit Concept |
|
|
The use of physical evidence to design service environments. |
The Servicescape (Visible) |
|
|
other than the primary service provider who briefly interact with the customer. |
Contact personnel |
|
|
the primary providers of a core service. |
Service providers |
|
|
Economies throughout the world tend to transition from an agricultural economy to an industrial economy. |
The growth of the global service economy |
|
|
According to _________, ______ is an electronic service available via the net that completes tasks, solves problems, or conducts transactions. |
Hewlett Packard e-service |
|
|
It plays a critical role in the transformation of the customer's online experience that progresses over time from a functional experience to a more personalized experience. · |
E-service |
|
|
It humanizes the net by providing various customer service activities while simultaneously reducing the online firm's operating costs. |
E-service |
|
|
Technologically based services that help customers help themselves. |
Self-service technologies |
|
|
The ability to meet current needs without hindering the ability to meet the needs of future generations in terms of economic, environmental, and social challenges. |
Sustainability |
|
|
Eco-efficiency focuses on the concept of the "__________." |
double dividend |
|
|
It includes the “soft parts” of the economy consisting of nine industry supersectors. |
Service economy |
|
|
The _____ sector includes schools, colleges, universities and training centers. |
educational services |
|
|
The ___________ sector is comprised of health services such as hospitals, nursing care facilities, physician’s offices and home health care services. |
health care and social assistance |
|
|
The ______ supersector consists of the banking and insurance subsector, as well as securities, commodities, and other investments |
financial activities |
|
|
The _________ supersector consists of three subsectors: advocacy, grantmaking, and civic orgnaizations; the federal government; and state and local government. |
government |
|
|
The ________ supersector consists of establishments that produce and distribute information and cultural products, provide the means to distribute or transmit these products and/or process data. |
information |
|
|
The _________ sectors are comprised of three subsectors: the arts, entertainment, and recreation subsector; food services and drinking places; and hotels and other accommodations. |
leisure and hospitality |
|
|
The _______ supersector is compromised of advertising and public relations services; computer systems design and related services; employment services, management, scientific, and technical consulting services; and scientific research and development services. |
professional and business services |
|
|
It consists of three subsectors: (1) air transportation; (2) truck transportation and warehousing; and (3) utilities. |
Transportation and warehousing and utilities |
|
|
The __________ supersectors consists of the wholesale trade subsector and the retail trade subsector which include: automobile dealers; clothing, accessory, and general merchandise stores; and grocery store. |
wholesale and retail trade |
|
|
Belief that without manufacturing there will be less for people to service and so more people available to do less work. |
Materialismo Snobbery |
|
|
The rich get richer and poor get poorer. |
Dichotomization of Wealth |
|
|
Branch of philosophy dealing with what is good and bad and with moral duty and obligation. |
Ethics |
|
|
Comprises moral principles and standards that guide behavior in the business world. |
Business ethics |
|
|
The distinction between ordinary decision and an ethical one is that values and judgement plays critical role in ethical decision, Ordinary decision are generally decided utilizing a set of preordained acceptable rules. |
Business ethics |
|
|
complicates the consumer's ability to evaluate objectively the quality of service provided. |
Intangibility |
|
|
reflects the difficulty in standardization and quality control. |
Heterogeneity |
|
|
reflects the human element involved in the service delivery process. |
Inseparability |
|
|
search attributes can be determined prior to purchase and include such attributes as touch, smell, visual cues, and taste. However, due to the intangibility of services, consumers of services often must base their purchase decisions on information provided by the service provider. |
Few search attributes |
|
|
Customers often resort to evaluating information that surrounds the service as opposed to the core service itself when forming evaluations since there is little to no information. |
Technical and specialized services |
|
|
service providers may not be held accountable for their actions in the short run. This could lead to a scenario where unethical service providers may maximize their short-term gains at the expense of consumers' long-term benefits. |
Time lapse between performance and evaluation |
|
|
when the consumer experiences difficulties with an unscrupulous provider, there are few or no means of seeking quick retribution. |
Service sold without guaranties and warranties |
|
|
many service providers deliver their services outside their firm, these particular service providers often are not under direct supervision and may act in a manner inconsistent with organizational objectives. |
Services performed by boundary-spanning personnel |
|
|
Many services are customized, requiring different skills of the service provider, and often consumers are exposed to different providers within the same firm. The bottom line is that variability in performance is unavoidable. |
Accepted variability in performance |
|
|
The reward system of an organization often dictates the behavior of its employees, this may encourage, albeit unintentionally, the unethical conduct of its employees. |
Outcome-Based Reward System |
|
|
consumers often feel that they didn't explain themselves clearly enough and will accept much of the blame to avoid a confrontation with the service provider, this situation further removes service providers from taking responsibility for their own actions. |
Consumer Participation in Production |
|
|
Service providers are often in close proximity to customers during the provision of services. |
Conflict of interest |
|
|
Service providers from working organizational relationships with a variety of role partners, including customers, suppliers, peers, subordinates, supervisors, and others. |
Organizational Relationships |
|
|
is a partner of truthfulness, integrity, and trustworthiness. |
Honesty |
|
|
is an outcome of just treatment, equity, and impartiality. |
Fairness |
|
|
Ethical issues also arise through the communication that the service organization releases to the public. |
Communication |
|
|
It refers to the process through which an individual adapts and comes to appreciate the values, norms, and required behavior patterns of an organization. |
Employee socialization |
|
|
As part of the socialization process, formal standards of conduct can be presented to service employees through a code of ethics |
Standards of Conduct |
|
|
mother of all unique differences |
Intangibility |
|
|
distinguishing characteristic of services that makes them unable to be touched or sensed in the same manner as physical goods. |
Intangibility |
|
|
the inter connection of service participant |
Inseparability |
|
|
reflects the interconnection among the service provider, the customer involved in receiving the service, and other customers sharing the same service experience. |
Inseparability |
|
|
the variable of service delivery |
Heterogeneity |
|
|
is the consistency of the service that has been given to the customer to one another |
Heterogeneity |
|
|
Balancing supply & demand |
Perishability |
|
|
reflects the challenge that services cannot be saved; their unused capacity cannot be reserved and cannot be inventoried. |
Perishability |
|
|
The ________ stage of the consumer decision process refers to all consumer activities occurring before the acquisition of the service. This stage begins when an individual receives a stimulus that incites a consumer to consider a purchase. |
prepurchase stage |
|
|
the thought, action, or motivation that incites a person to consider a purchase. |
Stimulus |
|
|
An event or motivation that provides a stimulus to the consumer and is a promotional effort on the part of the company. |
Commercial cue |
|
|
An event or motivation that provides a stimulus to the consumer, obtained from the individual’s per group or from significant others. |
Social cue |
|
|
A motivation, such as thirst, hunger, or another biological cue that provides a stimulus to the consumer. |
Physical cue |
|
|
The second phase of the prepurchase stage, in which the consumer determines whether a need exists for the product. |
Problem awareness |
|
|
The need for a product or service due to the consumer’s not having that particular product or service. |
Shortage |
|
|
The need for a productor service due to a consumer’s dissatisfaction with a current product or service. |
Unfulfilled desire |
|
|
The phase in the prepurchase stage in which the consumer collects information pertaining to possible alternatives |
Information search |
|
|
The set of alternatives of which a consumer is aware |
Awareness set |
|
|
An Alternatives that the consumer actually remembers at the time of decision making |
Evoked set |
|
|
A made up of the brands that are taken seriously by the consumer in his or her purchase decision. |
Consideration set |
|
|
A passive approach to gathering information in which the consumer’s own memory is the main source of information about a product. |
Internal search |
|
|
A proactive approach to gathering information in which the consumer collects new information from sources outside the consumer’s own experience. |
External search |
|
|
the prepurchase stage in which the consumer places a value or “rank” on each alternative |
Evaluation of alternatives |
|
|
Choosing among alternatives in a random fashion or by a “gut-level feeling” approach |
Nonsystematic evaluation |
|
|
Choosing among alternatives by using a set of formalized steps to arrive at a decision. |
Systematic evaluation |
|
|
A systematic model that proposes that the consumer creates a global score for each brand by multiplying the rating of the brand on each attribute by the importance attached to the attribute and adding the scores together. |
Linear compensatory approach |
|
|
A systematic model also known as “lazy decision makers” that try to minimize the effort involved. proposes that the consumer make a decision by examining each attribute, starting with the most important, to rule out alternatives. |
Lexicographic approach |
|
|
This decision is accompanied by a set of expectations about the performance of the product to be purchased. In the case of goods, the consumer then uses the product and disposes of any solid waste remaining. |
Choice |
|
|
During this stage, consumers may experience varying levels of cognitive dissonance doubt that the correct purchase decision has been made. Marketers often attempt to minimize the consumer’s cognitive dissonance by reassuring the customer that the correct decision has been made. |
Post purchase evaluation |
|
|
In contrast to consumers when purchasing goods, consumers of services tend to perceive a higher level of risk during the prepurchase decision stage. |
Perceived risk |
|
|
The possibility of a monetary loss if the purchase goes wrong or fails to operate correctly. |
financial risk |
|
|
The possibility that the item or service purchased will not perform the task for which it was purchased. |
performance risk |
|
|
The possibility that if something does go wrong, injury could be inflicted on the purchaser. |
physical risk |
|
|
The possibility of a loss in personal social status associated with a particular purchase. |
social risk |
|
|
The possibility that a purchase will affect an individual’s self-esteem. |
psychological risk |
|
|
Much of the heightened level of perceived risk can be attributed to the difficulty in producing a standardized service product. |
Risk and Standardization |
|
|
The involvement of the consumer in the “production process of services” is another source of increased perceived risk. |
Co-Producer Risk |
|
|
Others have argued that the higher levels of risk associated with service purchases is due to the limited information that is readily available before the consumer makes the purchase decision. |
Risk and Information |
|
|
Product attributes that can be determined prior to purchase. |
Search attributes |
|
|
Product attributes that can be evaluated only during and after the production process. |
Experience attributes |
|
|
Product attributes that cannot be evaluated confidently even immediately after receipt of the good or the service. |
Credence attributes |
|
|
Brand loyalty is based on the degree to which the consumer has obtained satisfaction in the past. If consumers have been satisfied in the past with their supplier of service, they have little incentive to risk trying someone or something new. |
Risk and Brand Loyalty |
|
|
the time costs associated with seeking out new alternatives. |
Search costs |
|
|
the monetary costs associated with first time visits, such as new x-rays when changing dentists. |
Transaction costs |
|
|
costs such as time and money that are associated with learning new systems, such as new versions of software packages. |
Learning costs |
|
|
Costs that can accrue when changing one service provider to another. . |
Switching costs |
|
|
costs in terms of the time it takes simply thinking about making a change in service providers. |
Loyal customer discounts |
|
|
costs associated with changing established behavior patterns. |
Customer habit |
|
|
the emotional turmoil that one may experience when severing a long-term relationship with a provider. Emotional costs are particularly high when a personal relationship has developed between the client and the provider. |
Emotional costs |
|
|
costs in terms of the time it takes simply thinking about making a change in service providers. |
Cognitive costs |
|
|
The consumption of goods can be divided into three activities: |
buying using and disposing. |
|
|
The post purchase evaluation of services is a complex process. It begins soon after the customer makes the choice of the service firm he or she will be using and continues throughout the consumption and post consumption stages. The evaluation is influenced by the unavoidable interaction of a substantial number of social, psychological, and situational variables. |
Post choice |
|
|
The theory proposing that consumers evaluate services by comparing expectations with perceptions. |
The Expectancy Disconfirmation Theory |
|
|
A model in which consumers evaluate services by the amount of control they have over the perceived situation. |
The Perceived-Control Perspective |
|
|
All the World’s a Stage and All the People Players - A psychology and sociology can be brought together in the ideas of a script. |
The Script Perspective |
|
|
argues that rules, mostly determined by social and cultural variables, exist to facilitate interactions in daily repetitive events, including a variety of service experience. |
script Perspective |
|
|
occurs when the actual scripts performed by customers and staff are consistent with the expected scripts. |
script congruence |
|
|
Understand the potential business impact of a problem with your products. Make sure that services are available to provide an appropriate level of response to minimize impact on customer's business. Assess the needs addressed by current offerings to determine if an opportunity exist to provide extended service coverage and if so at what price. |
Available for Service |
|
|
After maintaining a sheltered existence in stage 1, a service firm may face competition and may be forced to re-evaluate its delivery system. |
Journeyman |
|
|
Senior managers of firms in stage 3 have a vision of what creates value for the customer, and they also understand the role that operations managers must play in delivering the service. |
Distinctive Competencies Achieved |
|
|
Not satisfied with just meeting customer expectations, world class firms expand on these expectations to levels that competitors find it difficult to meet. World class service firms define the quality standards by which others are judged. Sustaining superior performance throughout the delivery system is a major challenge. |
World-class service delivery |
|
|
Thompson introduced the idea of a ________ the place within an organization where its primary operations are conducted. |
technical core |
|
|
In this model, efficiency is possible only if inputs, outputs, and quality happen at a constant rate and remain known and certain. |
Thompson's Perfect World Model |
|
|
• An operation that concentrates on performing one particular task in one particular part of the service experience. • Used for promoting experience and effectiveness through repetition and concentration on one task necessary for success. |
The Focused Factory Concept |
|
|
The strategy of breaking up large, unfocused activities into smaller units buffered from one another so that each can be focused separately. |
The Plant-Within-a-Plant Concept |
|
|
surrounding the technical core with input and output components to buffer environmental influences. |
Buffering |
|
|
managing the environment to reduce fluctuations in supply and/or demand. |
Smoothing |
|
|
mitigating the worst effects of supply and demand fluctuations by planning for them. |
Anticipating |
|
|
direct allocations of inputs and outputs when the demands placed on a system by the environment exceed the system's ability to handle them |
Rationing |
|
|
The servuction system itself is an operations nightmare. Customers do not arrive one at a time to be immediately processed. All too often, customers arrive in bunches resulting in wait times that are not characteristic of a peak efficiency model. |
Applying Efficiency Models to Service Firms |
|
|
Within the operations management and marketing literatures of the past decade, a growing list of strategies has emerged regarding overcoming some of the problems of service operations. |
Operations Solutions for Service Firms |
|
|
proposes the clear separation of the servuction system (the part of the service operation where the customer is present) |
Isolating The Technical Core |
|
|
The use of physical barriers, such as a well-placed counter in a service establishment, enable service providers to separate high contact areas where effectiveness is maximized from the technical core where operational efficiency is the major goal. |
Isolating The Technical Core |
|
|
Disassociating the technical core from the servuction system. |
Decoupling |
|
|
A second possible solution to tackle the operations problems of service firms involves production-lining the whole system. |
Production-lining the whole system |
|
|
is the application of hard and soft technologies to a service operation in order to produce a standardized service product |
Production-line approach |
|
|
The third method to effectively manage service operations is used to minimize the effects of variable demand |
Creating Flexibility Strategy |
|
|
A fourth approach to managing service operations involves increasing the customer's involvement with the service operation itself. |
Increasing customer participation |
|
|
Another strategy utilized to optimize the efficiency of service operations is the attempt to shift the time of demand to smooth the peaks and valleys associated with many services. |
Moving the time of demand to fit capacity |
|
|
It has the most direct effect on profitability and is the most easily controlled element of the marketing mix. |
price |
|
|
remains one of the least researched and mastered areas of marketing. |
Price |
|
|
The worth assigned to the product by the customer. |
Product Value |
|
|
The worth assigned to the service by the customer. |
Service Value |
|
|
The worth assigned to the service-providing personnel by the customer. |
Personnel Value |
|
|
The worth assigned to the image of the service or service provider by the customer. |
Image Value |
|
|
The actual money price paid by the consumer for a product. |
Monetary Cost |
|
|
The time the customer has to spend to acquire the service. |
Time Cost |
|
|
The physical energy spent by the customer to acquire the service. |
Energy Cost |
|
|
The mental energy spent by the customer to acquire the service. |
Psychic Cost |
|
|
• Service pricing is not finalized until after provision. • Cost-based pricing is more difficult for services. • Service industries are often characterized by a high fixed cost to variable cost ratio that leads to pricing challenges. • Mass production = limited economies of scale. • Many services are often customized based on the capacity of the customers. |
Cost consideration |
|
|
• Service demand tends to be inelastic than the demand for goods. • Cross-price elasticity considerations need to be examined. • Price discrimination – variable practice for managing demand and supply challenges. |
Demand Consideration |
|
|
• Service demand tends to be inelastic than the demand for goods. • Cross-price elasticity considerations need to be examined. • Price discrimination – variable practice for managing demand and supply challenges. |
Demand Consideration |
|
|
• Price tends to be one of the few cues available to consumer during prepurchase. • Service consumers are more likely to use price as a cue to quality. • Service consumers tend to be less certain about reservation prices. |
Customer consideration |
|
|
• Comparing prices more difficult for service consumers. • Self-Service = competitive alternative. |
Competitive Consideration |
|
|
• Price bundling is more complicated. • Price bundling is more effective in the service business area. |
Profit Consideration |
|
|
• Different price names in the service sector. • Consumers are less able to stockpile services by taking advantage of discount prices. • Product-line are more complicated to price. |
Product Consideration |
|
|
legal pricing is an opportunity for services than goods. |
Legal Considerations |
|
|
Due, to the many special considerations surrounding the pricing of services. traditional pricing strategies such as penetration prism, competitive pricing. and premium pricing may offer little benefit to service customers or service provider. True or False |
True |
|
|
The primary goal of ________ is to reduce the amount of perceived risk |
satisfaction-based pricing |
|
|
associated with the service purchase and appeal to target markets that value certainty. |
Satisfaction-based pricing |
|
|
can be achieved through offering guarantees, benefit-driven pricing, and flat-rate pricing |
Satisfaction-based pricing |
|
|
Focuses on the aspects of the service that customers actually use. The objective of this approach is to develop a direct association between the price of the service and the components of the service that customers value. |
Benefit-Driven Pricing |
|
|
Is fairly straightforward. Its primary objective is to decrease consumer uncertainty about the final price of the service by agreeing to a fixed price before the service transaction occurs. With _______, the provider assumes the risk of price increases and overruns. |
Flat-rate pricing |
|
|
The primary objective of _______is to enhance the firm's relationship with its targeted consumers. |
relationship pricing |
|
|
It is generally defined as a contract for the construction, installation, building, or manufacturing of property that begins in one year and is completed in a later tax year. |
long-term contracts |
|
|
a marketing strategy that combines two or more products to sell them at a lower price than if the same products were sold individually. |
Price bundling |
|
|
It enables consumers to either buy Service A and Service B together or purchase one service separately. |
mixed bundling |
|
|
The primary goal of _______ is to appeal to economically minded consumers who are looking for the best price. |
efficiency pricing |
|
|
It focuses on delivering the best and most cost-effective service available for the price. Operations are streamlined, and innovations that enable further cost reduction become part of the operation's culture. |
Efficiency pricing |
|
|
communicates the firm's positioning strategy to its target markets, including consumers, employees, stockholders, and suppliers for the purpose of achieving organizational objectives. |
Communication strategy |
|
|
the array of communications tools available to marketers including advertising, personal selling, publicity, sales promotions, and sponsorships. |
Communication mix |
|
|
the only communication tool that enables two-way communication between the service provider and the customer. |
Personal selling |
|
|
no other communication tool is faster in creating overall awareness |
Advertising |
|
|
the only communication tool that enables two-way communication between the service provider and the customer. |
Publicity |
|
|
the primary strategic advantage of this is to increase short-term sales. |
Sales promotion |
|
|
It allow the service firm to target narrow, but highly desirable target audiences and provide an option for service firms to adapt to consumers’ changing media habits. |
Sponsorship |
|
|
The _______ is the market segment that becomes the focus of a firm’s marketing efforts. |
target market |
|
|
when demand for the service is infrequent, and therefore the success of the communication strategy may not be realized until a later point in time. |
Lagged effect |
|
|
service staff is required to deal with customers quickly and effectively in “once only” situations where large numbers of customers are present. |
Type 1 service staff |
|
|
service staff who deal with numerous, often repeat customers in restricted interactions of somewhat longer duration. |
Type 2 service staff |
|
|
is an interactive process between the service provider and the customer. |
Service delivery |
|
|
Service staff is required to have more highly developed communication skills because of more extended and complex interactions with customers. |
Type 3 service staff |
|
|
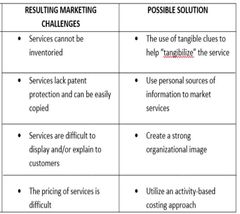
Intangibility |
|
|
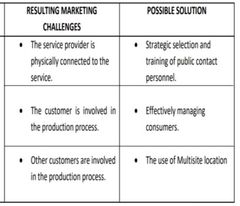
Inseparability |
|

|
Heterogeneity |
|
|
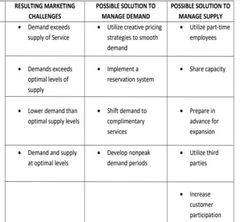
Perishability |
|
|
objectives tend to be the first step. |
Informal communications |
|
|
During the growth and maturity stage, the PLC tends to lean toward ______ and ______content. |
informational and persuasive |
|
|
During the maturity and decline stage, it utilizes _____ and _____ communication. |
persuasive and reminder communication |
|
|
It is covered in most introductory marketing classes and includes the corporate-level approaches |
Budget Setting Techniques |
|
|
It should provide the necessary resources for the service firm to meet its established communication objective |
Communication budget |
|
|
It speaks to the firm’s differential advantage. |
Positioning strategy |
|
|
______ is developed by customers comparing their expectations to their perceptions of the actual service delivery process. |
customer satisfaction |
|
|
It is a well-established characteristic of services marketing that consumers of services perceive higher levels of risk prior to purchase than their goods-purchasing counterparts. |
E SERVICE IN ACTION: The Growth of Personal Communications via Social Media |

