![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
195 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
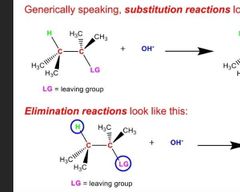
Whats the difference btw sub and elim |
|
|
|
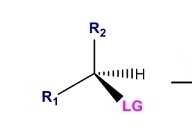
What are the common LG and what is the trend that makes them better |

|
|
What does and Sn1 rxn look like? |
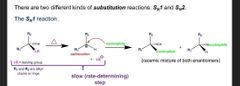
Heat kicks out LG to make carbocat then nuc comes and attaches to make a racemic mix of enan |
|
|
Sn1 details |

5. Uses weak nucs 6. Nuc will attack from front and back to make racemic enabled 7. Carbocat rearrangement can happen |
|
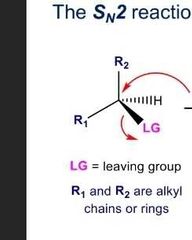
What does and sn2 rxn look like? |
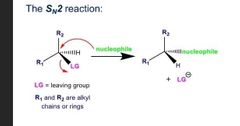
|
|
|
Sn2 details |
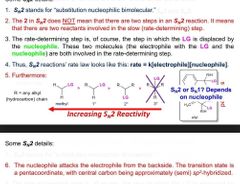
7. Sn2 uses strong nucs bc nuc attacks electrophoresis in 1 step and no inter forms 8. If electrophoresis has stereocenter. And inversion must happen |
|
|
What is the inversion for sn2 rxns |
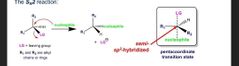
If there are different R groups then inversion of the stereocenter happens If there are different R groups then inversion of the stereocenter happens |
|
|
How to choose btx sn1 and 2 |
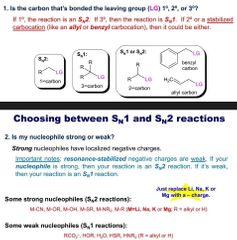
|
|
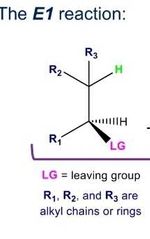
What does the e1 expect look like? What is the RDS |
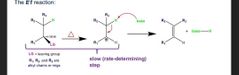
Rds=where LG leaves and Carbocat forms |
|
|
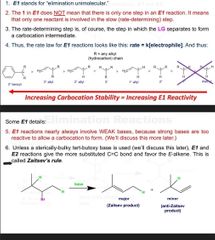
E1 details |
|
|
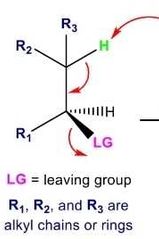
What does an E2 rxn look like? |
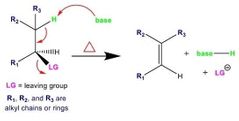
|
|
|
E2 details |

|
|
|
What DOES elimination rxn favor? |
Zaitsev product which is the most fa order substituted prod.E alkene over Z Zaitsev product which is the most fa order substituted prod.E alkene over Z |
|
|
How to choose btw E1 and 2 |
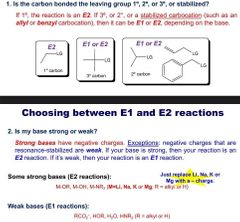
|
|
|
General view on how to choose between sn1, SN2, E1 or E2 |

|
|

|
Base=E, nuc=Sn -th3 bigger the b/n=b, the smaller the b/n= n -bigger or equal to ethanol or epoxide= big |
|
|
protic slovents |
solvents that have H atoms bonded to an oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. -EX: CH3OH, CH3CH2OH, acetic acid (CH3COOH), or H2O. |
|
|
aprotic solvents |
-opposite of protic Ex: DMSO, acetone, acetonitrile and DMF. |
|
|
-protic solvent react with, and thereby stifle? what does this mean? -
|
-strong nucleophiles/bases. - solvents are bad for strong nucleophiles/bases(SN2 and E2 reactions), but are good for weak nucleophiles/bases (SN1 and E1reactions). -they do ok with E2 |
|

|

|
|

Nuc and base |
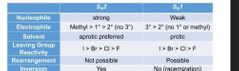
|
|
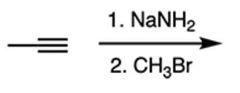
|

|
|
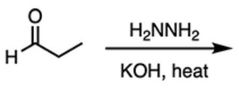
|

|
|
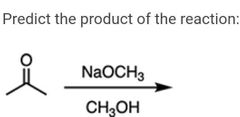
|
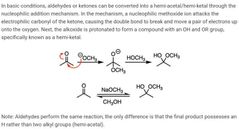
|
|
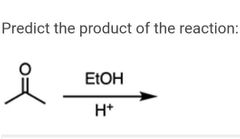
|
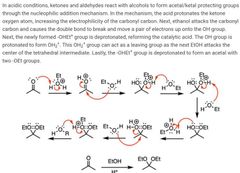
|
|
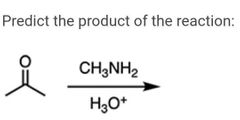
|
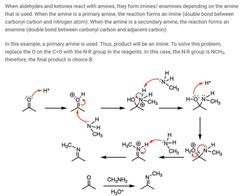
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
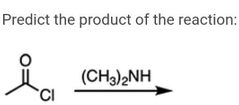
|
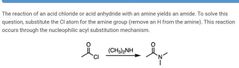
|
|
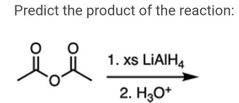
|

|
|
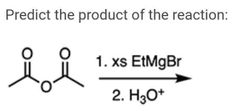
|
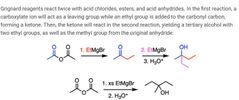
|
|
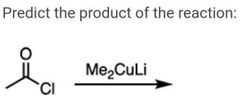
|

|
|
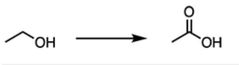
|
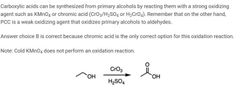
|
|
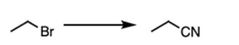
|

|
|

|
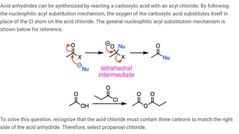
|
|
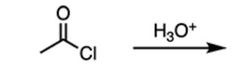
|
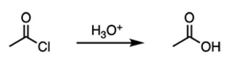
|
|
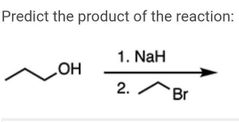
|

|
|

|
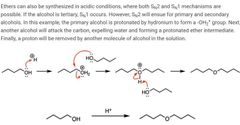
|
|
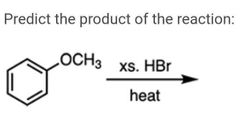
|
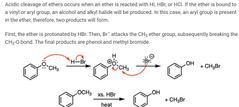
|
|
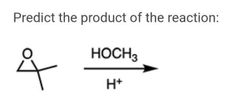
|
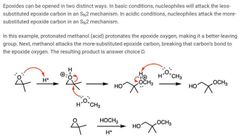
|
|

|

|
|
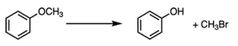
|

|
|

|
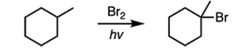
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
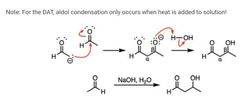
|
|
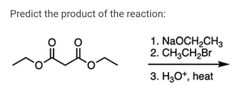
|

|
|
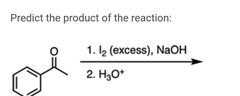
|
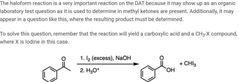
|
|
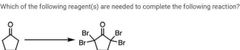
|
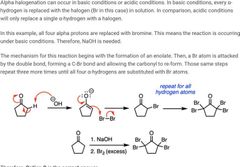
|
|
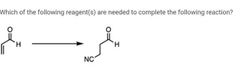
|

|
|
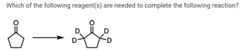
|
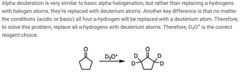
|
|
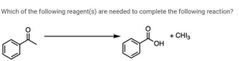
|
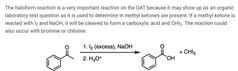
|
|

|
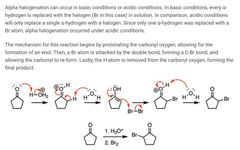
|
|

|
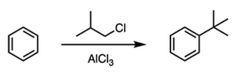
|
|
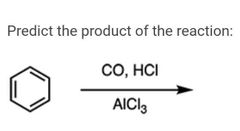
|

|
|
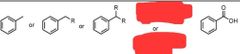
|
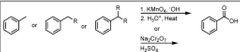
|
|
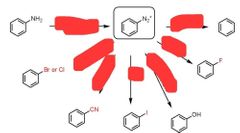
|
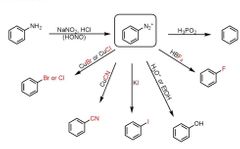
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

2 |
|

|

|
|
|
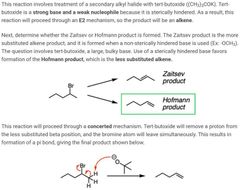
|
|
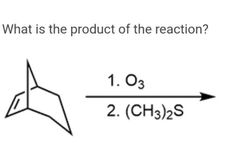
|
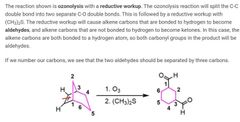
|
|
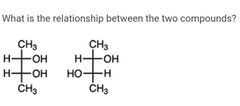
|

|
|

|
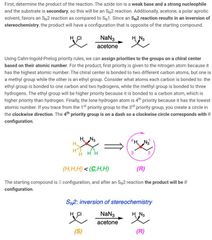
|
|

|

|
|

|
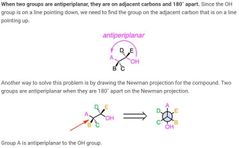
|
|

|

|
|
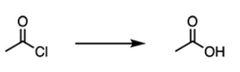
|
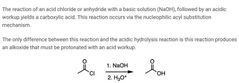
|
|

|
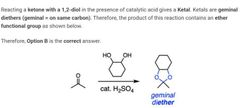
|
|
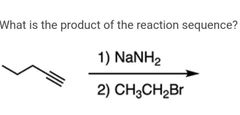
|
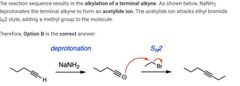
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
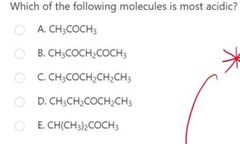
|
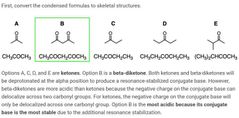
|
|
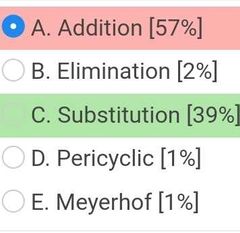
|
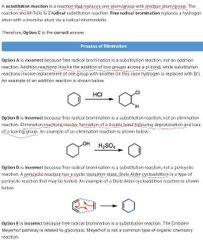
|
|

|

|
|

|
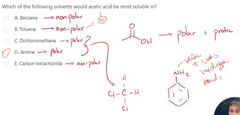
|
|
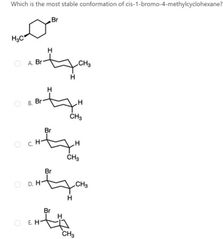
|

|
|

|
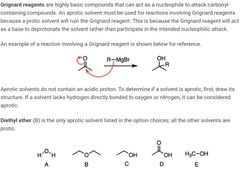
|
|
|
Electron donators vs withdrawers and what they do |

|
|
|
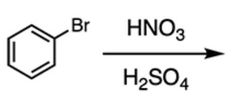
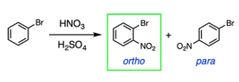
Ortho par vs meta reactors |
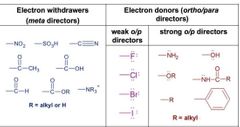
|
|

|
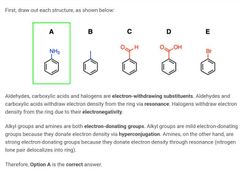
|
|

|

|
|
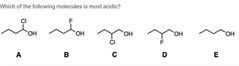
|

|
|

|
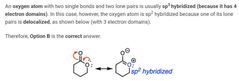
|
|
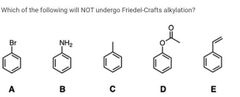
|
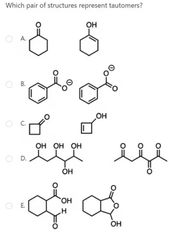
B and E |
|

|
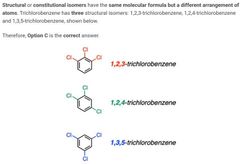
|
|
|
|
|
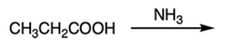
|
|
|

|
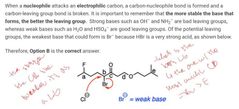
|
|

|

|
|

|
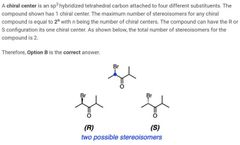
|
|

|

|
|

|
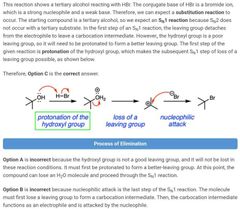
|
|
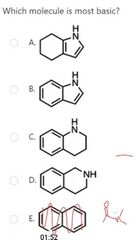
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
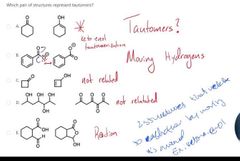
|
|
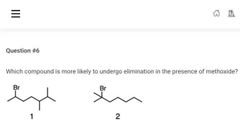
|

|
|
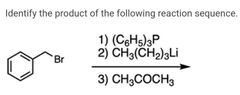
|
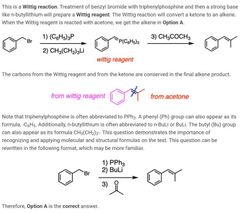
|
|
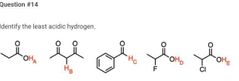
|
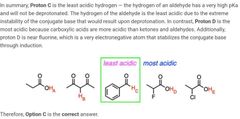
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
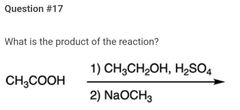
|
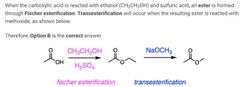
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
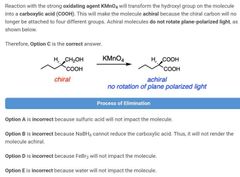
|
|

|

|
|
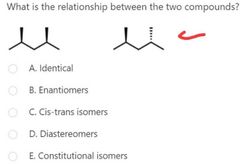
|

|
|
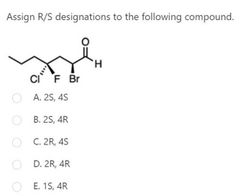
|
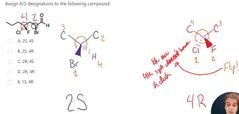
|
|

|
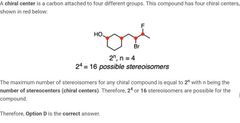
|
|

|
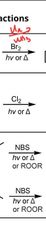
|
|
|
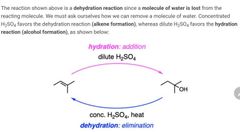
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
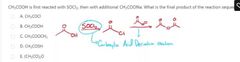
|
|
|

|
|

|
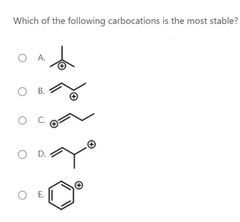
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

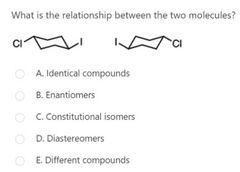
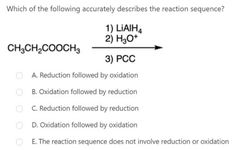
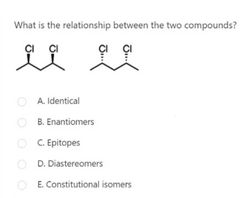
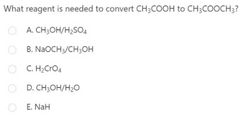
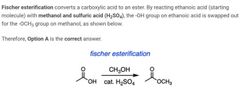
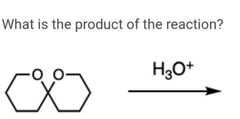
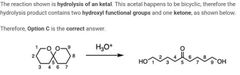
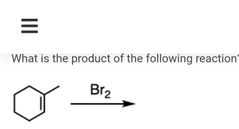
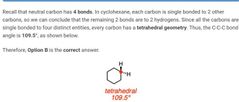
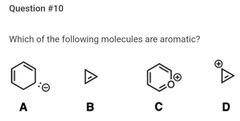
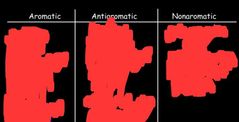
B |
|
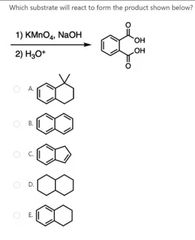
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
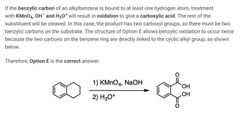
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
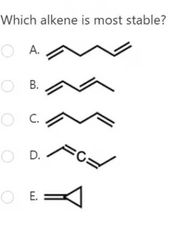
|
|

|
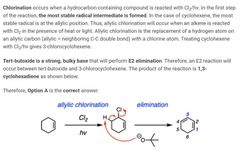
|
|
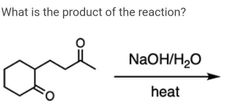
|
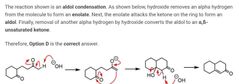
|
|
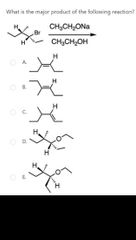
|

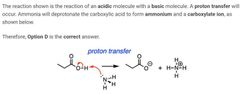
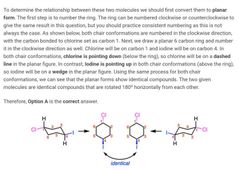
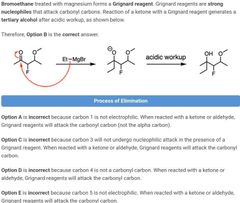
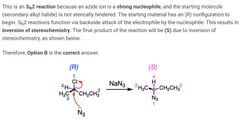
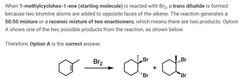
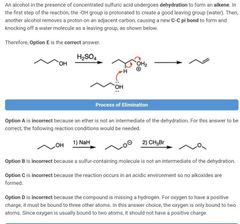
A |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
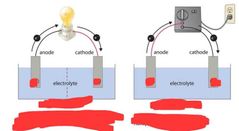
|
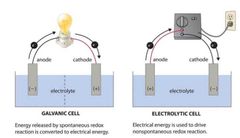
|
|
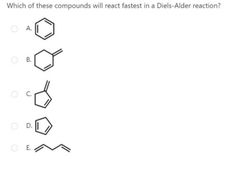
|

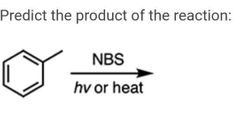
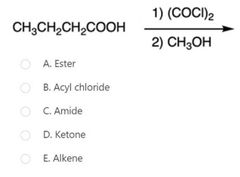
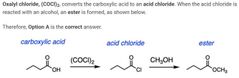
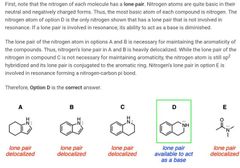
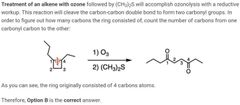
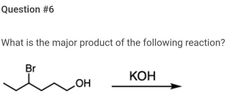
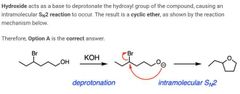
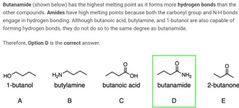
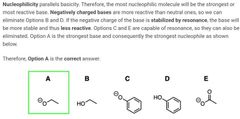
D |
|

|
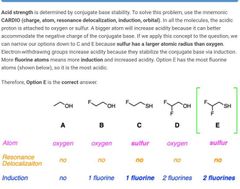
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
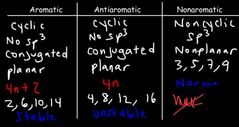
|
|
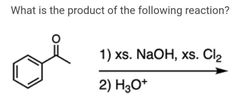
|
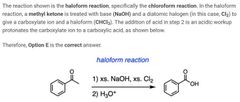
|
|

|
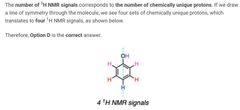
|
|
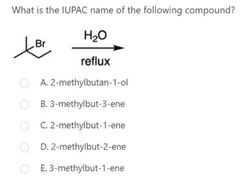
|

|
|

|
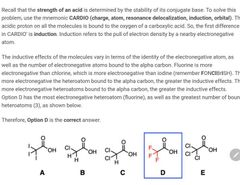
|
|
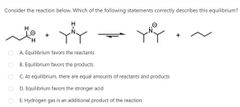
|
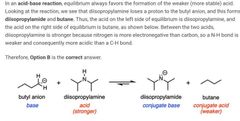
|
|

|
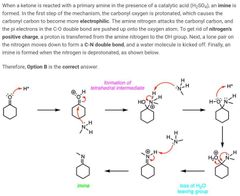
|
|
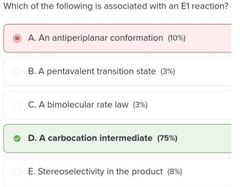
|
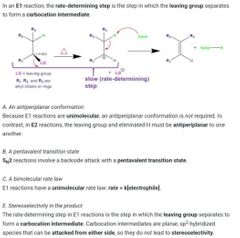
|
|
|
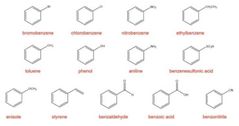
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
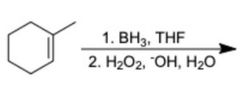
|

|
|
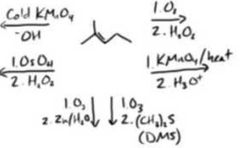
|

|
|
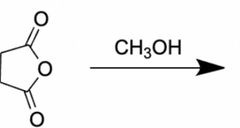
|
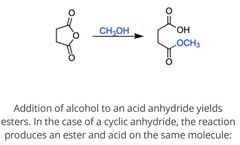
|
|
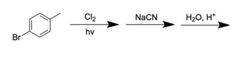
|
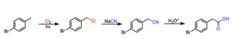
|
|
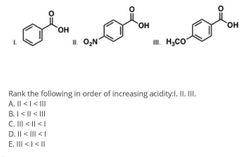
|

|
|
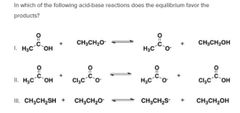
|

|
|
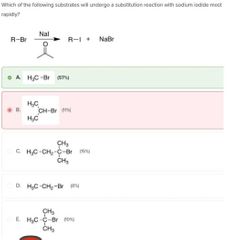
|

|
|

|

|
|
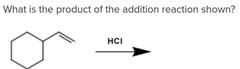
|
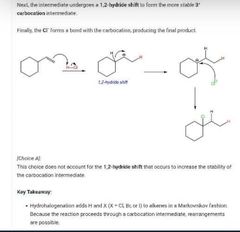
|
|

|
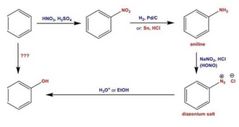
|
|

|
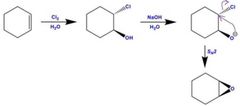
|
|

|

|
|
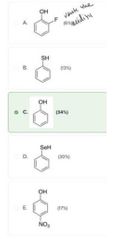
|
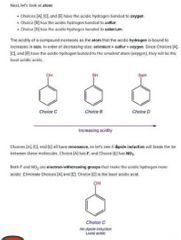
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
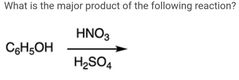
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
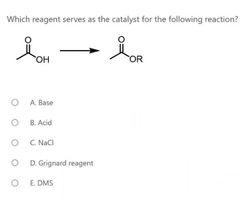
|
|
|

|

|
|
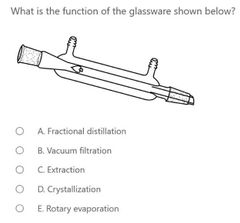
|

|
|

|
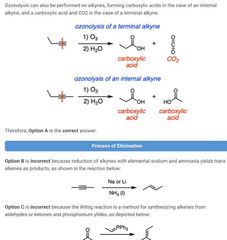
|
|
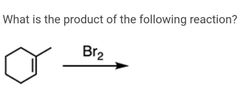
|
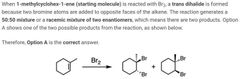
|
|

|
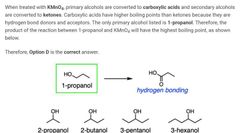
|
|
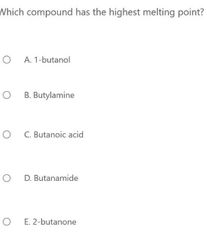
|
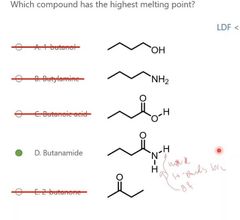
|
|
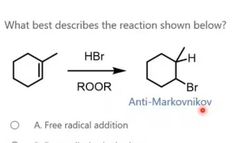
|

|
|

|

|
|
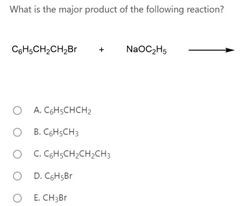
|
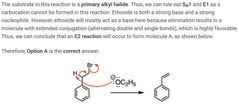
|
|

|
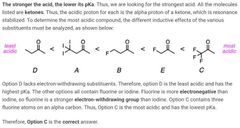
|

