![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe the two arterial systems that supply the spine. |
2 major arterial systems supply the spine. Vertical system= 1 anterior spinal artery, 2 posterior spinal artery. segmental system=branches off the aorta that join onto the vertical system at each vertebral level. |
|
|
Origins of the vertical system? |
both the ant & post spinal arteries originate off the vertebral arteries at the foramen magnum and descend the length of the spine. They also get inferior supply from branches of iliac. |
|
|
describe the segmental system? |
Radicular arteries = most vertebral levels have small arteries that come in via the nerve roots to the ant & post spinal arteries cervical spine = radicular arteries off deep cervical artery. Thoracic= radicular off post intercostal art. Lumber= off lumber arteries. Also some major radicular arteries that don't go via nerve roots but join straight to vertical spinal arteries = artery of ADAMKIEWICZ is the major one. |
|
|
Draw the segmental arterial supply. |
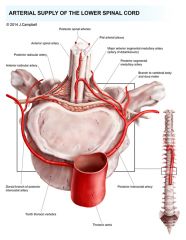
identify normal radicular arts that go via nerve root to vertical arts. These are separate to major radicular artery of adamkiewicz |
|
|
What is the artery of adamkeiwicz, where is it and why do we care? |
Aka radicularis magna. The biggest radicular artery in the segmental supply to the spinal cord. provides large proportion of supply to thoracolumber region - issue if interrupted in thoracic aorta repair. can be T8 to L4 but in 80% of people is T9-T12. |
|
|
Risk factors for spinal ischaemia in aortic repair? |
Patient: PVD. Surgical: open worse than EVAR. emergency. long segment. duration or repair/duration of clamp. not re-implanting segmental arteries. Anaesthetic: hypotension. |
|
|
How to prevent spinal cord ischaemia? |
Increase perfusion: MAP > 80. CSF drain. use shunt across clamped aorta. re-implant major arteries (can't do with EVAR). Decrease spinal cord metabolism: cool to 34 or DHCA. ?drugs can help but no evidence - e.g. steroids. Monitor for ischamimia and treat if present: SSEP's or MEP's. SSEPs - measure the sensory pathway (i.e. the dorsal columns) - therefore SSEPs measure the POSTERIOR spinal artery territory. MEPs: - measure the motor pathways that are antero and lateral. - therefore MEPs measure the anterior spinal artery territory |
|
|
what is rational for CSF drain? is there evidence for it? |
spinal cord perfusion = MAP - lumber CSF pressure. therefore if decrease CSF pressure can improve perfusion. Aim for PP of 70. MAP=80 and CSF of 10. Cochrane r/v showed protective effect in thoracic aneurysms. |

